Musculoskeletal
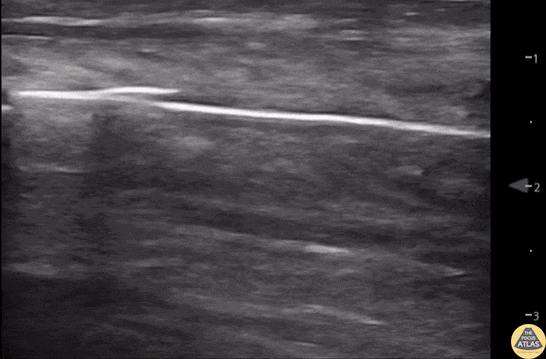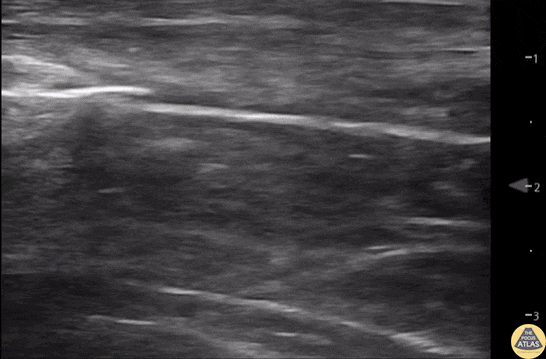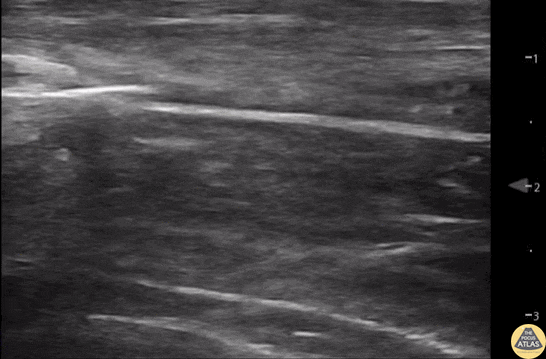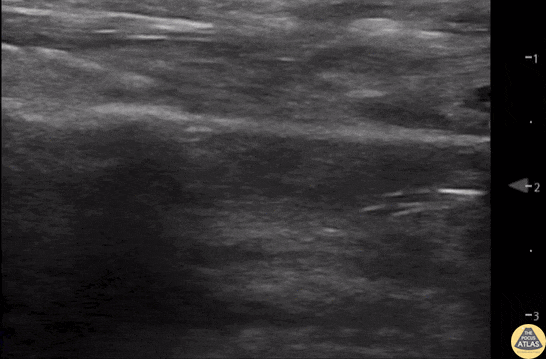
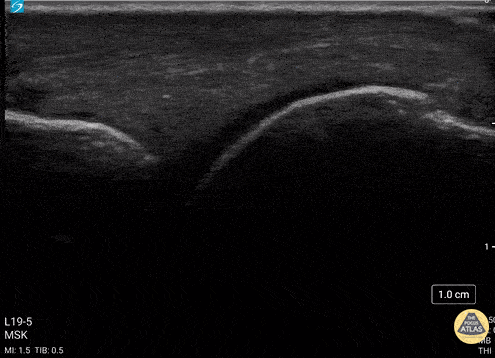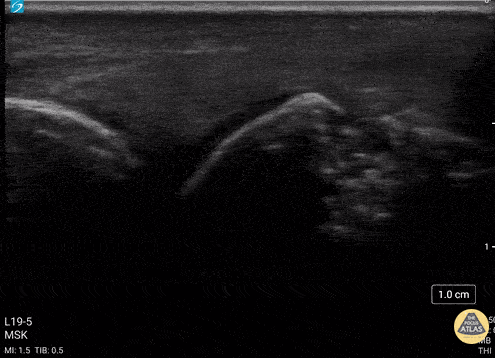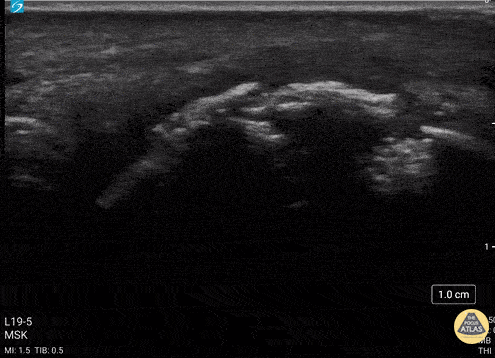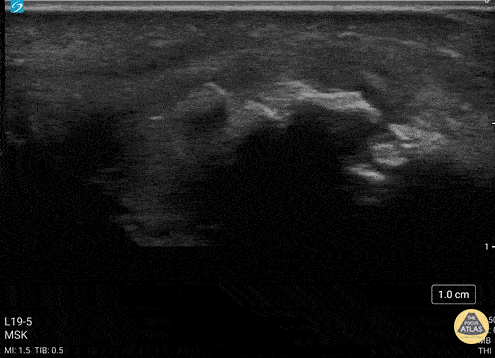
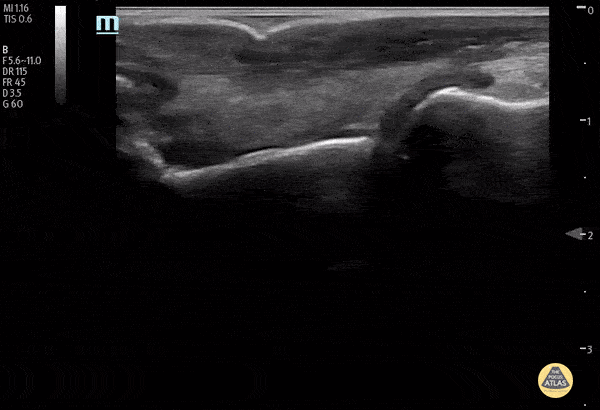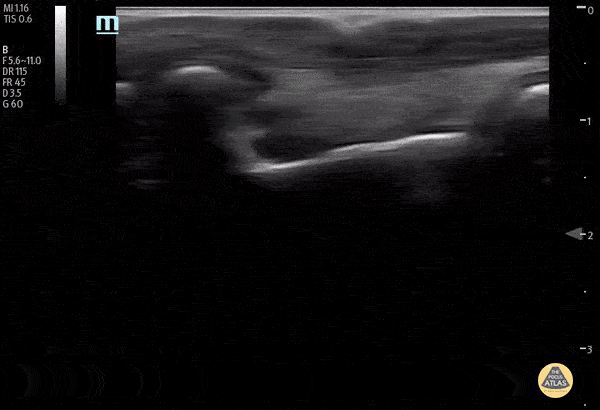