Musculoskeletal
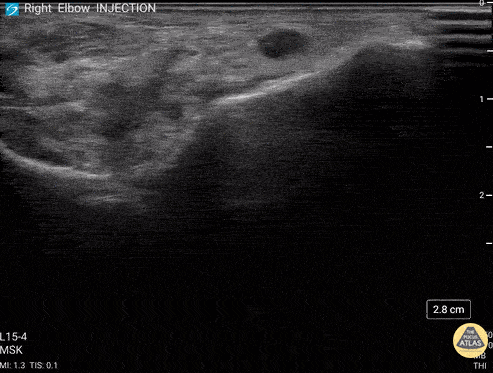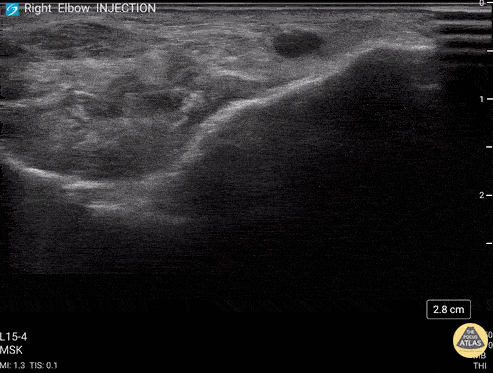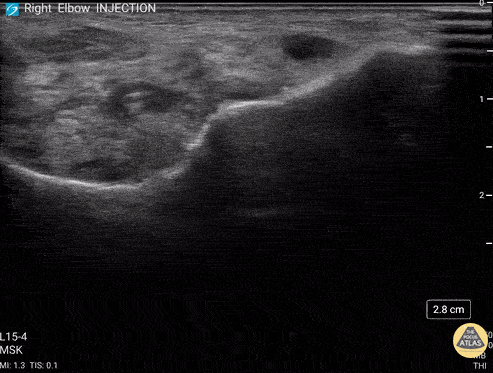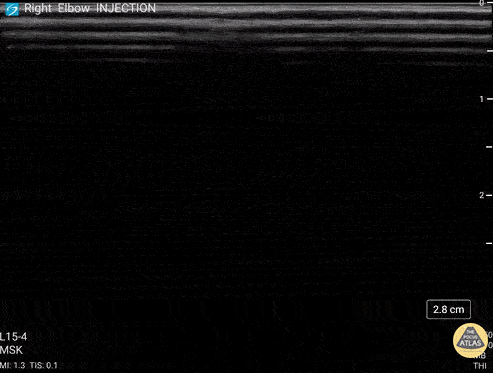
Posterior Elbow Joint Injection
92 y/o M presented with moderate to severe osteoarthritis on elbow x-ray who was treated with ultrasound-guided corticosteroid joint injection.
Video shows transverse view of the posterior elbow as corticosteroid is injected with a posterolateral approach deep to the posterior elbow fat pad located in the olecranon fossa. This area is continuous with the elbow joint capsule. Posterolateral approach is advantageous due to decreased risk of disrupting neurovascular structures or the articular cartilage from other approaches to the joint space. Posterior approach is also advantageous compared to lateral approach in moderate to severe arthritis due to limited access to the radiocapitellar joint space.
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
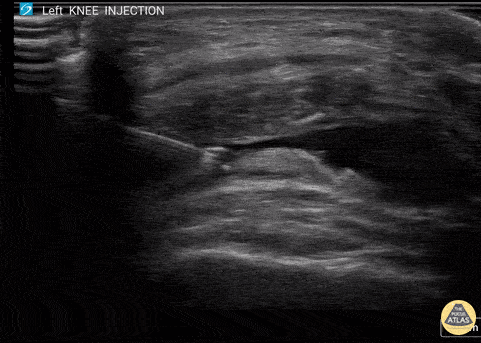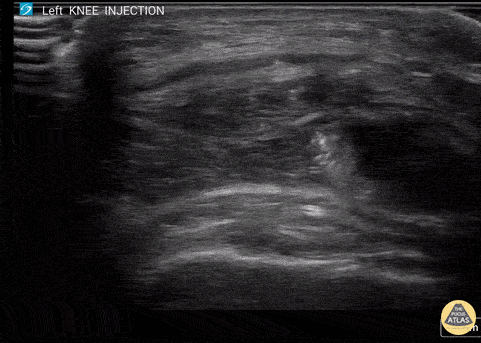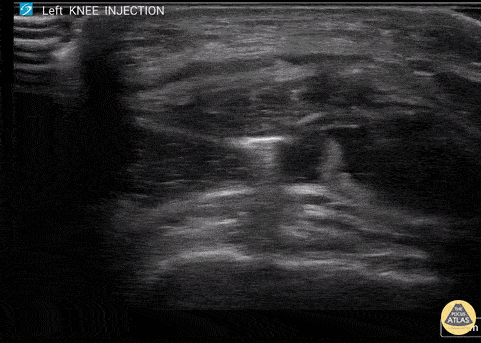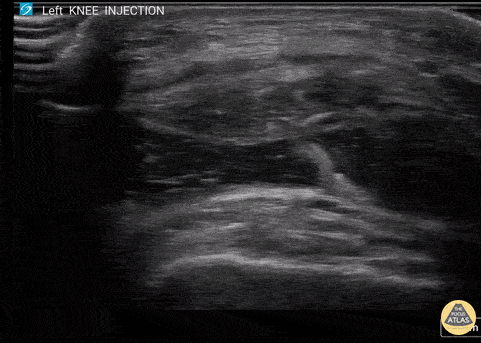
Corticosteroid Joint injection in Suprapatellar Recess
60 y/o F with knee arthritis getting corticosteroid joint injection in left suprapatellar recess.
Ultrasound probe in transverse axis just superior to the patella. Needle approach lateral to medial. Infiltrate seen injected into anechoic suprapatellar recess. The suprapatellar recess is continuous with the tibiofemoral joint. Deep to suprapellar recess in this video is the prefemoral fat pad. Just superior to the suprapatellar recess in this image is the quadriceps tendon in short axis appearing as a fibrillar structure.
