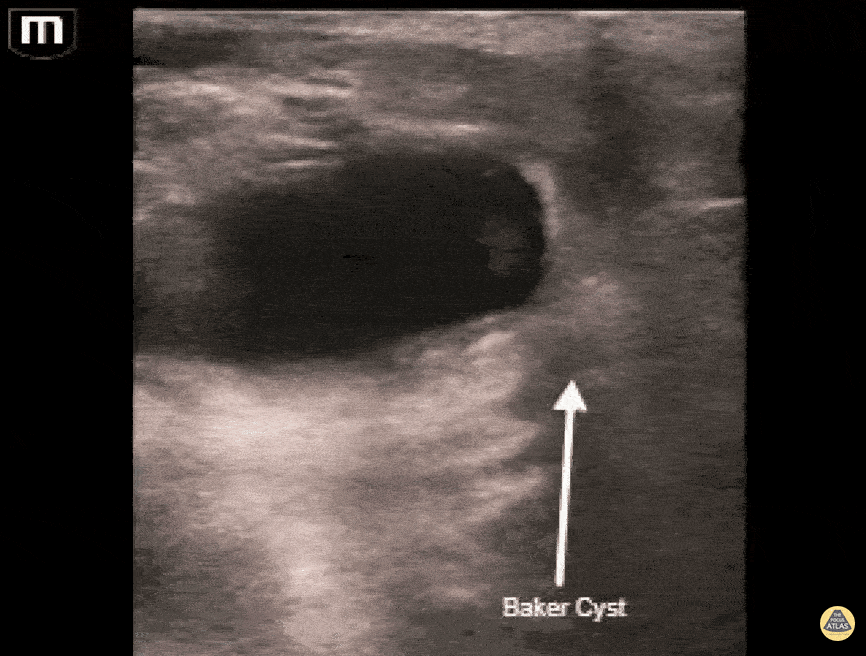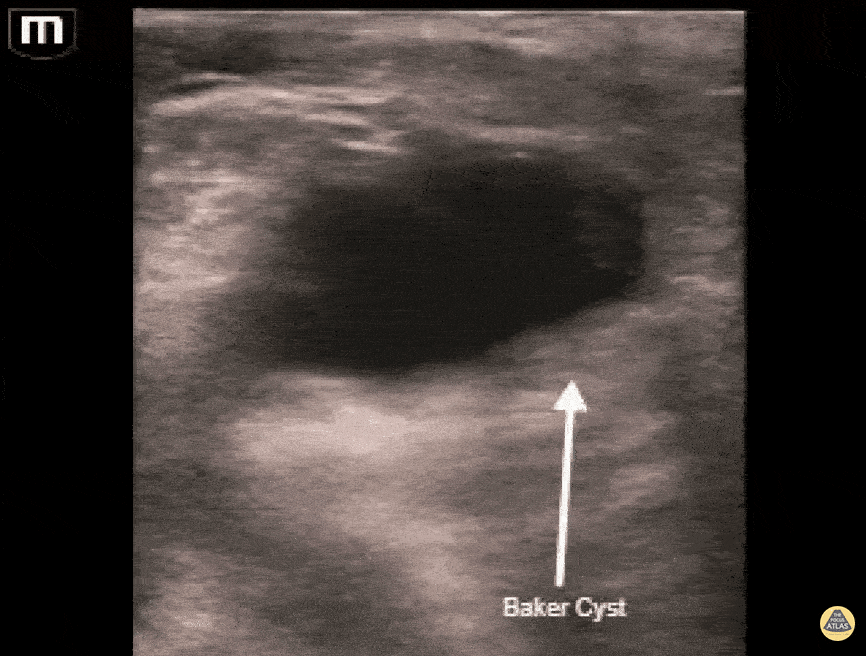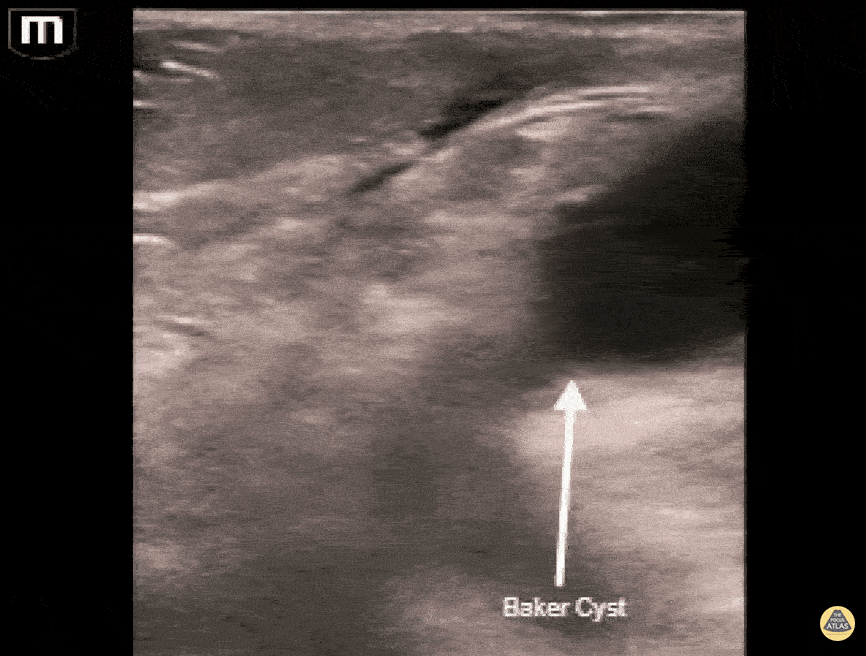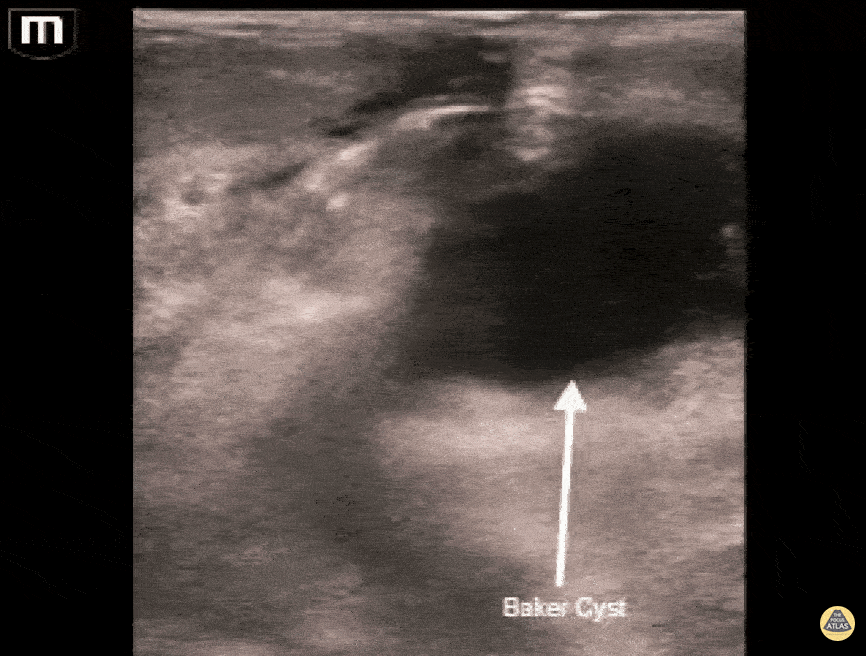
Musculoskeletal
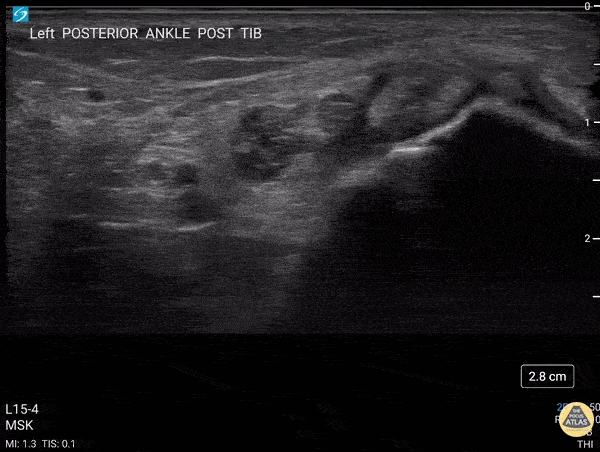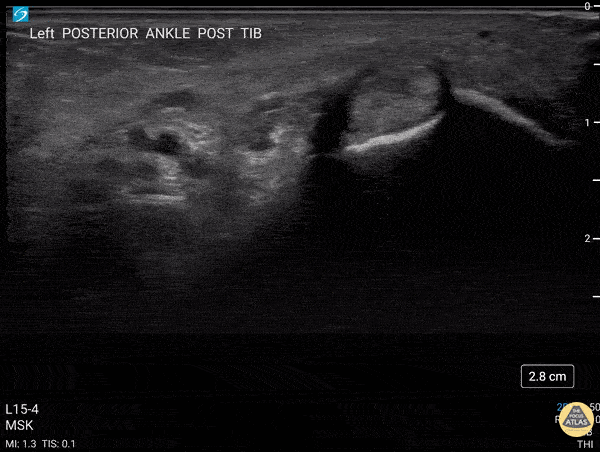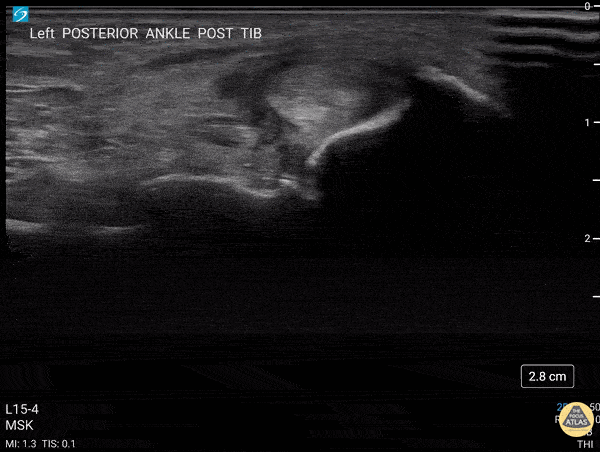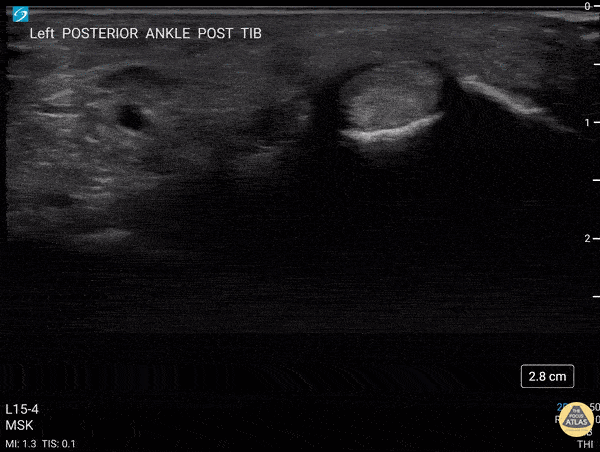
Transverse view scanning Proximal to Distal at the Posteromedial Ankle
40 y/o F presented with 9 month history insidious onset L medial ankle pain and was found to have tibialis posterior tendon partial tear.