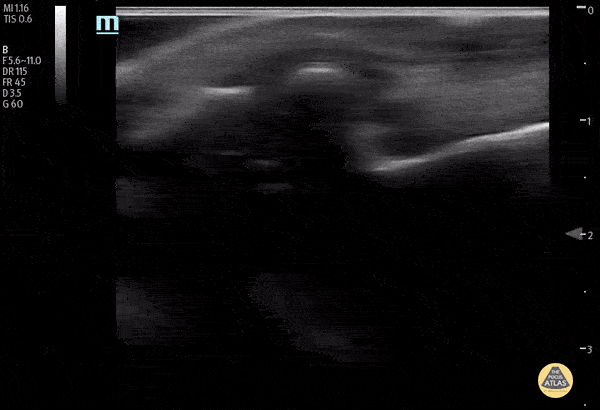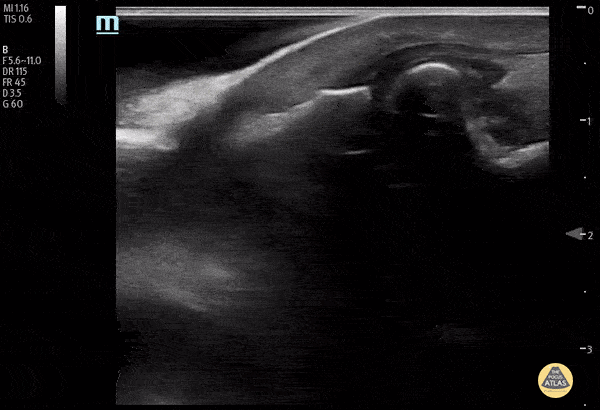
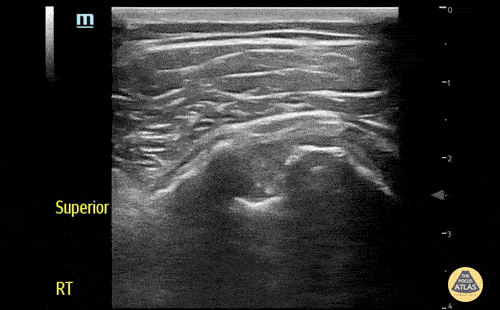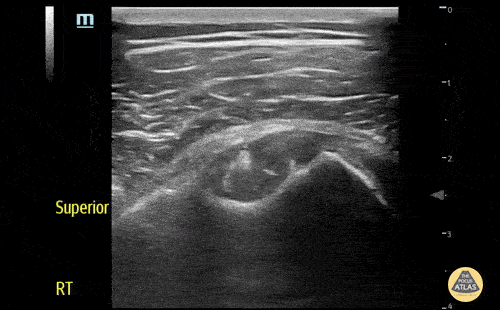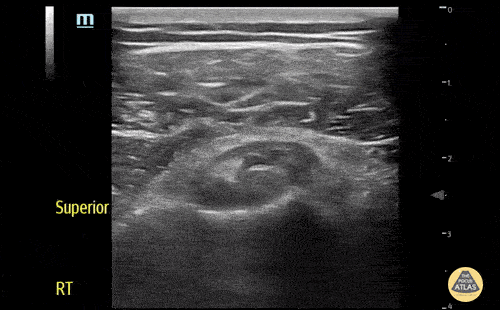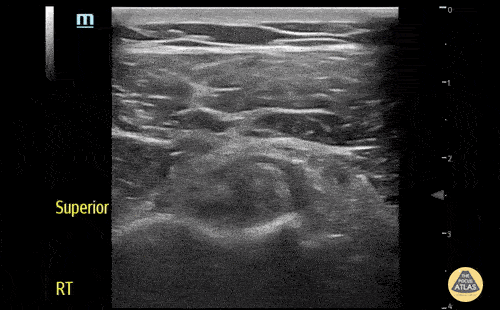
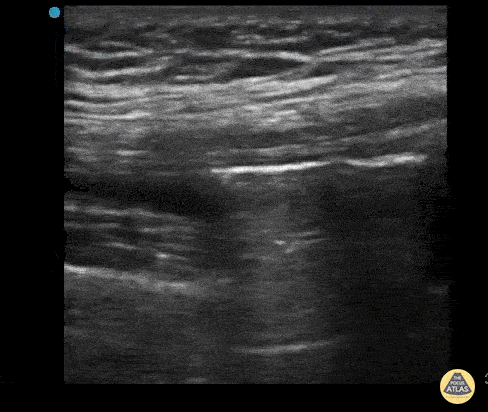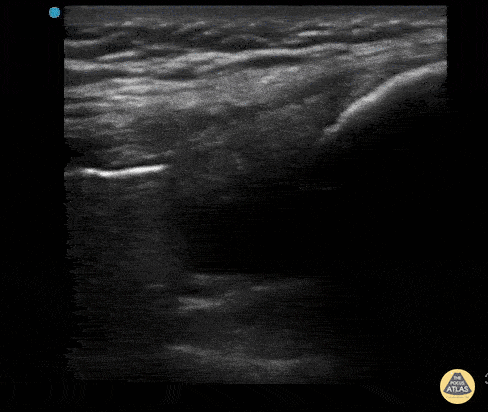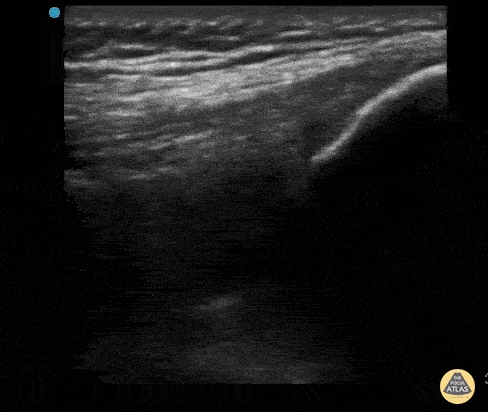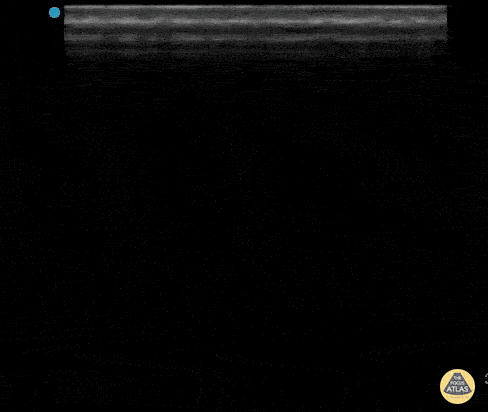