Contributors:
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
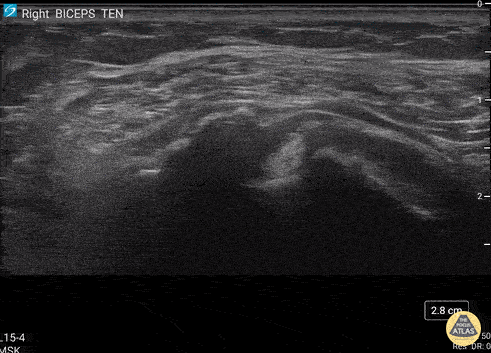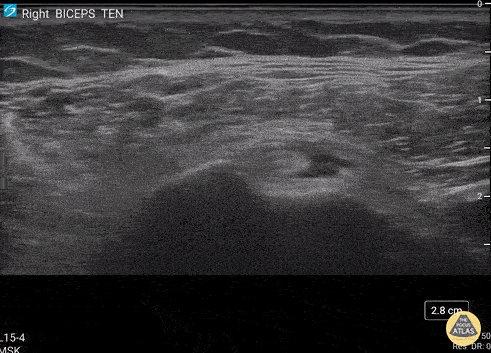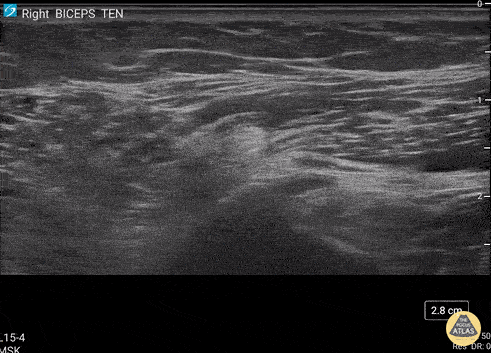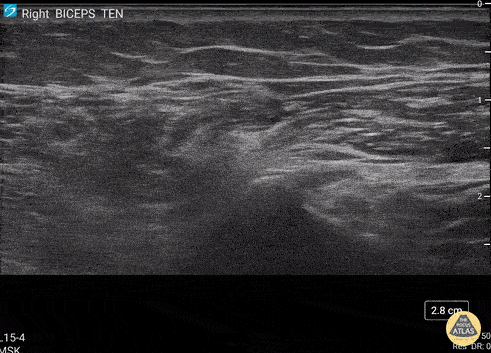
Biceps Tendon Sheath Effusion
55 y/o F presented 2 months after a FOOSH with adhesive capsulitis and a biceps tendon sheath effusion.
Ultrasound scanning transverse axis proximal to distal along humeral shaft (left screen is lateral). Anechoic space around hyperechoic biceps tendon (center of screen) represents fluid that is continuous with the glenohumeral joint space. Inflammation from the adhesive capsulitis is drawing in fluid into the joint that is extending into biceps tendon sheath.
Contributor:
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
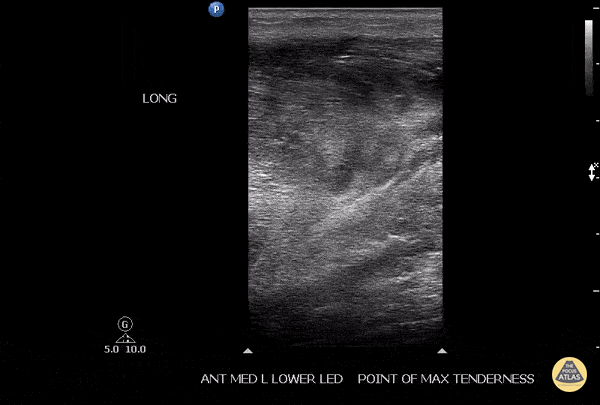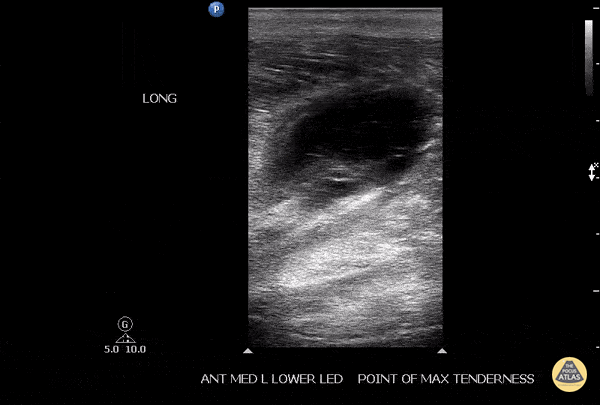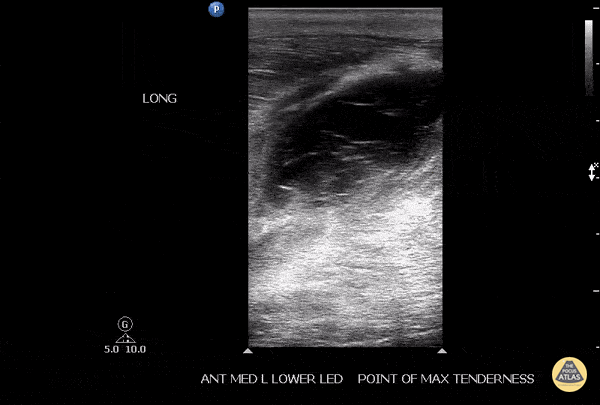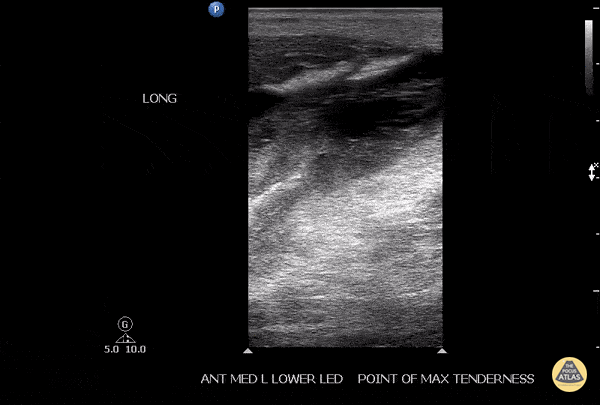
Soleus Hematoma
This is a patient who presented to the emergency department with left calf pain, swelling, previous history of DVT and currently on Xarelto. A patient with such a presentation would cause concern for ruling out a new DVT however a subsequent DVT scan proved to be negative. The key approach for this patient was to evaluated the area of maximal tenderness with ultrasound, which in this case, revealed a hematoma within their soleus muscle!