Video shows transverse view scanning proximal to distal at the posteromedial ankle (left is posterior). There is thickening of the posterior tibialis tendon with an anechoic tendon sheath effusion. At the level of the medial malleolus there are two moderate interstitial tears extending distally. Flexor digitorum and hallicus longus appear unaffected.
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
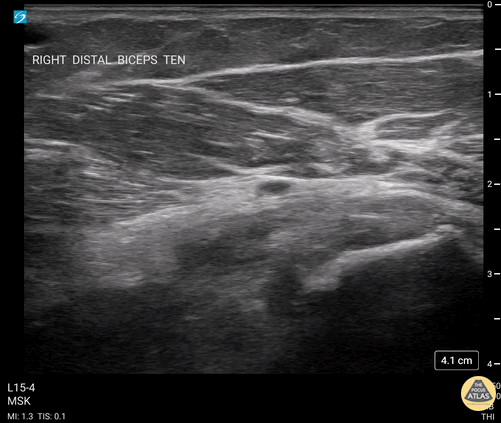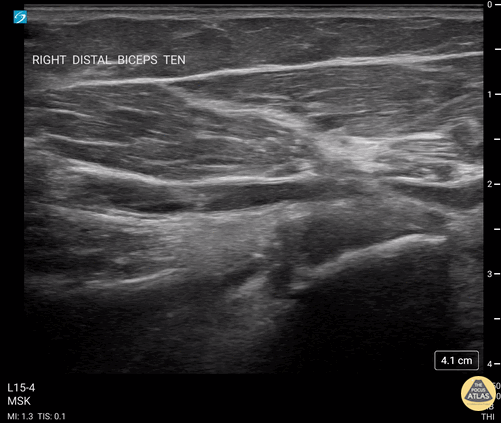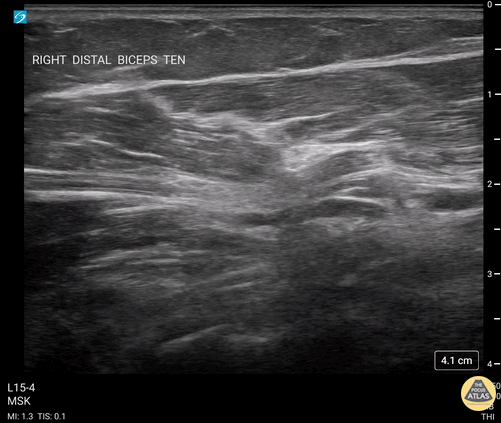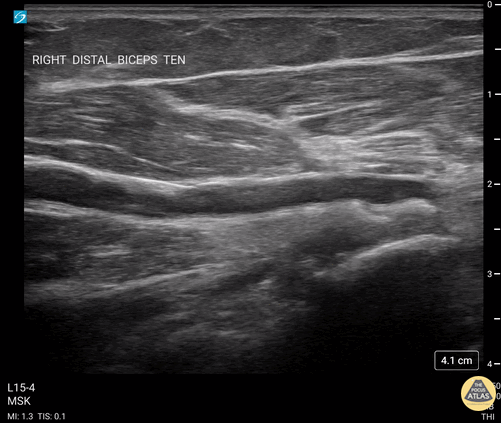
Biceps Tendinosis
60 y/o F w/R elbow pain for 8 months found to have distal biceps tendinosis.
L=proximal; R=distal. Medial long-axis view of distal biceps tendon. Radial artery seen pulsating directly superficial to biceps tendon. Distal biceps tendon diffusely thickened with decreased echogenicity at its attachment site.
Contributor:
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
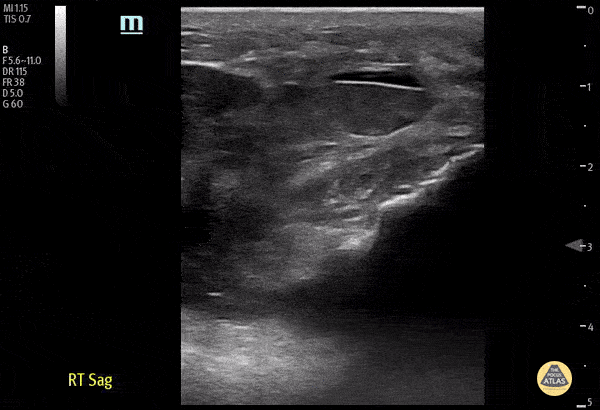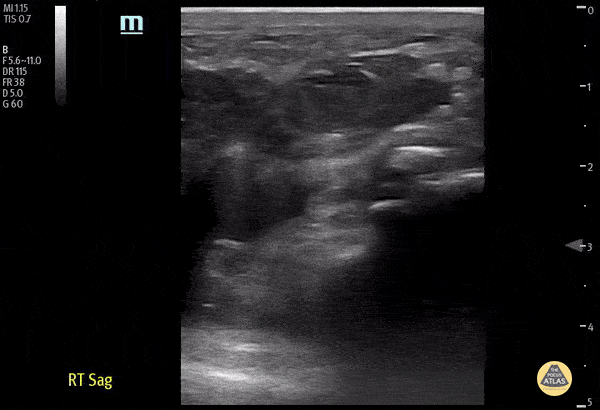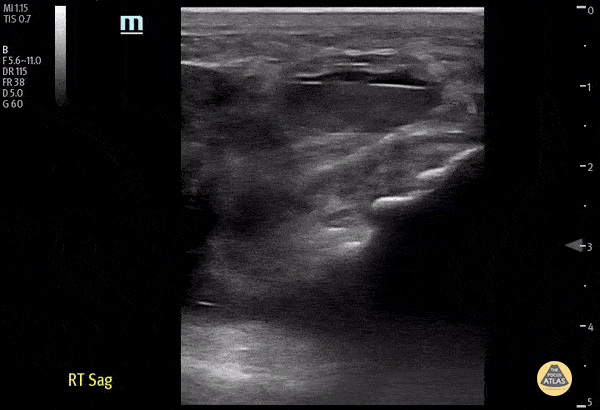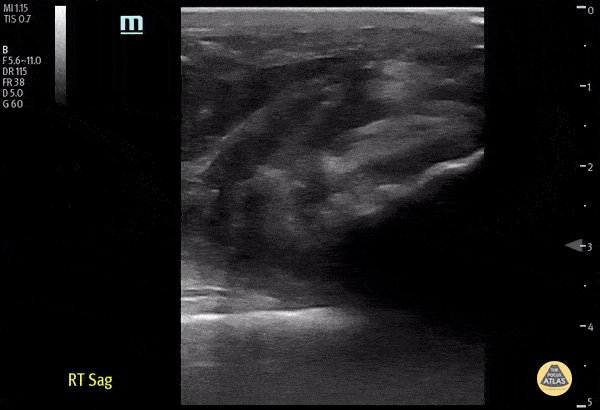
Distal Quadriceps Muscle Rupture
70 y/o male fell onto his right knee presented with visible deformity of the distal quadriceps muscle. Physical exam demonstrated weakness to active extension of the right knee. POCUS with a linear transducer demonstrated complete loss of tendon architecture of the right knee, including a hypoechoic defect between the tendon fibers. When compared to normal knee radiographs, the patient has significant displacement of the patella distally. Radiologists interpreted this as possible quadriceps tendon rupture. During operative repair, a complete rupture of the quadriceps was discovered and repaired.
Justin Morin, DO PGY-1 @justinjmorin; Alex Schlangen, DO PGY-1; Lauren Lowes, DO PGY-3; EM Residents at Central Michigan University
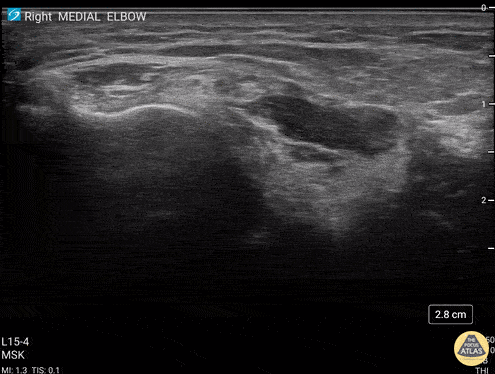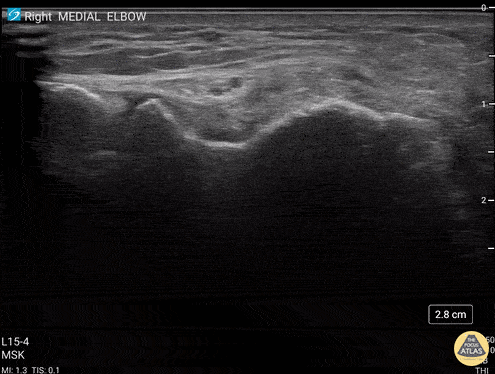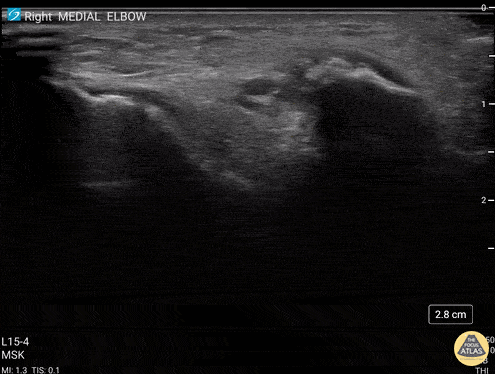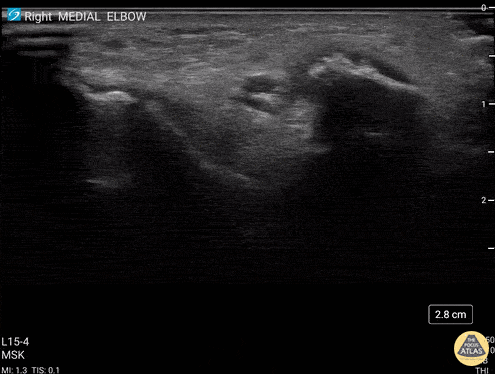
Common Flexor Tendon Tear At Elbow
59 y/o M presented with 1 year history of insidious onset R medial elbow pain especially worse with playing golf and was found to have a high grade tear of the common flexor tendon.