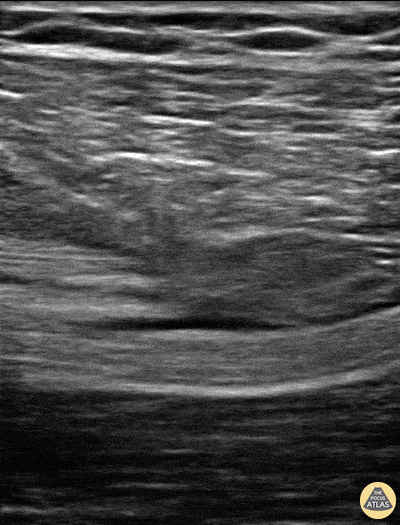
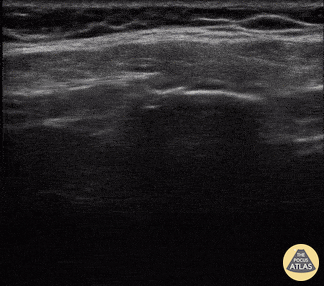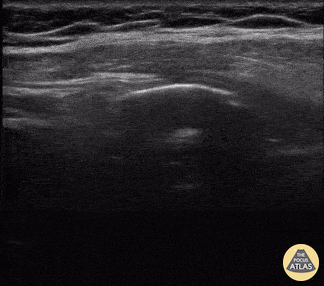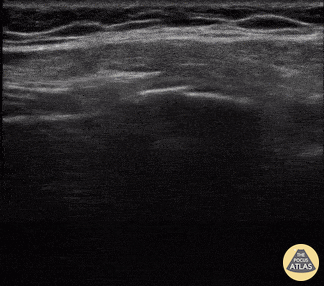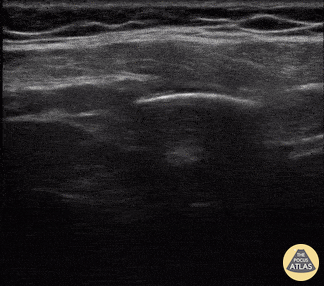
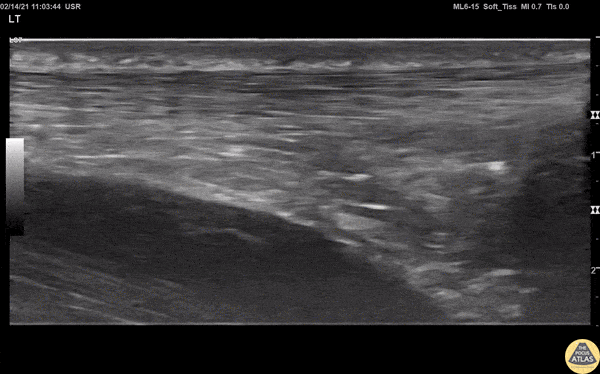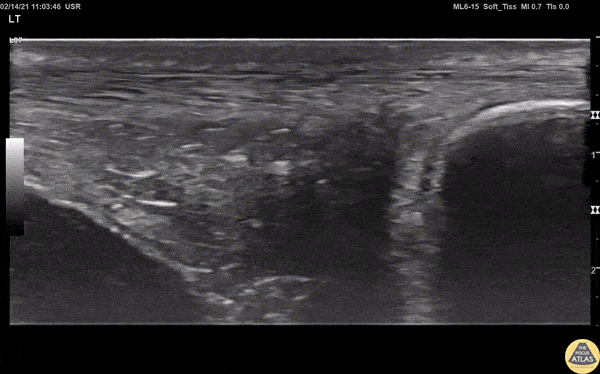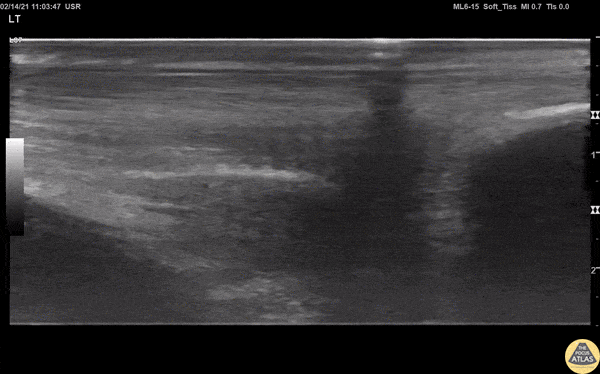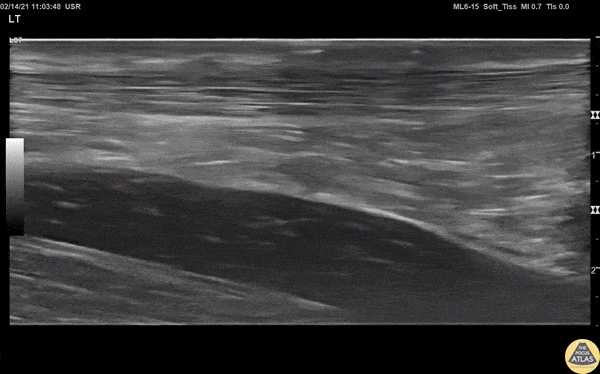