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
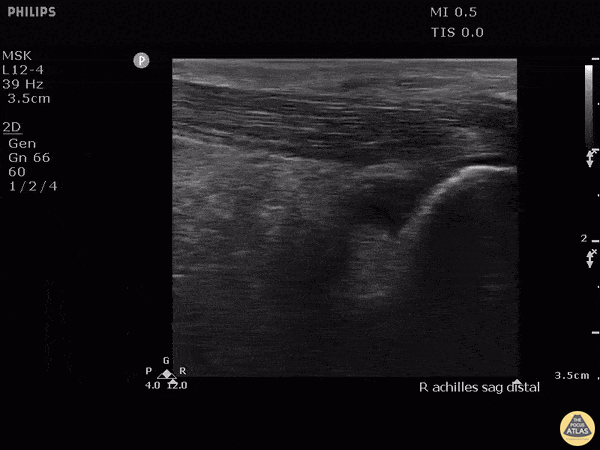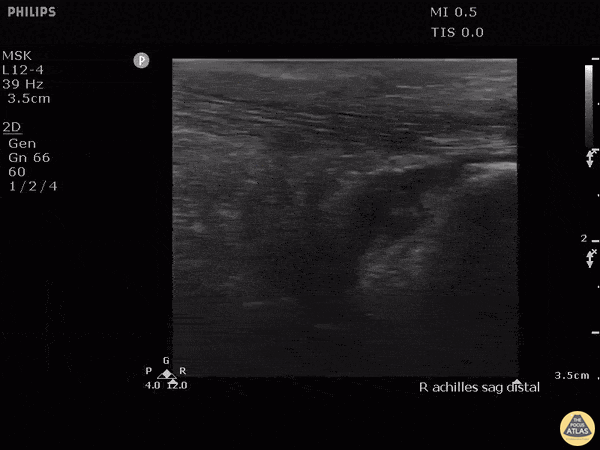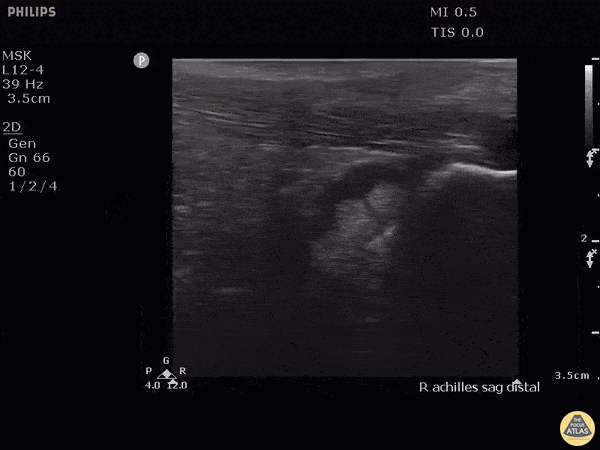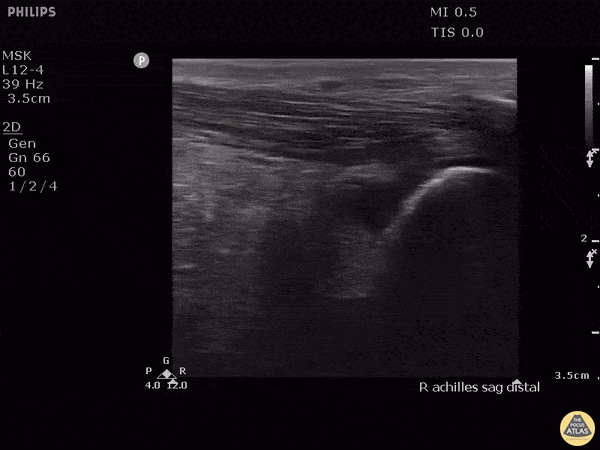
Retrocalcaneal Bursitis
Hockey player with progressive posterior ankle/heel pain. Felt sudden worsening while skating. Clip shown reveals retrocalcaneal bursitis along with insertional Achilles tendinopathy.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
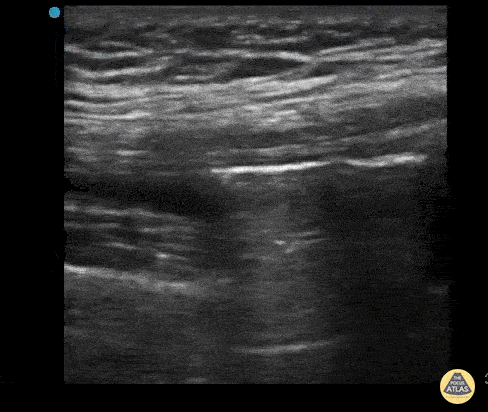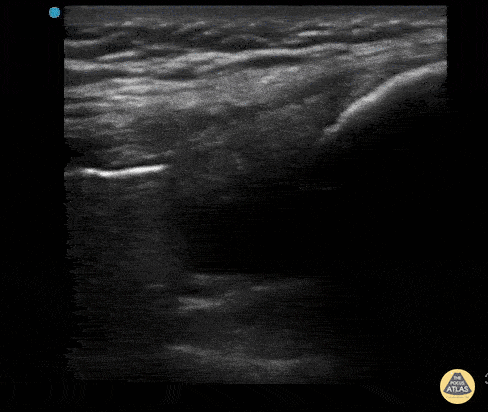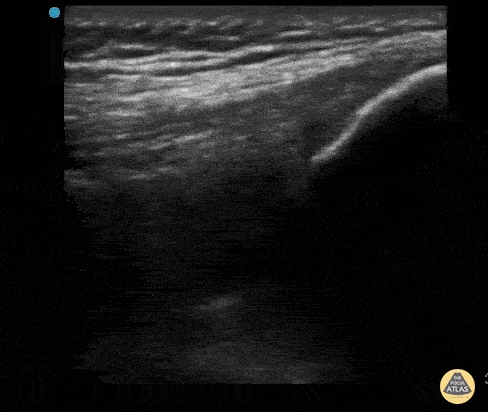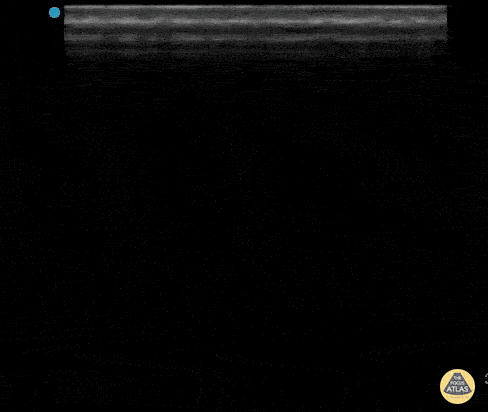
Intra-Articular Air
This is an ultrasound clip from a patient who presented to the ED after sustaining a laceration near the knee. There was concern for violation of the knee joint so ultrasound was used to evaluate.