Video shows coronal view scanning posterior to anterior at the medial epicondyle (right is proximal). There is decreased echogenicity throughout the entire length of the tendon, but normal fibrillar tendon appreciated at deep aspect of tendon. There is an enthesophyte noted at the insertion site.
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
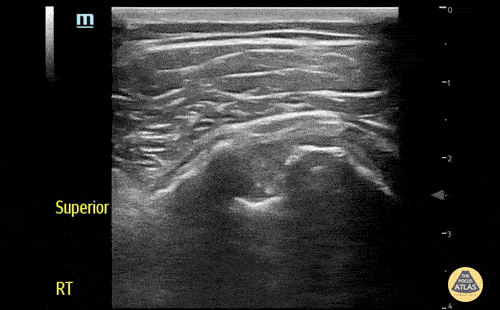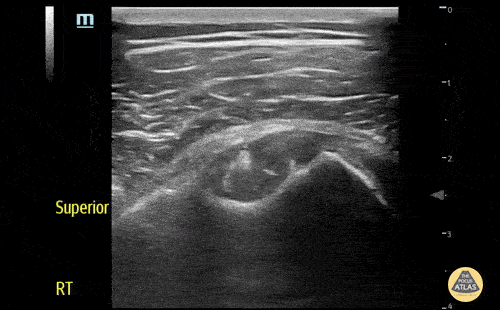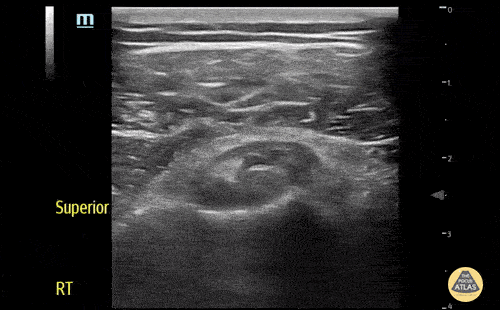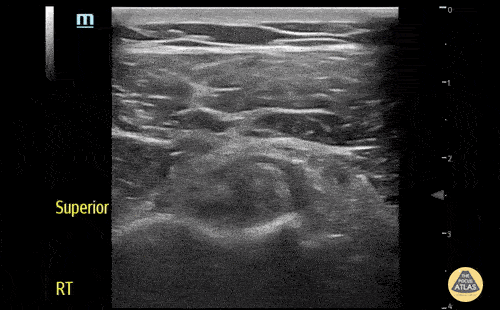
Biceps long head tendon rupture, transverse view
The patient presented with sudden onset right shoulder pain. On physical examination, there was tenderness to palpation anteriorly over the humeral head. POCUS demonstrated a heterogeneous structure within the bicipital groove representing a tendon stump surrounded by a developing anechoic haematoma. This study is in keeping with a complete rupture of the biceps long head tendon. This case illustrates the utility of POCUS as a diagnostic tool for the rapid identification of MSK injuries in the ED.
Contributors: Andrew Namespetra(@AndrewNamespet1), MB BCh BAO MSc; Nava Kendall, MD
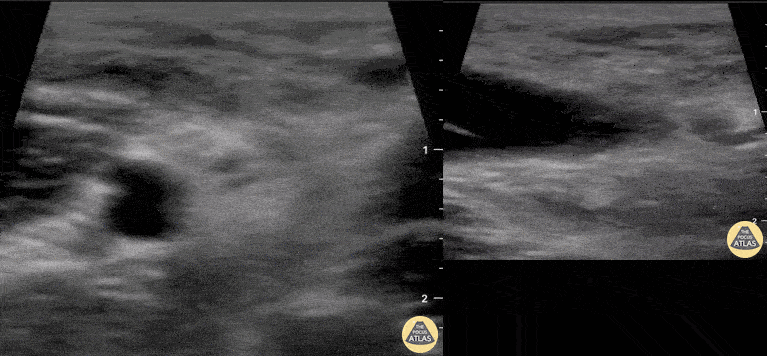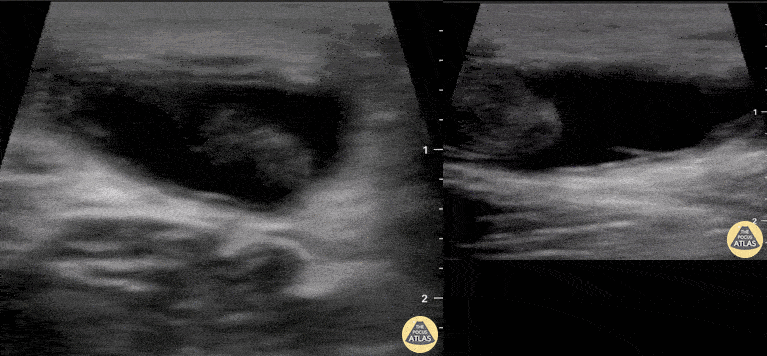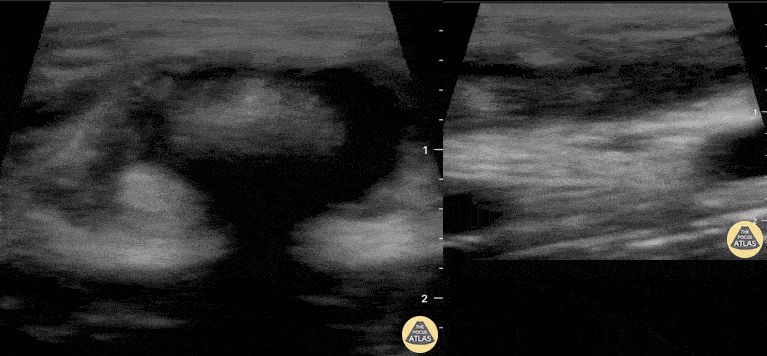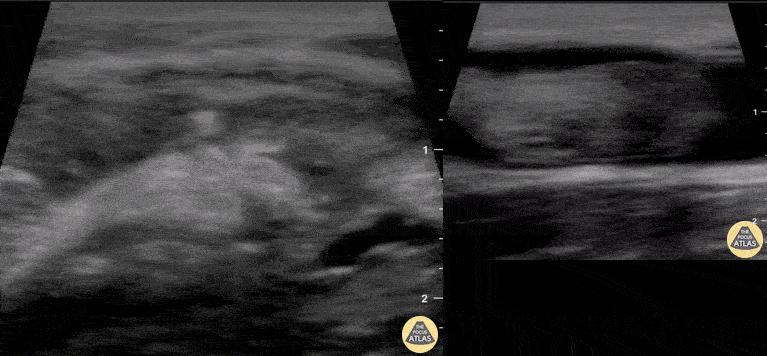
Distal Biceps Tendon Rupture
A 30-year-old male presented with acute-onset left anterior elbow pain after feeling a “pop” while weight-lifting. On exam, there was an obvious reverse popeye sign, swelling and mild ecchymosis. There was slight weakness in flexion and supination. Hook test was positive. A Butterfly IQ was used on an MSK soft tissue setting to assess the tendon in long and short axis via an anterior approach. Discontinuity of the tendon and surrounding anechoic fluid representing hematoma were noted. Orthopaedic surgery was consulted and reviewed ultrasound images. As a result, the patient had an urgent MRI and underwent expedited surgical repair.
Melanie Leclerc, MD CCFP(EM). @MelanieLecler19
David Lewis MB,BS FRCS FCEM CFEU PGDipSEM
Saint John Regional Hospital, New Brunswick, Canada

ACL/LCL Injury
A 32-year-old male pedestrian struck by a jeep traveling at 30 mph was evaluated with POCUS for left knee injury. He sustained a left-sided rupture of ACL, LCL, and an avulsion fracture of his IT band. Pictured here is his left lateral knee US performed 10-days after the acute injury. You can appreciate the popliteus notch in the lateral femur, typically both the origin of the popliteus muscle and the plane the LCL traverses to the fibula; here only notable for diffuse edema.
Eben Alexander

Ligamentous Knee Injury
A 34-year-old male trauma patient was evaluated with POCUS for left knee swelling. He was appreciated to have multi-ligamentous injury of the left knee, with imaging notable for hypoechoic fluid within the suprapatellar plica (bursa) and evolving septation of the fluid.