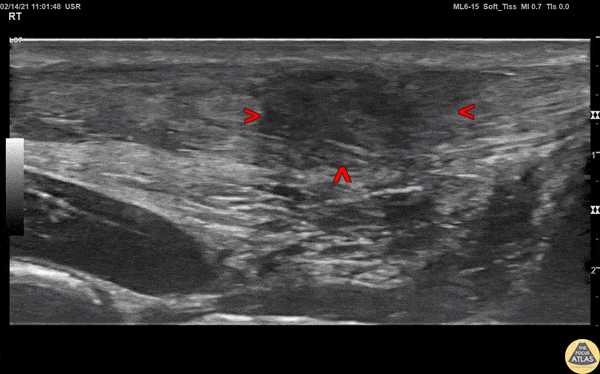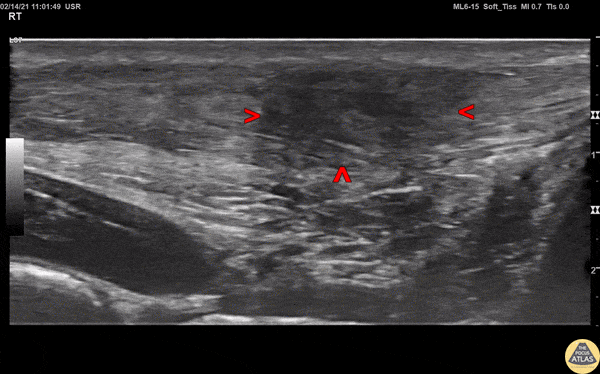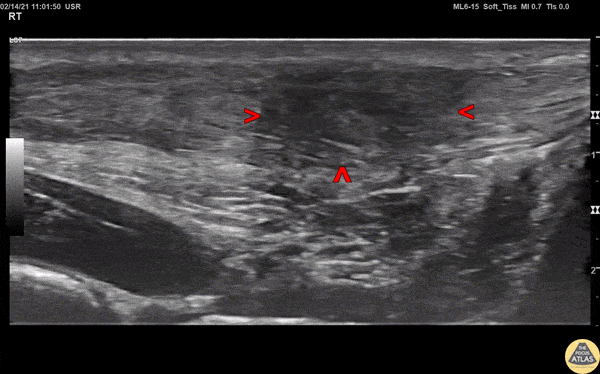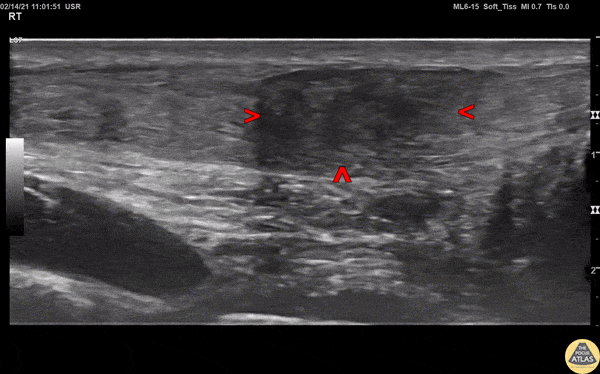
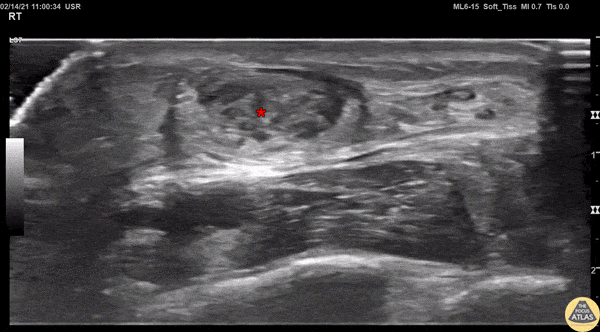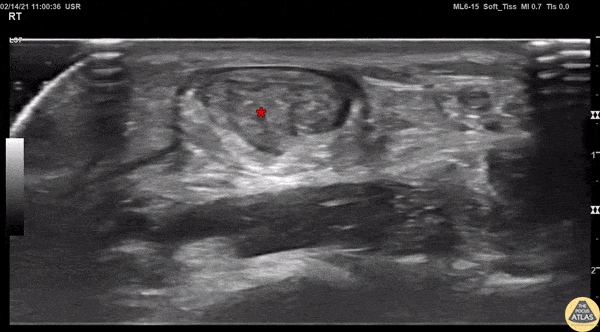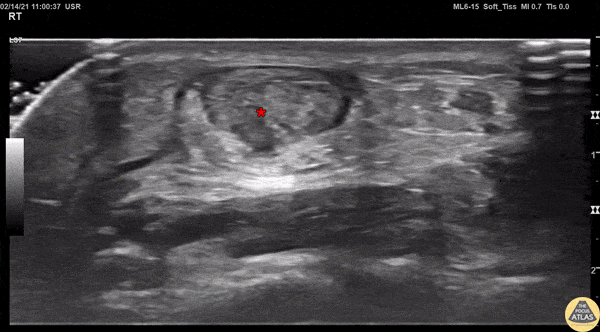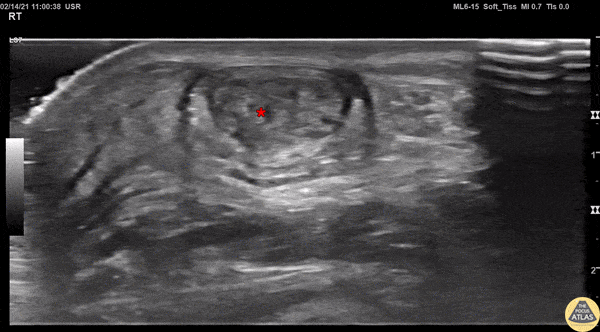
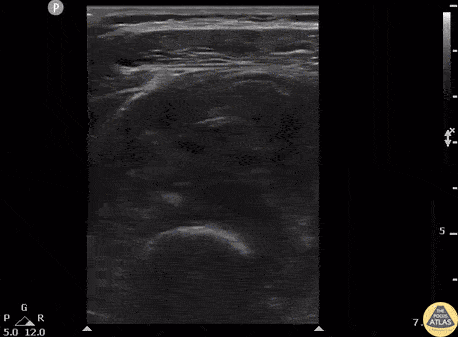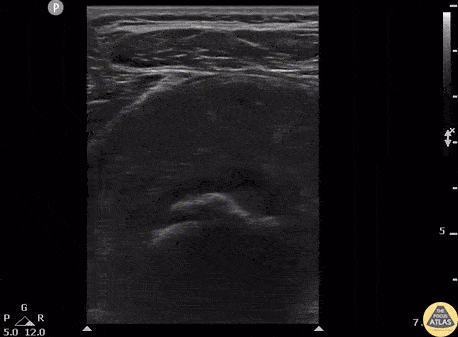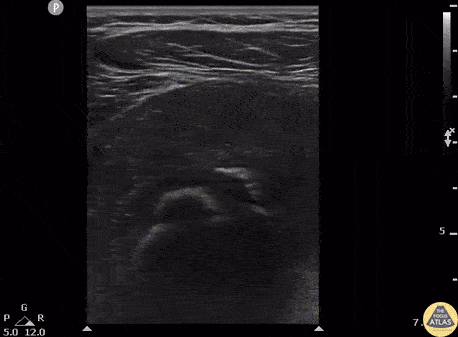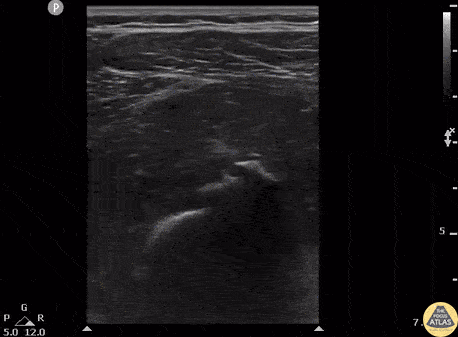