The probe is held in an sagittal orientation, just proximal to the patella, overlying the quadriceps tendon. A hyperechoic line with shadowing (similar in appearance to an A-line seen on lung US) can be seen deep to the quadriceps tendon confirming intra-articular air and therefore violation of the knee joint from the laceration. A small joint effusion can also be appreciated.
Clip courtesy of Dr. Daniel Mantuani and Highland Ultrasound
Twitter: @HGHED
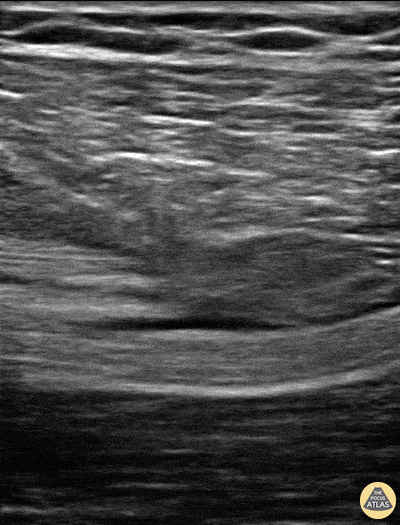
Sciatic Nerve Hematoma
Patient sustained a gun shot wound through left mid thigh.
Image is long axis view of sciatic nerve mid thigh. Nerve is running distal to proximal from left to right at approximately 3cm depth. There is a hypoechoic fluid collection seen superficial to the nerve. The epineurium is intact and we can see smaller nerve fibers contained in it.
Patient had 0/5 plantar/dorsiflexion of ankle on admission, consistent with a sciatic nerve injury. The ultrasound exam on the sciatic nerve did not show any gross abnormality other than this fluid collection around the nerve. Within 7 days (4 days after this image) he regained strength in plantar/dorsiflexion in the ankle.
Mike Guju, MD @MichaelMGujuMD
Resident PM&R EVMS