Kwasi Ampomah
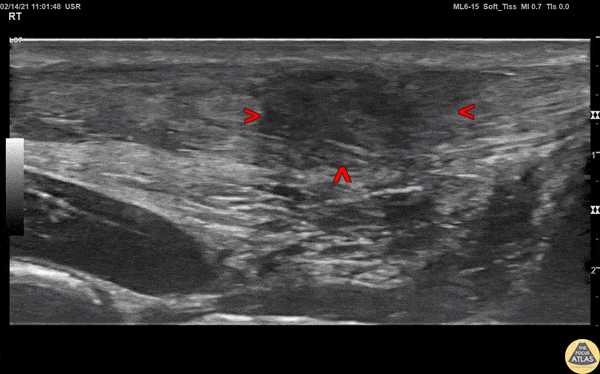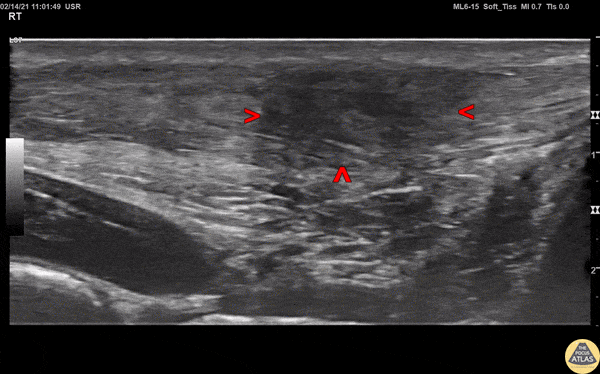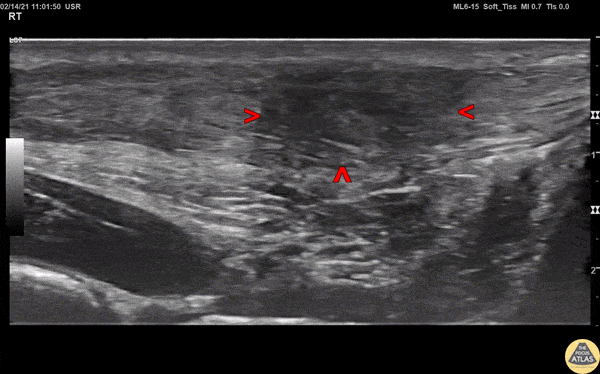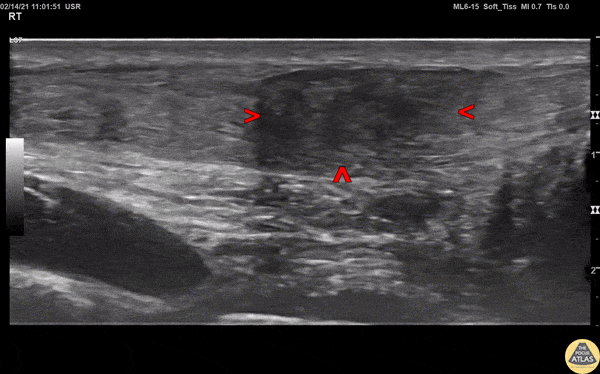
Achilles Tendon Injury
A 20s M presented with an ankle injury after landing a skateboard trick and feeling a painful pop in his posterior ankle. He had a positive Thompson test on exam. POCUS of the affected Achilles tendon was performed. This clip shows a long axis view of the Achilles tendon using the linear transducer, with inferior at the right of screen and superior at the left of screen. There is a relatively hypoechoic area (within red arrowheads) within the normally hyperechoic tendon, and the thickness is increased in this area as well, indicating focal injury to the tendon. Orthopedics was consulted, and the patient was placed into a splint in plantar flexion and discharged with outpatient follow up. MRI later confirmed a full thickness Achilles tendon tear and the patient was scheduled for surgery.
Jaimie Trenney, PA-C
Denver Heath Medical Center
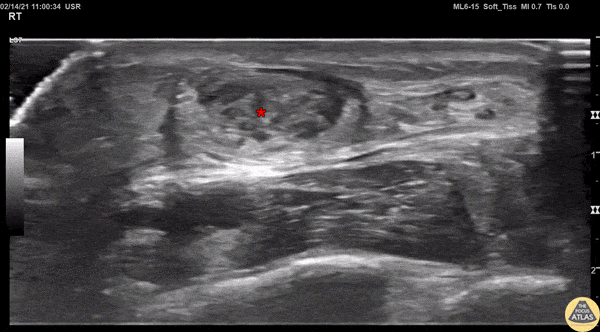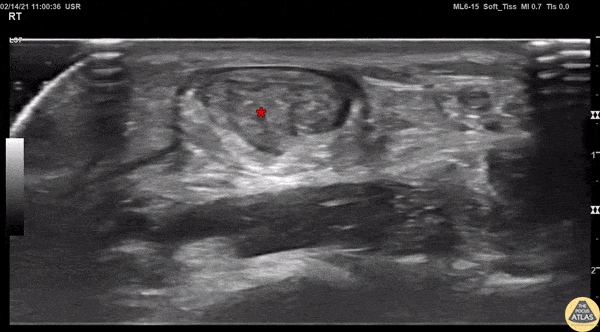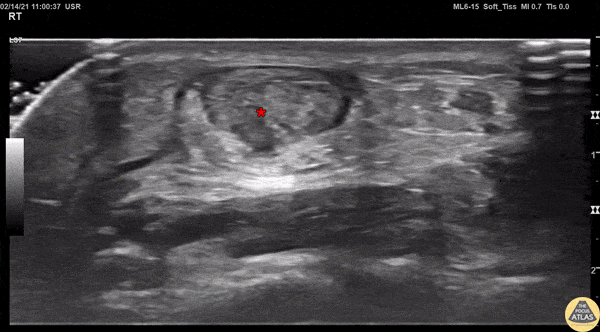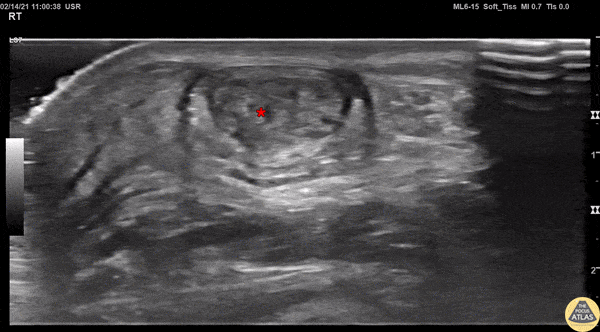
Achilles Tendon Injury Short Ais
A 20s M presented with an ankle injury after landing a skateboard trick and feeling a painful pop in his posterior ankle. He had a positive Thompson test on exam. POCUS of the affected Achilles tendon was performed. This clip shows a short axis view of the Achilles tendon using the linear transducer. There is a relatively hypoechoic area (*) within the normally hyperechoic tendon, indicating focal injury to the tendon. Orthopedics was consulted, and the patient was placed into a short leg splint in plantar flexion and discharged with outpatient follow up. MRI later confirmed a focal full thickness Achilles tendon tear and the patient was scheduled for surgery.
Jaimie Trenney, PA-C
Denver Heath Medical Center
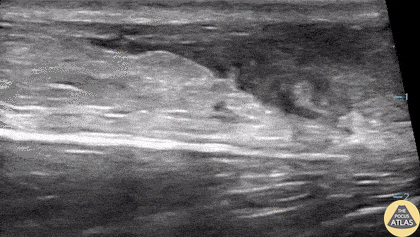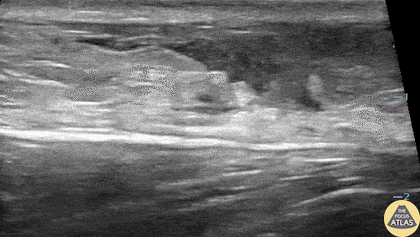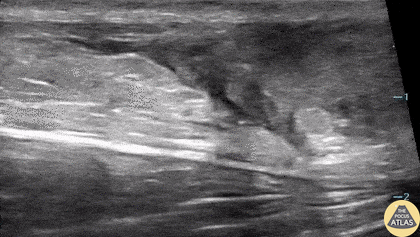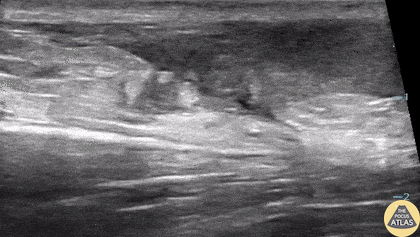
Ruptured Achilles Tendon
16-year-old male presented with acute onset sharp pain to his LE and inability to bare weight after having landed oddly while playing basketball. POCUS revealed a near-complete disruption of his Achilles Tendon.