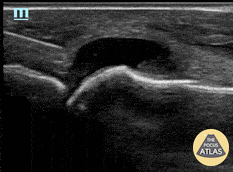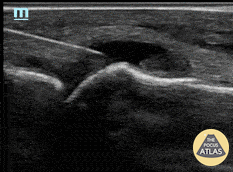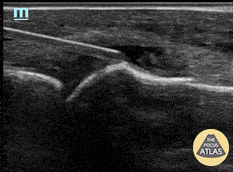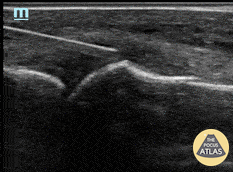
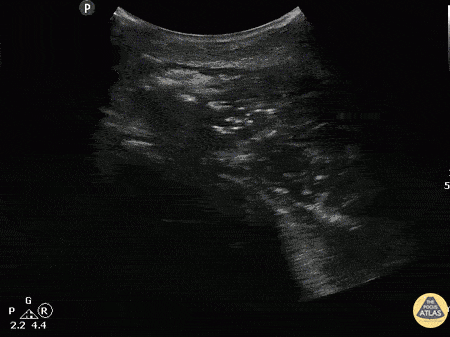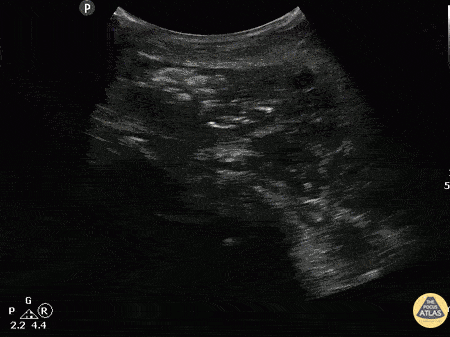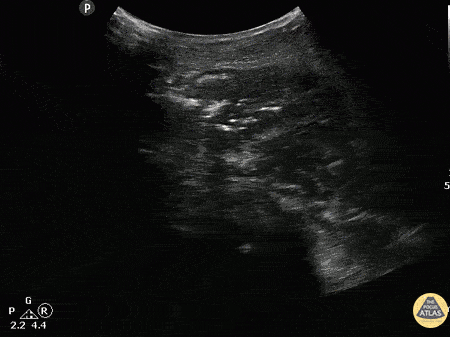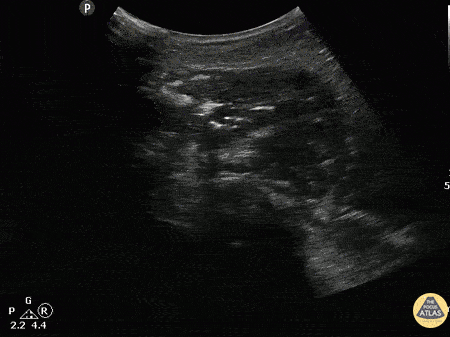