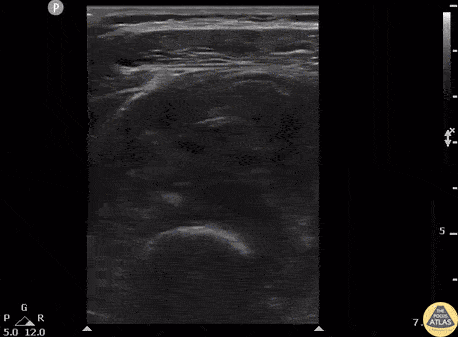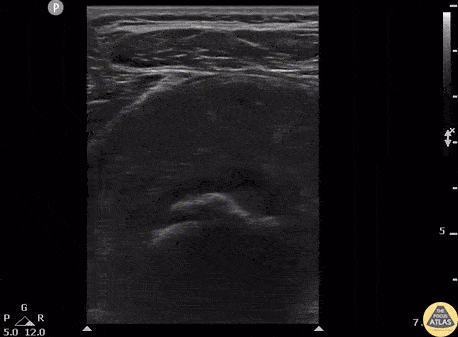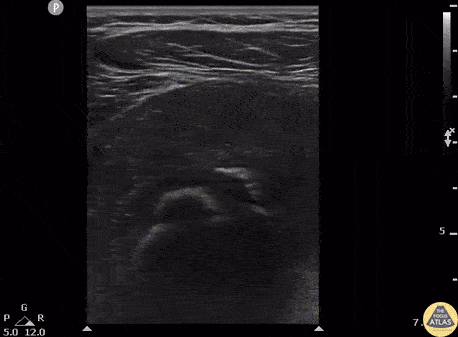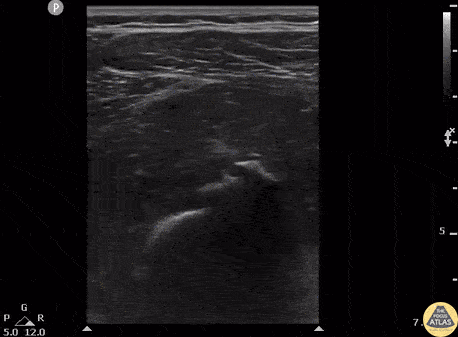
Myositis Ossificans
Patient presents to the ED with severe thigh pain following a subacute MMA injury. After proximal DVT was ruled out, POCUS revealed hypoechoic oval masses in the vastus intermedius and peripheral calcifications with shadowing adjacent to the femur.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
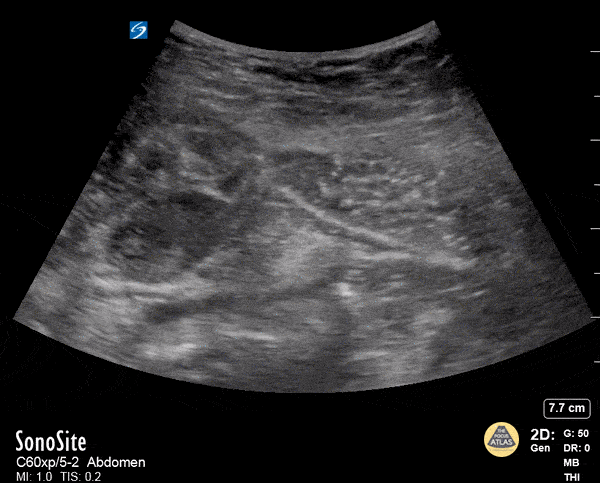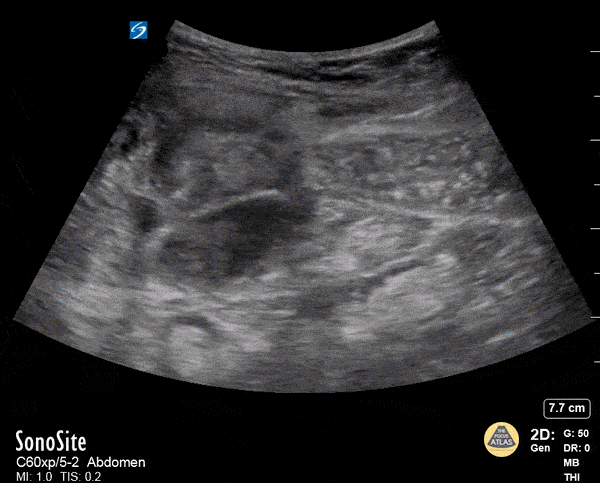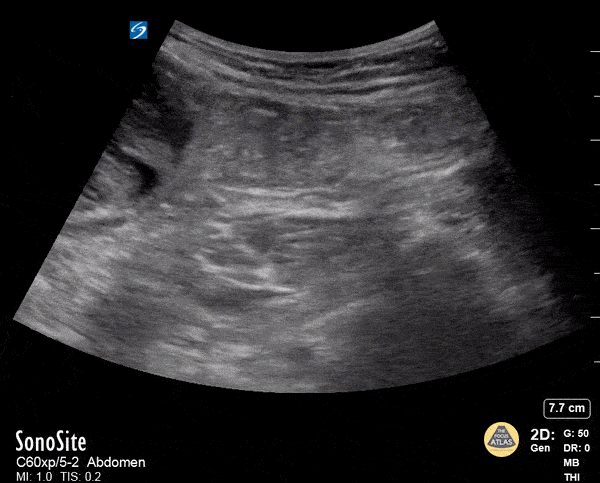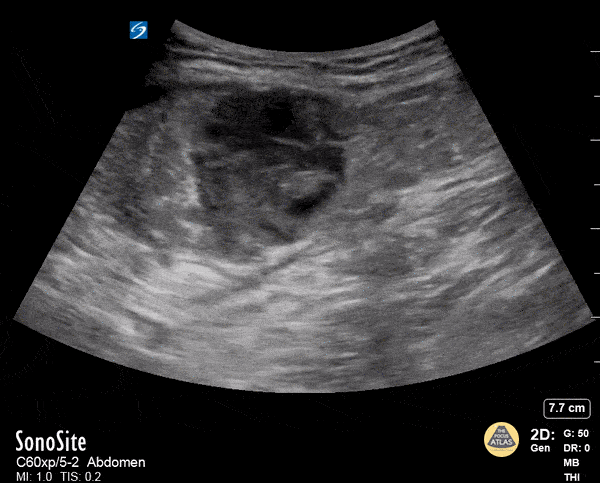
Rectus Abdominis Hematoma
A 41 year old male presented to the ED with a painful right sided abdominal mass. On examination the area of swelling was tender to palpation and initially suspected to be a hernia. Patient had engaged in strenuous exercise the day before. Using the abdominal probe, a bedside ultrasound demonstrated a hypoechoic 4.9 x 4.7 cm hematoma within the right lower rectus muscle with active extravasation. This patient underwent successful interventional radiology embolization and had unremarkable hospital course. POCUS for abdominal masses can quickly narrow the differential for such patients, which can expedite decision making particularly in those who are hemodynamically unstable and on anti-coagulation.
