1
AAA with Intramural Thrombus
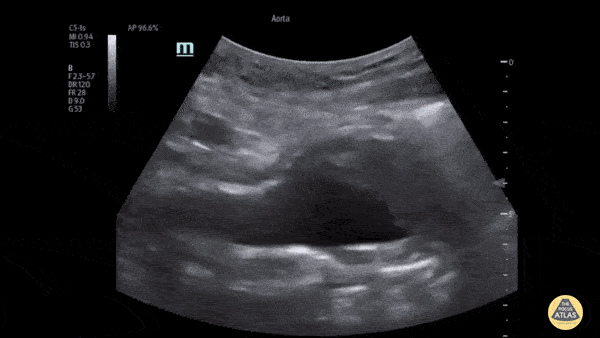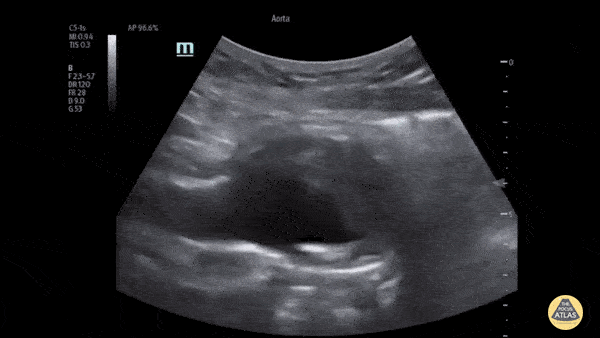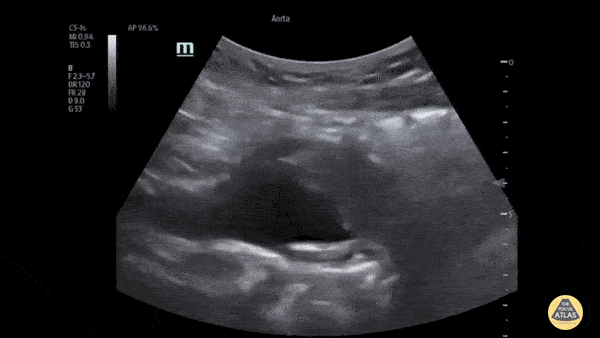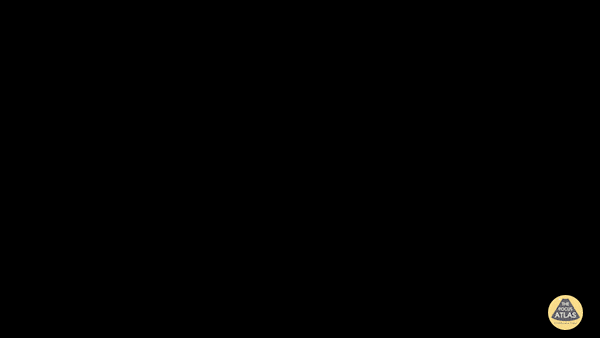
The patient presented to the ED with a known abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). A point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) examination of the abdominal aorta was performed using a curvilinear probe (longitudinal view shown). An infrarenal AAA was noted adjacent and superior to the bifurcation and measured a maximum diameter of approximately 5cm. Heterogeneous echogenic material was seen within the lumen of the aneurysm in keeping with intramural thrombosis, along with a hyperechoic line representing a chronic dissection.
This demonstrates the utility of POCUS in the rapid diagnosis of AAA and evaluation of size and intraluminal features such as intramural thrombus and dissection.
Andrew Namespetra, MB BCh BAO MSc
PGY-1 Emergency Medicine Resident, Central Michigan University (CMU)
Chad Bambrick, MD
PGY-2 Emergency Medicine Resident, CMU
Ryan Davis
MS4, CMU College of Medicine