Paul Khalil, MD. Assistant PEM POCUS director at University of Louisville/Norton Children’s
@Khalil3Paul
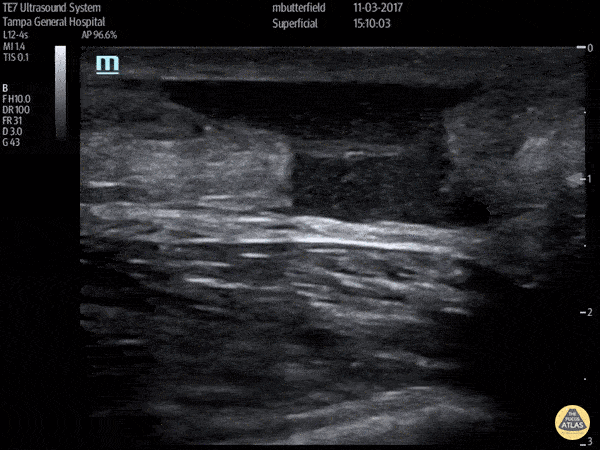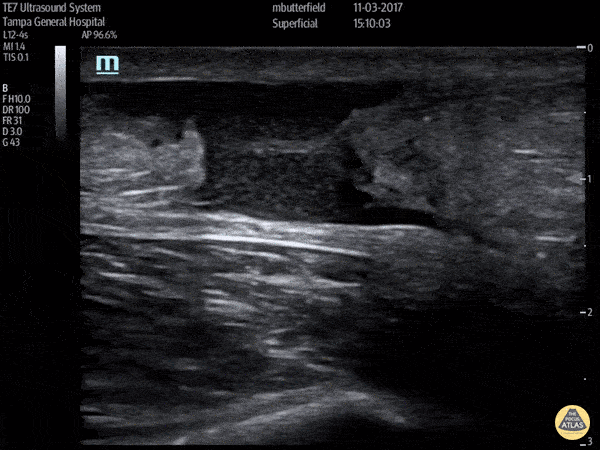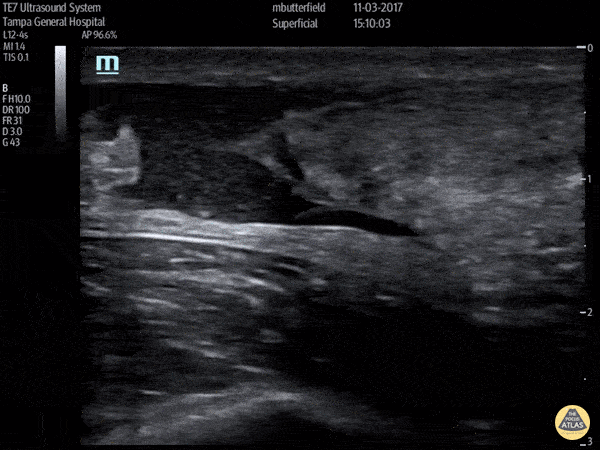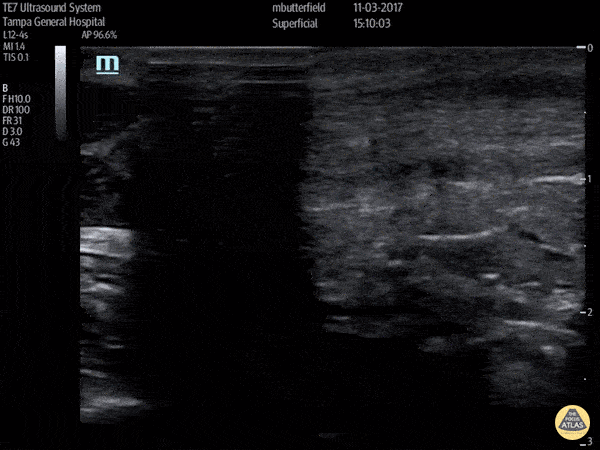
Achilles Rupture (Long Axis)
Full thickness tear of right achilles tendon after a skateboarding accident. (Long Axis)
Dr. Mike Butterfield
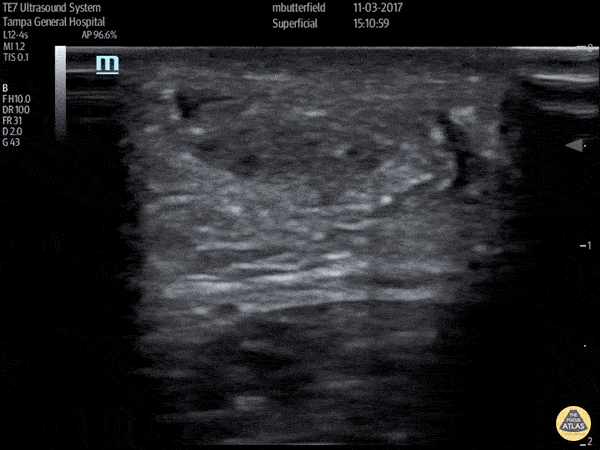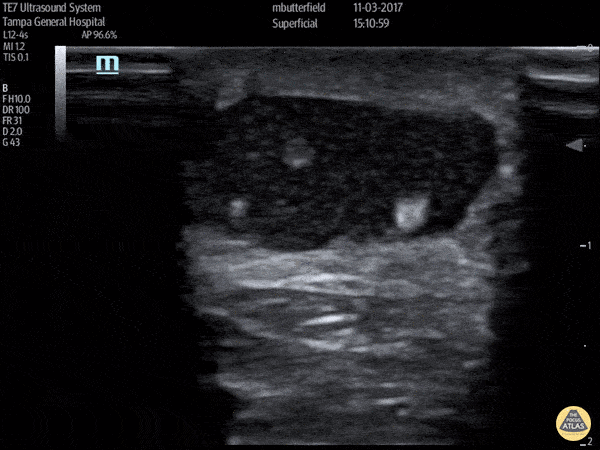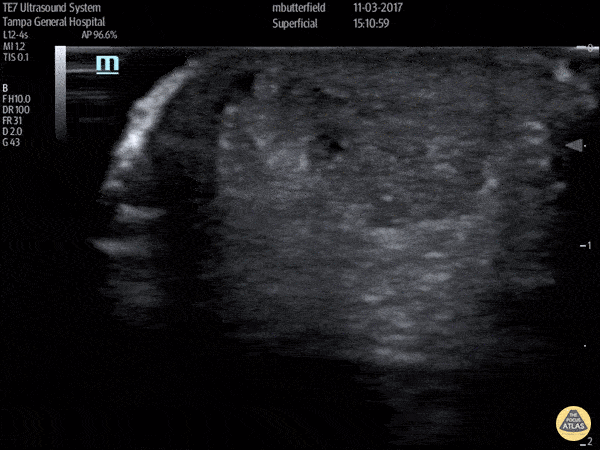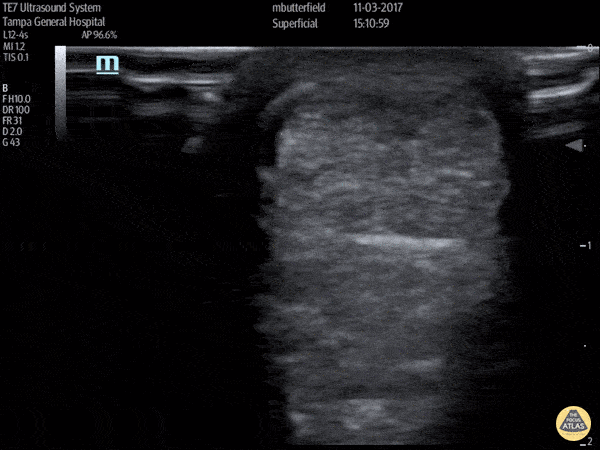
Achilles Tendon Rupture (Short Axis)
Full thickness achilles tendon rupture of the right leg after a skateboard accident. (Short Axis)
Dr. Mike Butterfield
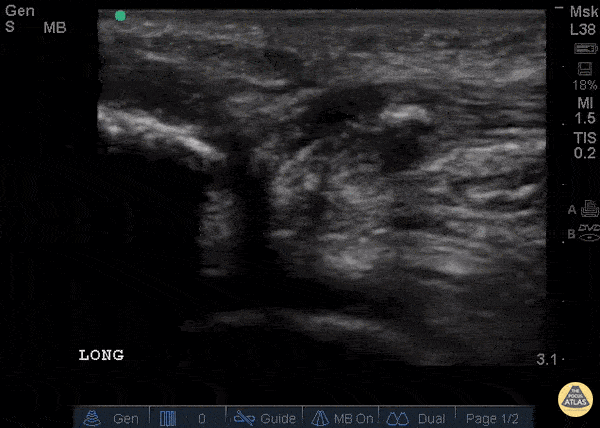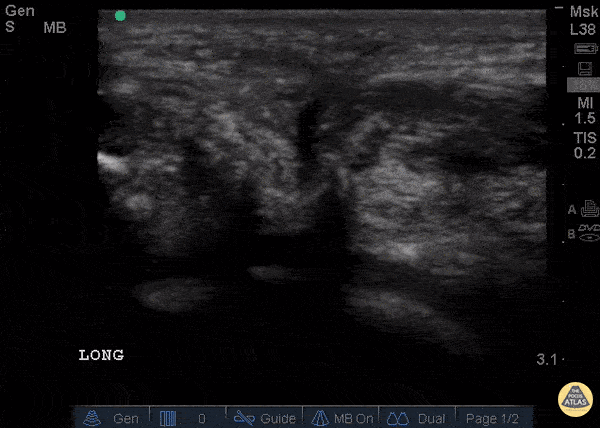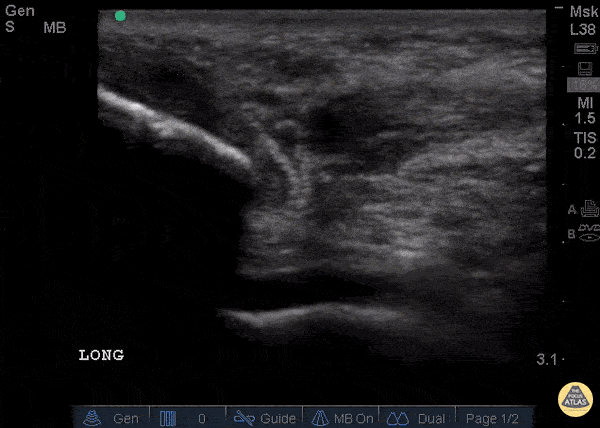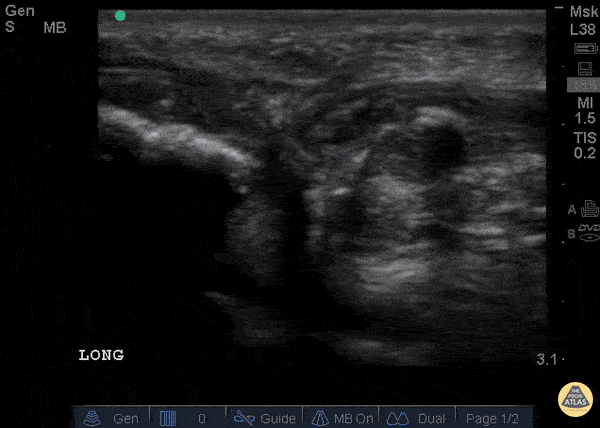
Patellar Tendon Rupture Longitudinal
34 y/o M presented with swelling and pain inferior to his knee following hearing a pop when he jumped playing basketball. Pt unable to extend leg and x-ray demonstrated a high riding patella. Longitudinal ultrasound showed a hyperechoic tendon that is not continuous between the patella and tibia, with an anechoic area of hemorrhage consistent with patellar tendon rupture.
Patellar tendon rupture can be diagnosed with H&P and POCUS can be used to confirm this diagnosis. In one study, diagnosis of tendon rupture by physical exam had a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 76%, while diagnosis by POCUS had a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 95%. Ultrasound is especially useful in patients who cannot cooperate with a physical exam, and serial ultrasound can also be used to monitor healing of a tendon rupture.