Max Cooper, MD Ultrasound Fellowship Director Crozer-Chester Medical Center
Kevin Conor Welch, DO Ultrasound Fellow Crozer-Chester Medical Center
Elena Grill, MD EM Resident Physician Crozer-Chester Medical Center
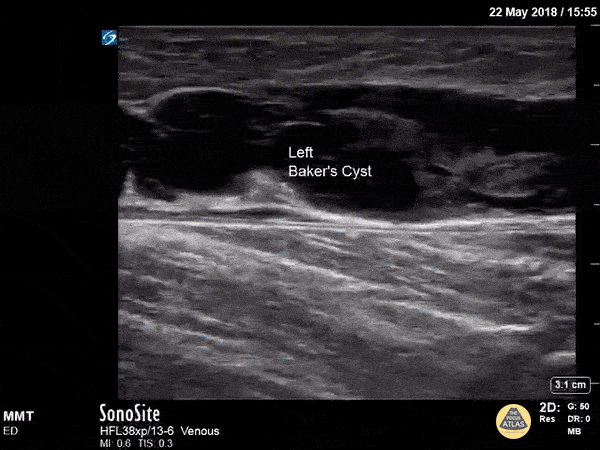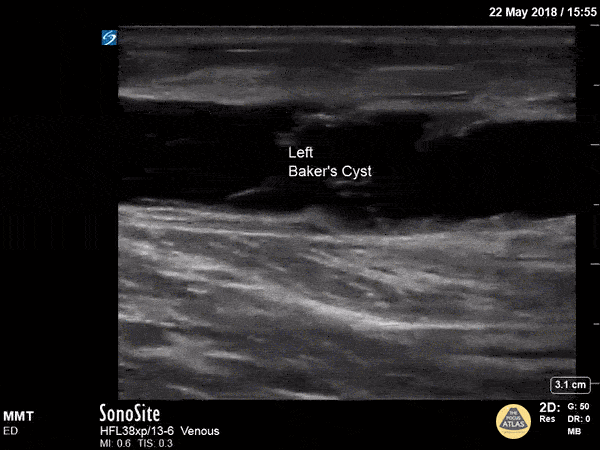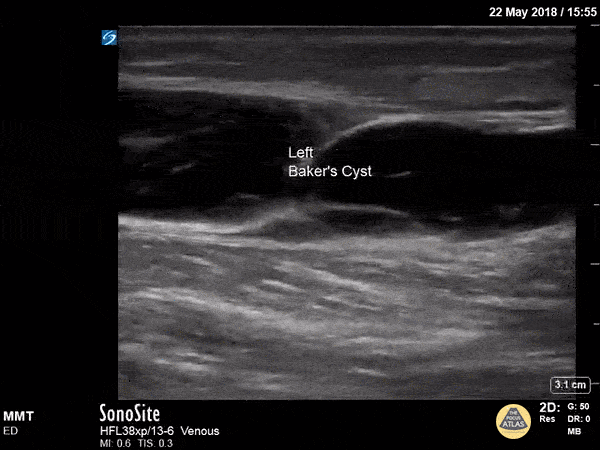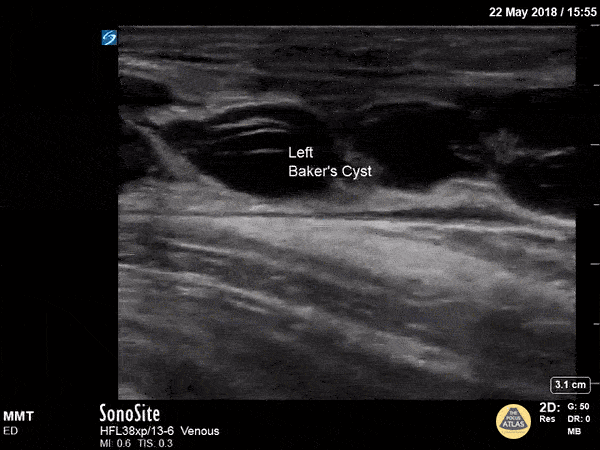
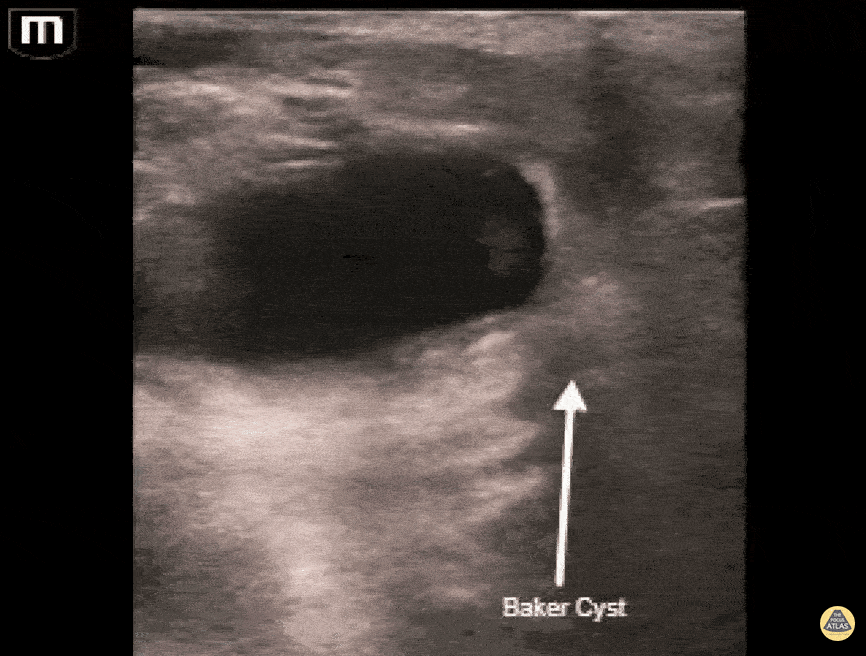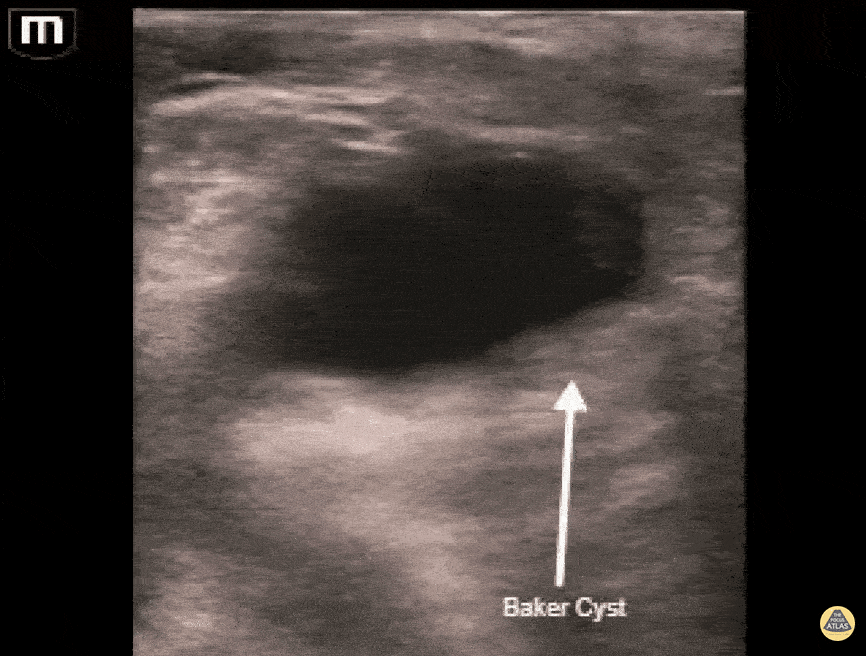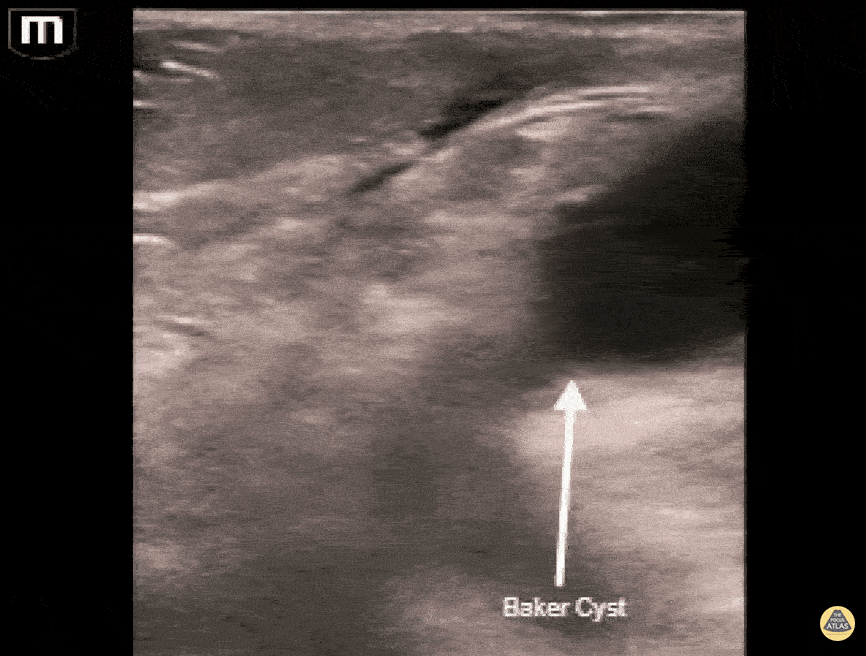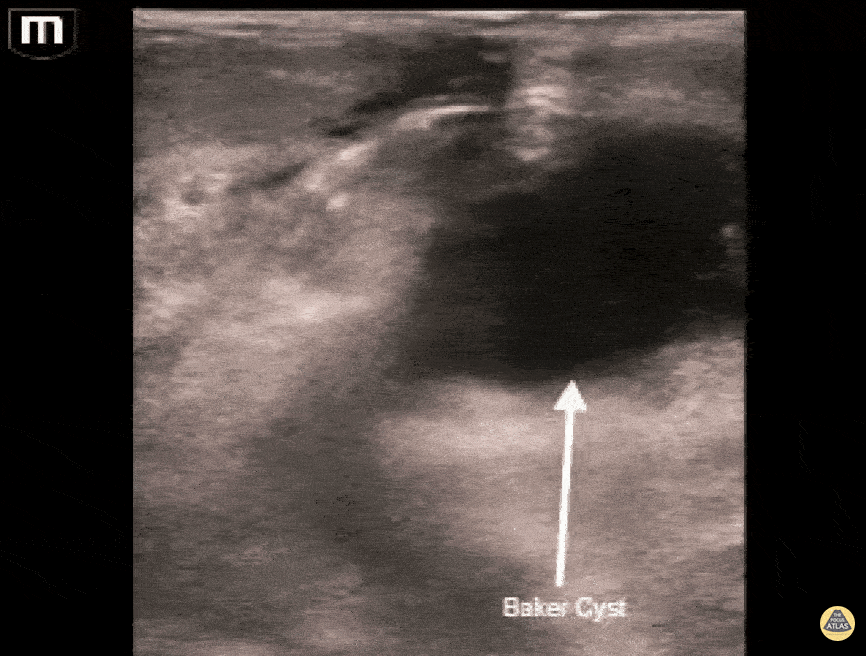
Baker's Cyst
A longitudinal view of a ruptured Baker's cyst. When performing a DVT scan, always look out for incidental findings that may explain the patient's presentation!
Dr. Michael Trauer
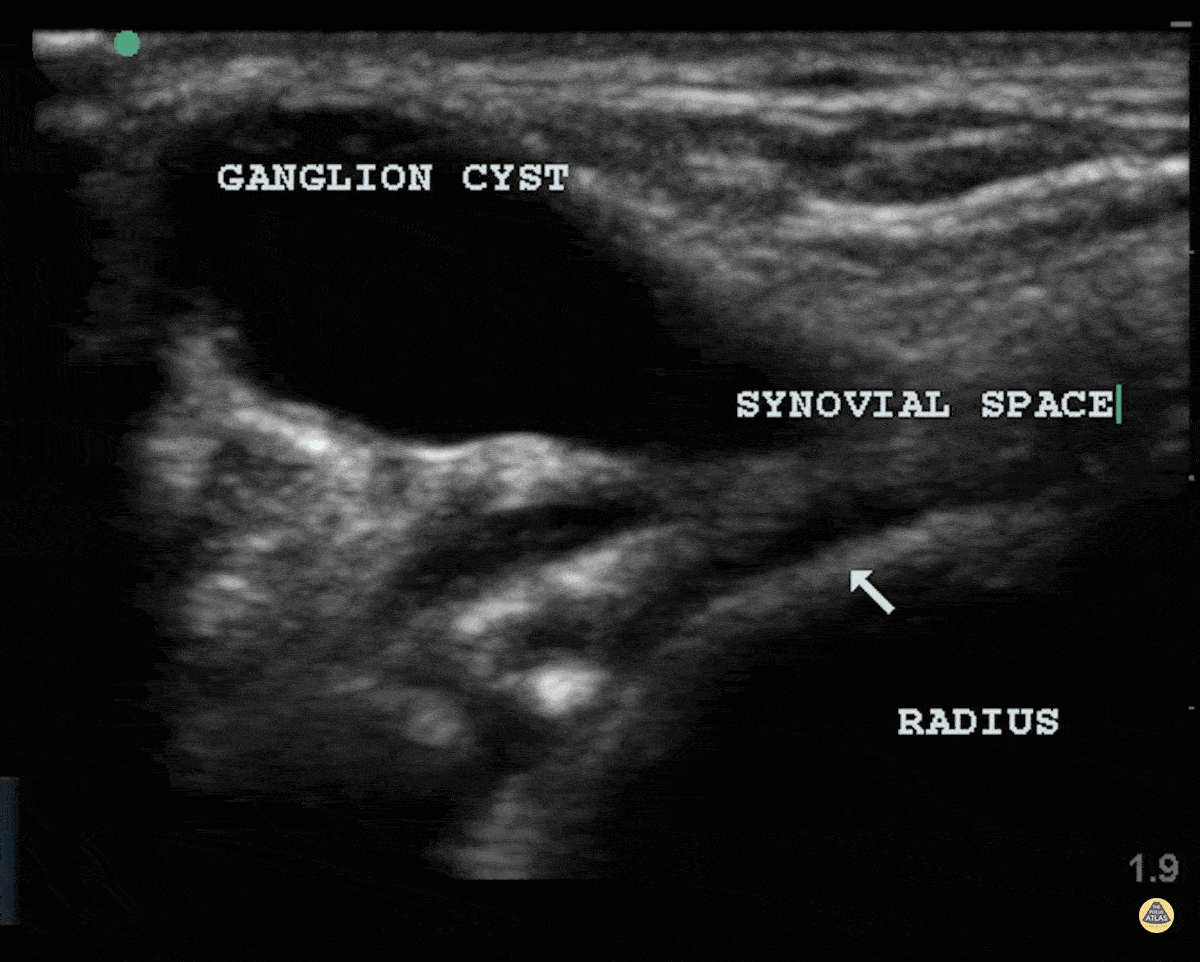
Ganglion Cyst
Patient struck his wrist several days ago and noted a deformity. There is a clear cystic structure with no doppler flow diving between the bones and involving the synovium representing a ganglion cyst.