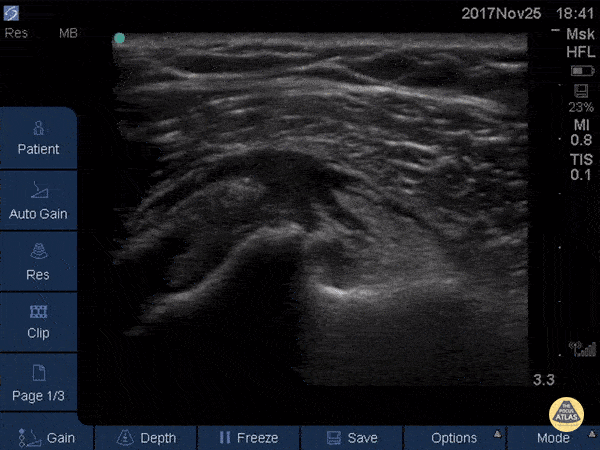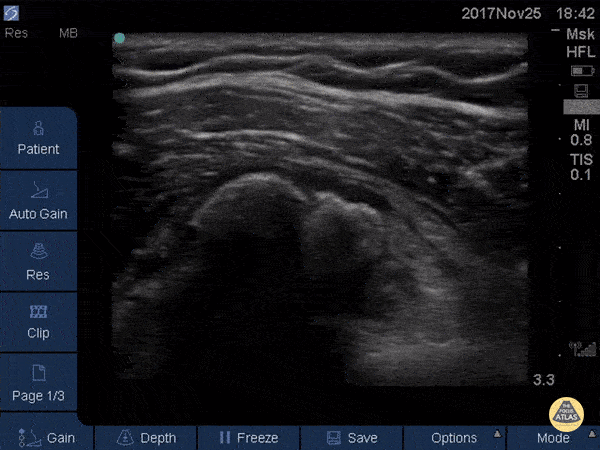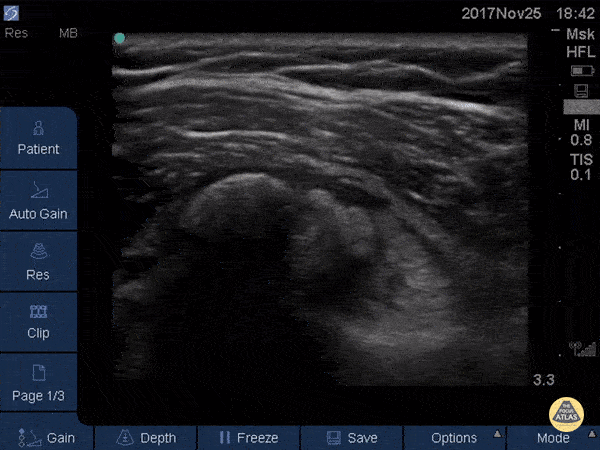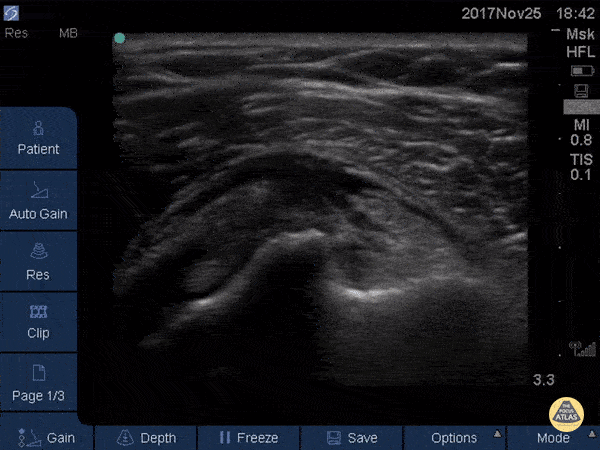
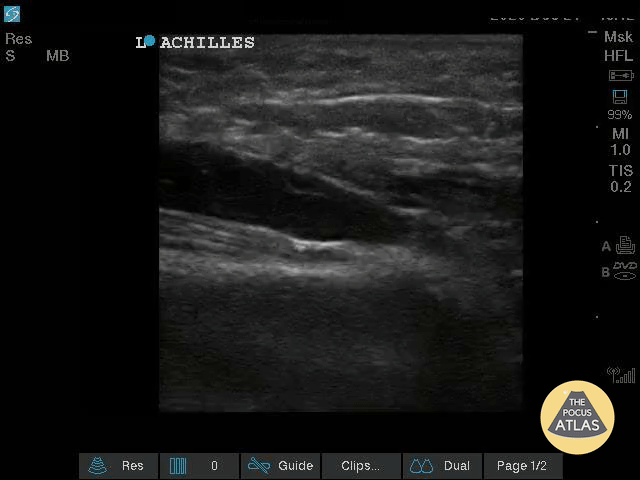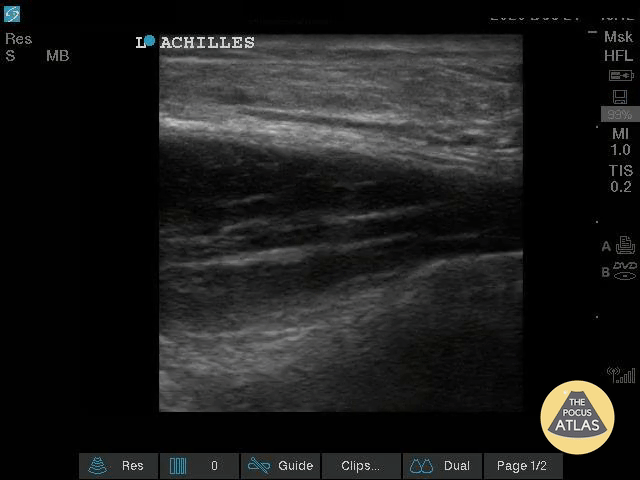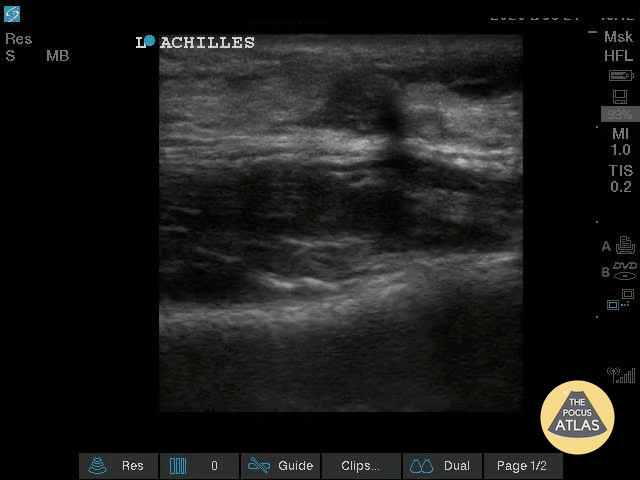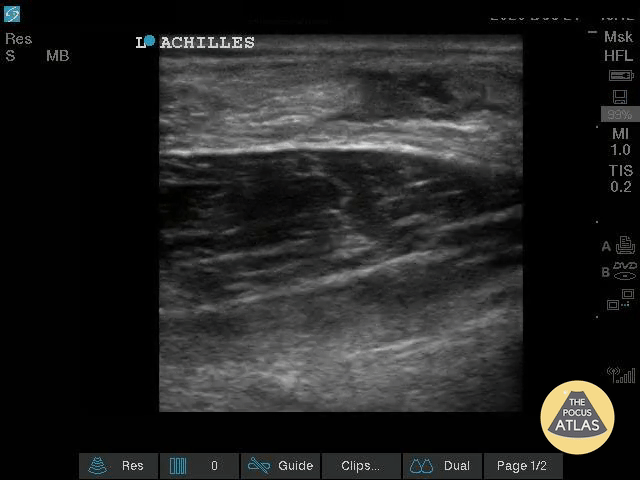
Normal Knee US in TKA Patient
55 yo F s/p RT TKA w/ revision presents after a fall. POCUS was w/o tendinous/bony abnormality. RT knee x-ray was w/o definite acute fracture.