Caroline Rago - MS4, Dr’s Bryan Jarrett and Joshua Schechter - Kings County Emergency Medicine
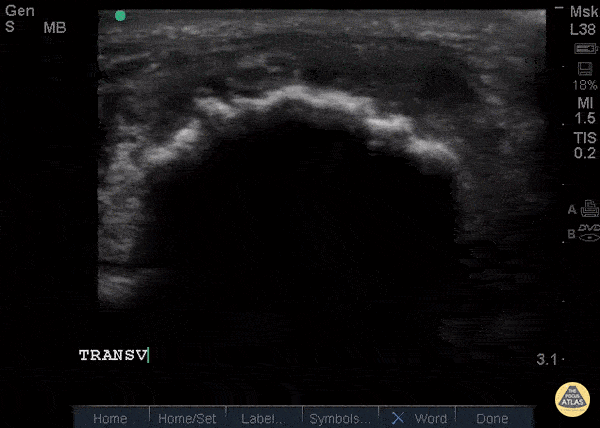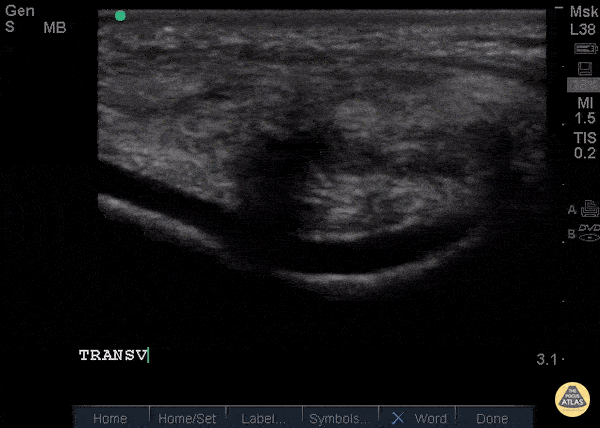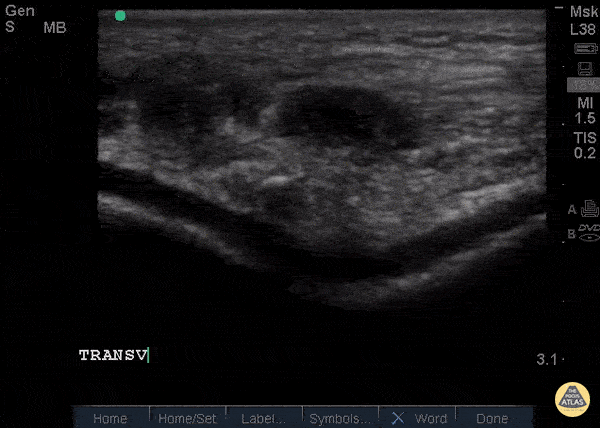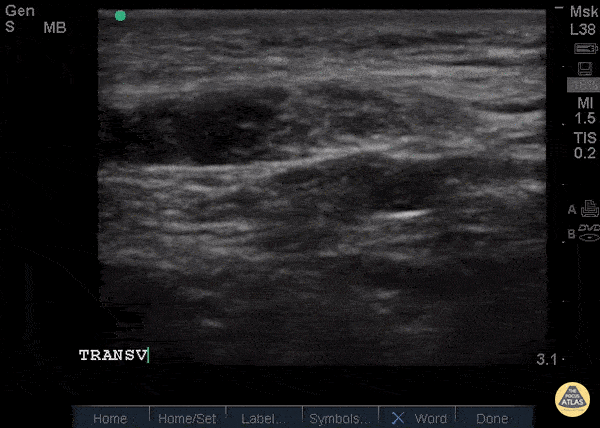
Patellar Tendon Rupture Transverse
34 y/o M presented with swelling and pain inferior to his knee following hearing a pop when he jumped playing basketball. Pt unable to extend leg and x-ray demonstrated a high riding patella. Longitudinal ultrasound showed a hyperechoic tendon that is not continuous between the patella and tibia, with an anechoic area of hemorrhage consistent with patellar tendon rupture.
Patellar tendon rupture can be diagnosed with H&P and POCUS can be used to confirm this diagnosis. In one study, diagnosis of tendon rupture by physical exam had a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 76%, while diagnosis by POCUS had a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 95%. Ultrasound is especially useful in patients who cannot cooperate with a physical exam, and serial ultrasound can also be used to monitor healing of a tendon rupture.
Caroline Rago - MS4, Dr’s Bryan Jarrett and Joshua Schechter - Kings County Emergency Medicine
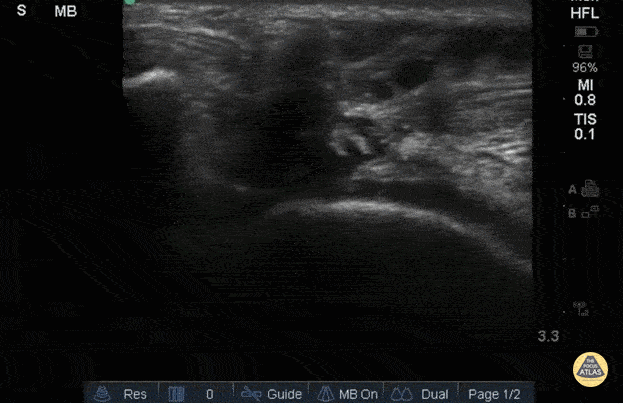
Right Patellar Tendon Rupture
56yo M with right knee swelling after getting foot stuck under a pallet and falling backwards, found to have patella alta and right patellar tendon rupture. Longitudinal image using linear 13-6MHz probe along proximal (left) and distal (right) patellar tendon with hypoechoic fluid at site of tendon rupture. Dynamic ultrasound is useful in diagnosing tendon ruptures as the site and extent of rupture can be easily visualized, which facilitates triage to surgery, if indicated.
Dr. Jasmin Harounian
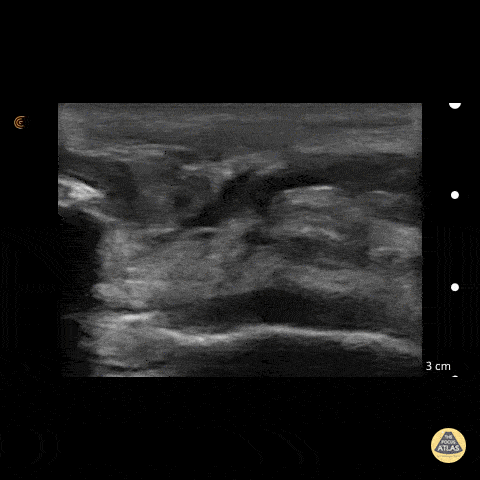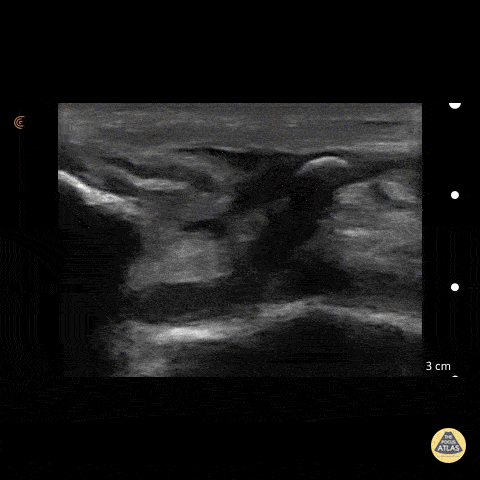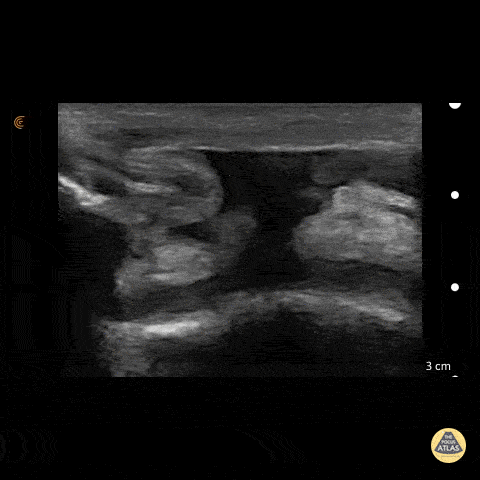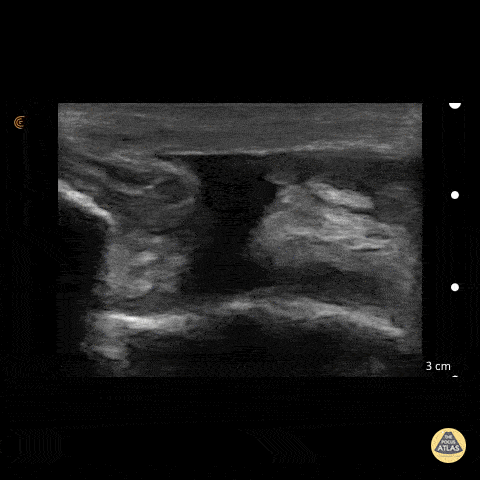
Patellar Tendon Rupture
50 y/o M presents with acute left anterior knee pain after fall. On exam, patient noted to have high riding patella.
Longitudinal sonogram of the infrapatellar region showed marked discontinuity of the normally hyperechoic linear patterned tendon. The discontinuity is replaced with an anechoic collection indicative of hemorrhage. Comparison to normal knee can be seen on the next post.
Of note, anisotropy may be encountered when utilizing ultrasound, leading to artifact. Depending on the angle of the insonating beam, a normally hyperechoic structure may be falsely viewed as hypoechoic due to poor return of echo. Ensure US probe remains perpendicular to the tendon to minimize this artifact.