Dr. Dustin Morrow

Plantar Fasciitis
84 y/o F who couldn’t bear weight on her left foot. Pt usually ambulatory with no known trauma.
L side thickened plantar fascia on symptomatic side (>4.5mm) and a hypoechoic fascia compared to a normal R side.
Dr. John F Kilpatrick - Kings County/SUNY Downstate Emergency Medicine
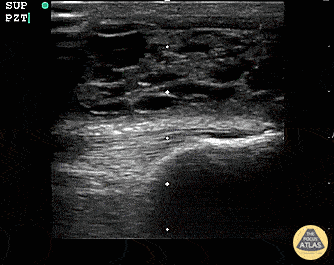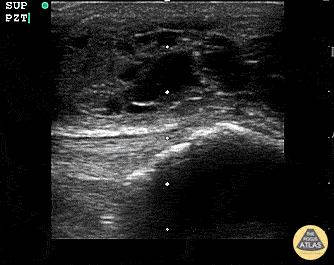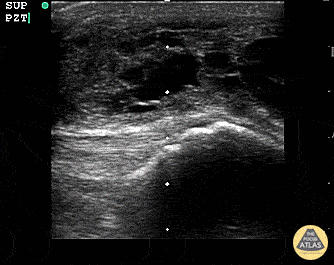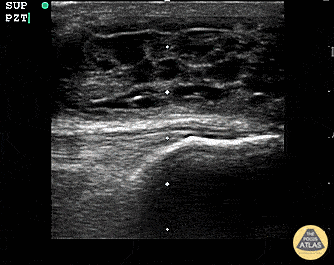
Suprapatellar Bursitis
Suprapatellar bursitis from repetitive trauma of playing on the floor with grandchildren. Presented with over a week of knee pain and swelling. Superficial involvement and septae are possible for abscess, however it is contained within the bursal space above the patella. Arthrocentesis revealed no infection, and conservative therapy yielded improvement.
Dr. Dustin Morrow
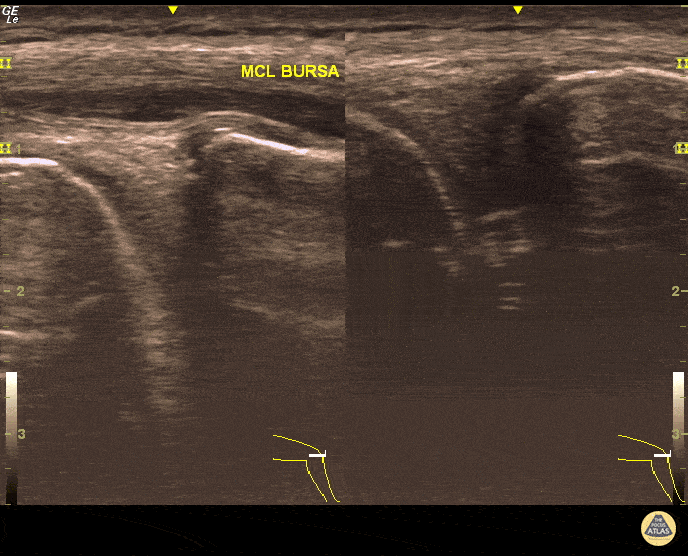
MCL Bursitis
29 year-old elite level soccer player with medial knee pain. He describes this being 'the worst episode ever', as he was having recurrent episodes of such pain. Valgus and flexion deformity due to prior surgery 15 years ago at the affected knee. Sharp, non-radiating pain 9/10 on NPRS, wakes him up at night. Palpation of medial knee and valgus stress test positive. Concomitant recent trauma. Unable to train/compete. USG of his knee revealed both MCL insertional edema (grade 1 injury) and MCL bursitis. Guided aspiration (3cc) and corticosteroid injection to MCL bursae revealed excellent outcomes. He returned to play 3 days later. Pitfall: It was not an MCL injury. Key point : Intervention was necessary and US-guidance allowed correct needle positioning without complication.
Dr. Omer Batin Gozubuyuk, Sports Medicine Specialist, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey.