Dr. Hannah Moreira, Dr. Tareq Azad, Dr. Kyle Kelson - Kings County/SUNY Downstate Emergency Medicine
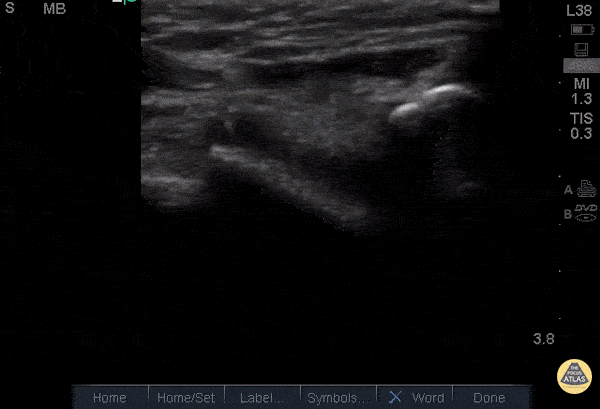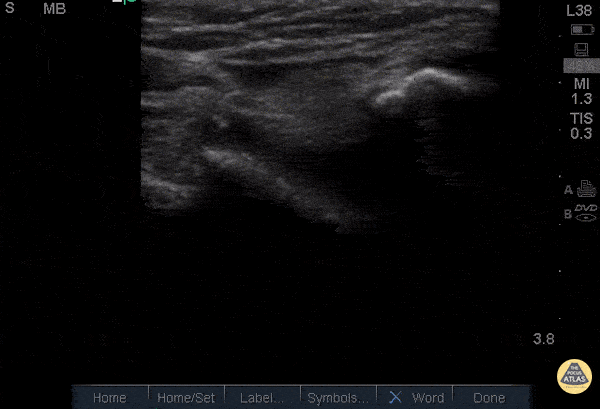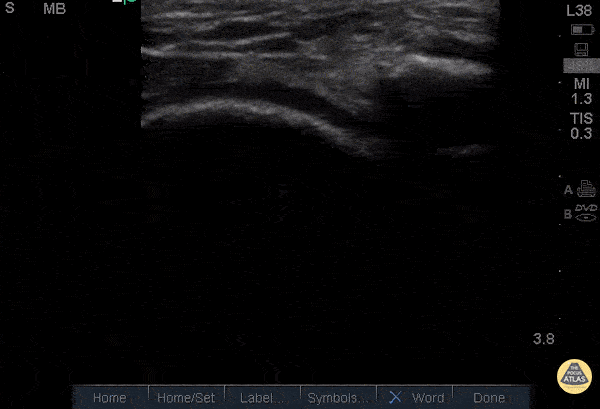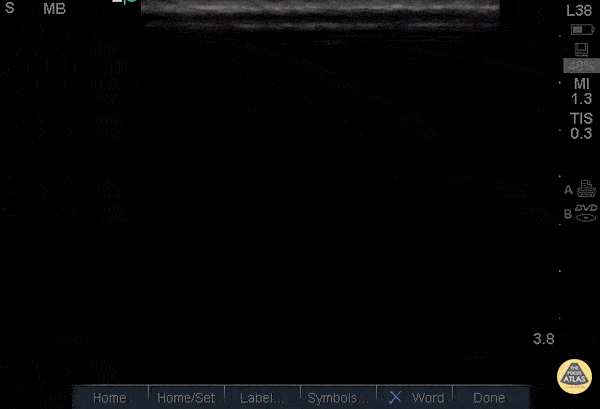
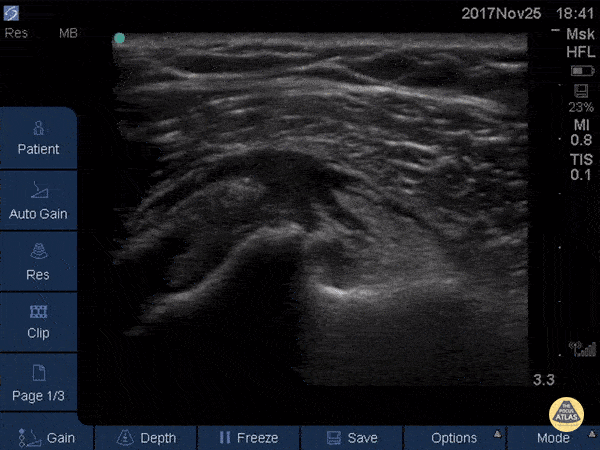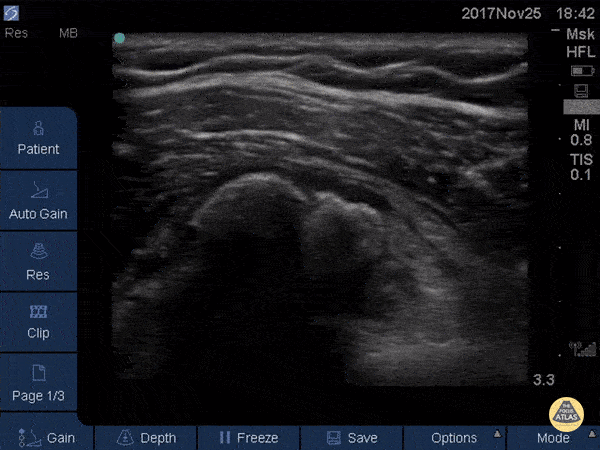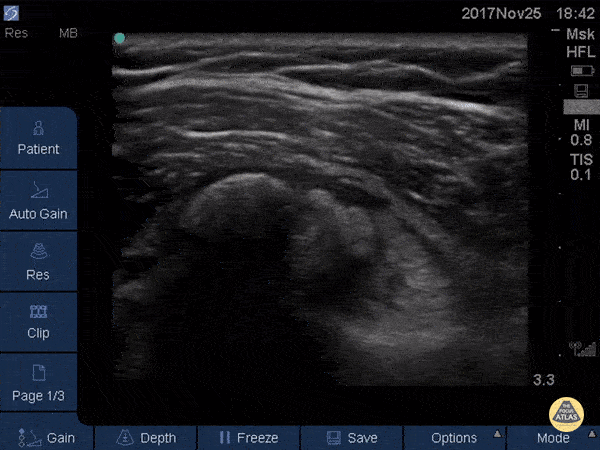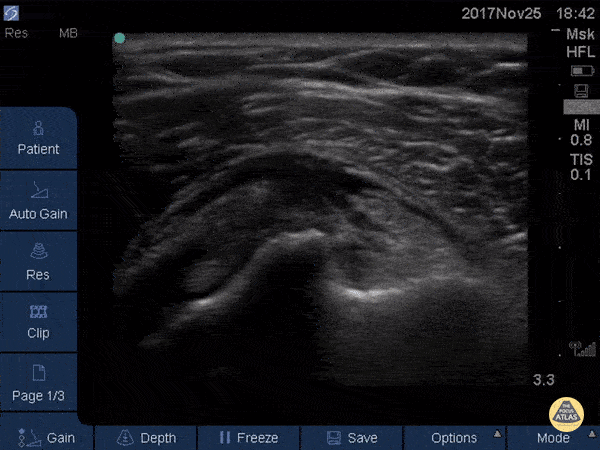
Quad Tendon Rupture (Bilateral)
40 year old M presented with bilateral knee pain and inability to extend knees after injuring knee while carrying heavy plywood boards.
POCUS confirmed the diagnosis of bilateral quadriceps tendon rupture. On ultrasound you can see the retracted tendon independent of the patella as the knee is being actively ranged. Also visible is a surrounding traumatic hematoma. One should look for discontinuity in the tendon in longitudinal view to diagnose any sort of tendon rupture. Often, there is an adjacent fluid collection reflecting hematoma. Be careful not to interpret the anisotropy of the ultrasound as discontinuity. Anisotropy is that the US looks different in cross section vs longitudinal views, any variation in the direction of the tendons and the positioning of the probe can lead to a false positive.
Dr. Nathan Frank, Dr. Benjamin Weissman, Dr. Walter Valesky - Kings County/SUNY Downstate Emergency Medicine
Subscapularis Tendinopathy
50 year-old woman with anterior left shoulder pain; severe subscapularis tendinopathy with calcification and several small tears.
Dr. Mike Butterfield
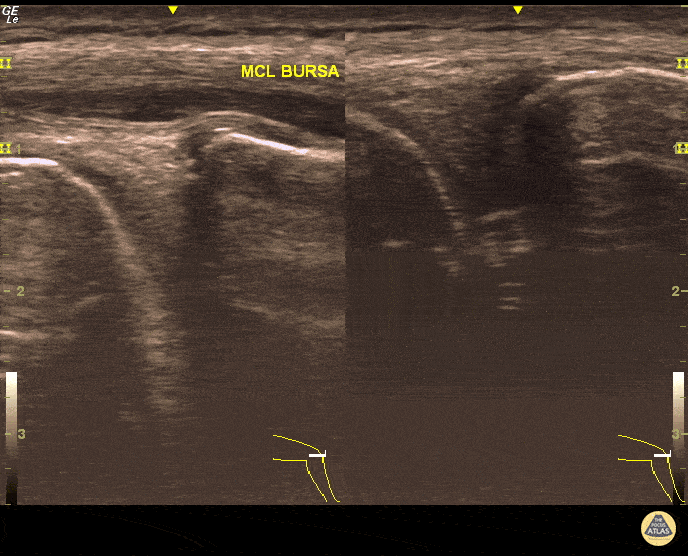
MCL Bursitis
29 year-old elite level soccer player with medial knee pain. He describes this being 'the worst episode ever', as he was having recurrent episodes of such pain. Valgus and flexion deformity due to prior surgery 15 years ago at the affected knee. Sharp, non-radiating pain 9/10 on NPRS, wakes him up at night. Palpation of medial knee and valgus stress test positive. Concomitant recent trauma. Unable to train/compete. USG of his knee revealed both MCL insertional edema (grade 1 injury) and MCL bursitis. Guided aspiration (3cc) and corticosteroid injection to MCL bursae revealed excellent outcomes. He returned to play 3 days later. Pitfall: It was not an MCL injury. Key point : Intervention was necessary and US-guidance allowed correct needle positioning without complication.
Dr. Omer Batin Gozubuyuk, Sports Medicine Specialist, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey.
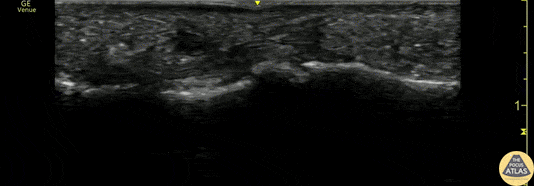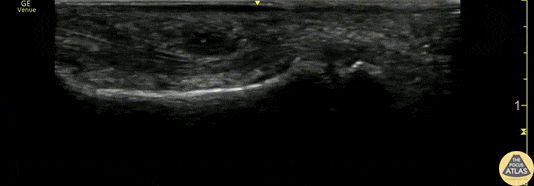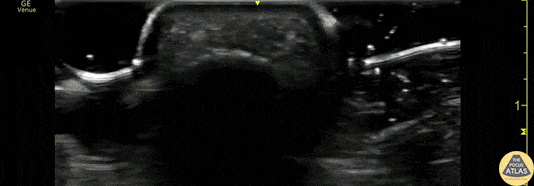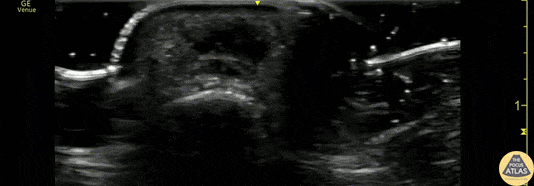
Flexor Tendonitis
A 50s M presented with atraumatic finger pain/swelling x2 weeks. On exam, he had focal swelling localized the volar aspect of the ring finger over the proximal phalanx, without fusiform edema/erythema or any limitation of ROM. POCUS showed a small fluid collection adjacent to the flexor tendon. The flexor tendon is shown in long axis, with linear fibers seen just superficial to the bone cortex, and then is seen in short axis. The hypoechoic area superficial to the tendon represents the fluid collection. As the patient had intact ROM and no signs of infection, he was splinted and will follow up for a recheck of tendonitis.
Kristy Karkula, PA and Dr. Ruth Foss
Denver Health Medical Center
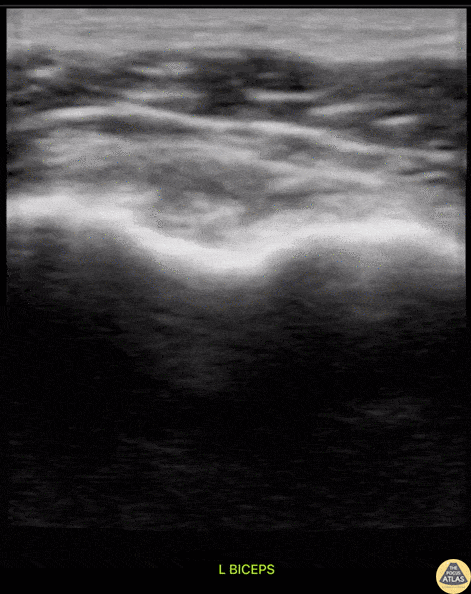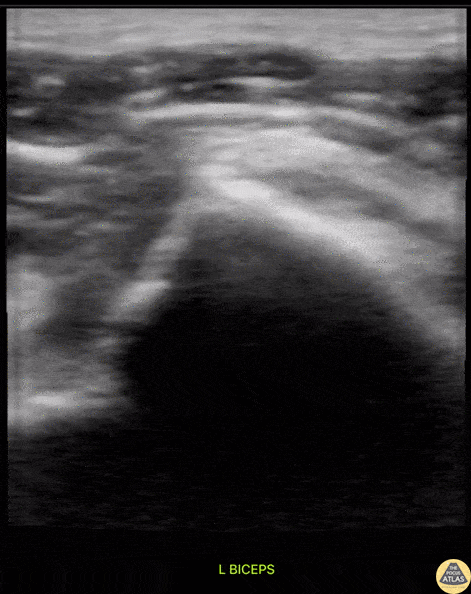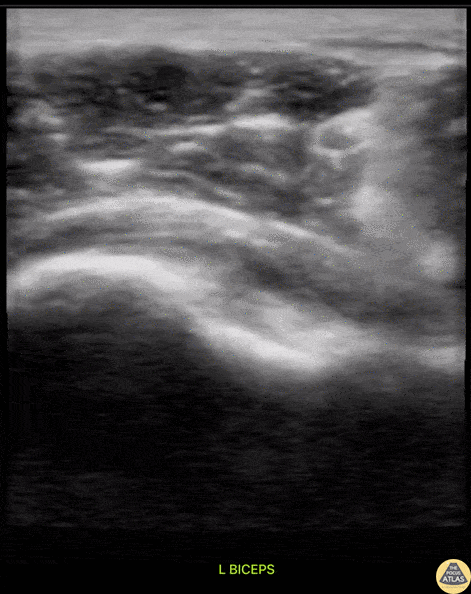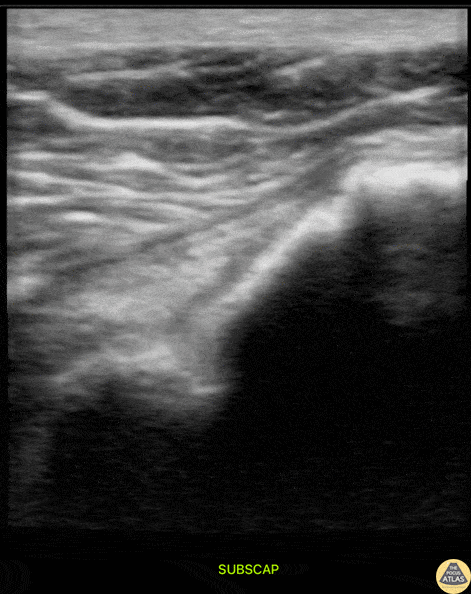
Subscapularis Tendon Tear
A middle aged male presented to the ED with shoulder pain after skiing crash. POCUS of the shoulder was performed, showing a subscapularis tendon tear. Here, the proximal humerus is shown in short axis, with the linear probe placed in transverse orientation at the anterior aspect of the shoulder. The biceps tendon is seen in the biceps groove, between the greater tuberosity (lateral or right of screen) and lesser tuberosity (medial or left of screen). The patient is asked to externally rotate the arm, which brings the subscapularis tendon into view, and a hypoechoic, thickened area is seen, indicating a tendon tear.
Dr. Matthew Riscinti
Denver Health Medical Center
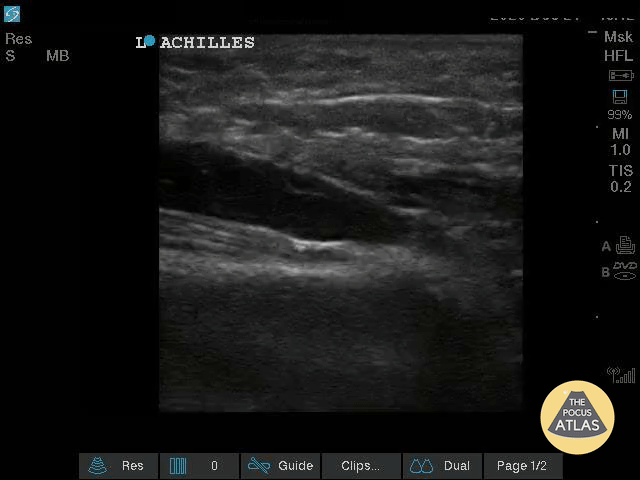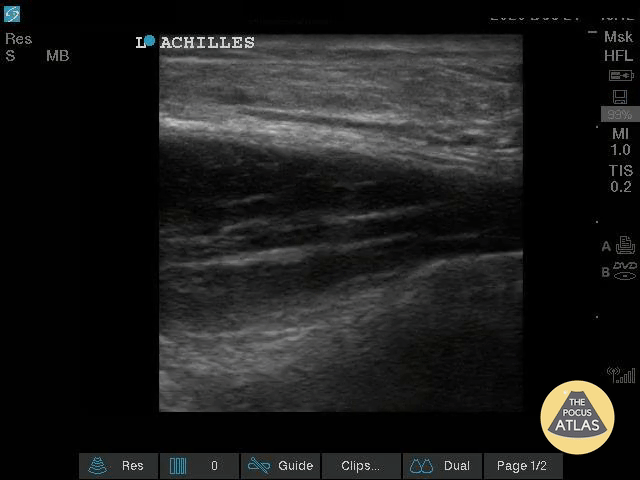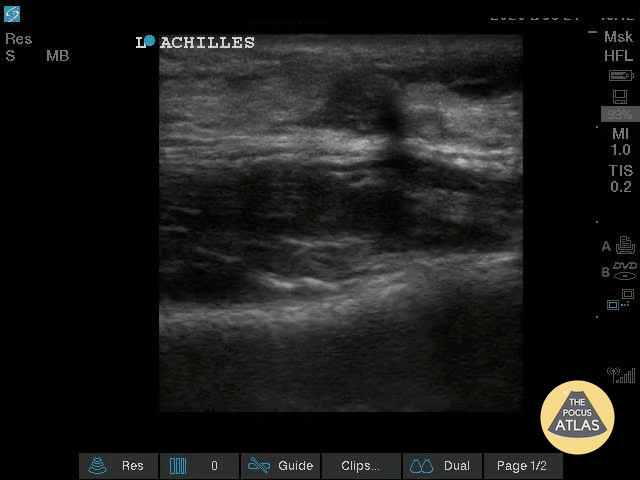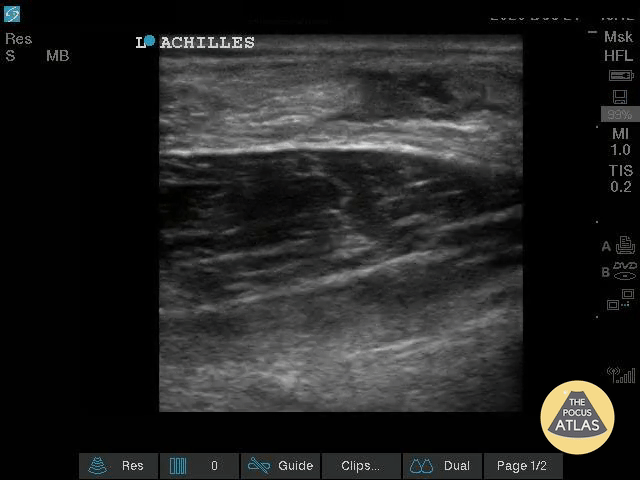
Nearly Complete Achilles Tear
Healthy male in late-20s trying to do a backflip off a diving board. Still was able to plantarflex (very weak and with significant pain).
Submitted by Dr. Elias Jaffa

Achilles Tendon Rupture
20s M presented with calf/heel pain after skateboarding, found to have a positive Thompson test. POCUS confirmed a full thickness tear of the achilles tendon. The patient was splinted and referred to orthopedic surgery for repair.
Alexandrea Netto PA, Denver Health and Hospital Authority
Lois Isaksen MD, Attending Physician, Denver Health Residency in Emergency Medicine
