The American College of Radiology (ACR) promotes US evaluation of “pain after...(TKA with) suspect(ed) periprosthetic soft-tissue abnormality unrelated to infection” after radiographic evaluation as “usually appropriate”.
Although ACEP US Guidelines boast 96.8% sensitivity and 99.7% specificity for diagnosing fractures, POCUS evaluation of traumatic arthroplasty complications does not exist. This creates an area of interest within POCUS.
Contributors: Lauren Lowes, DO; Justin Morin, DO; Garrett Richardson, MS4; Nava Kendall, MD
Central Michigan University Residency of Emergency Medicine
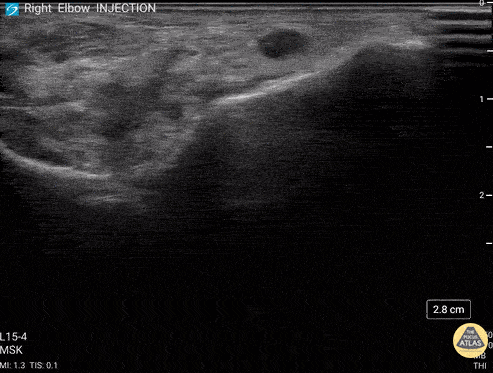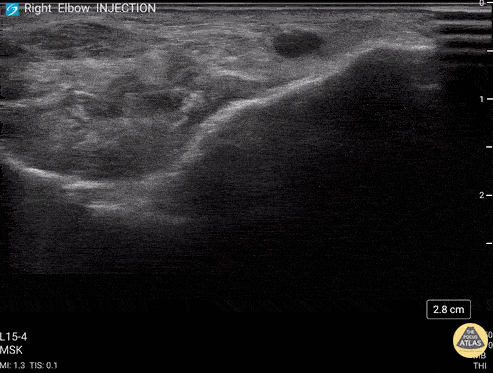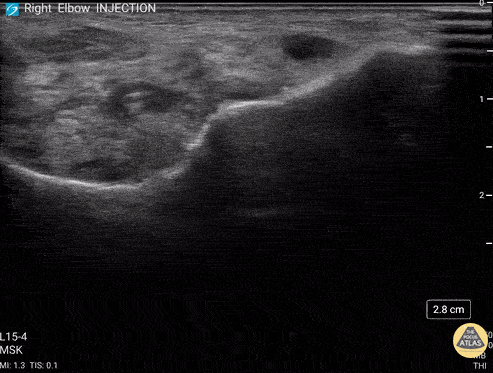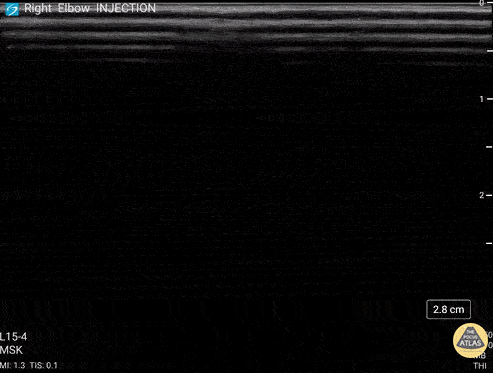
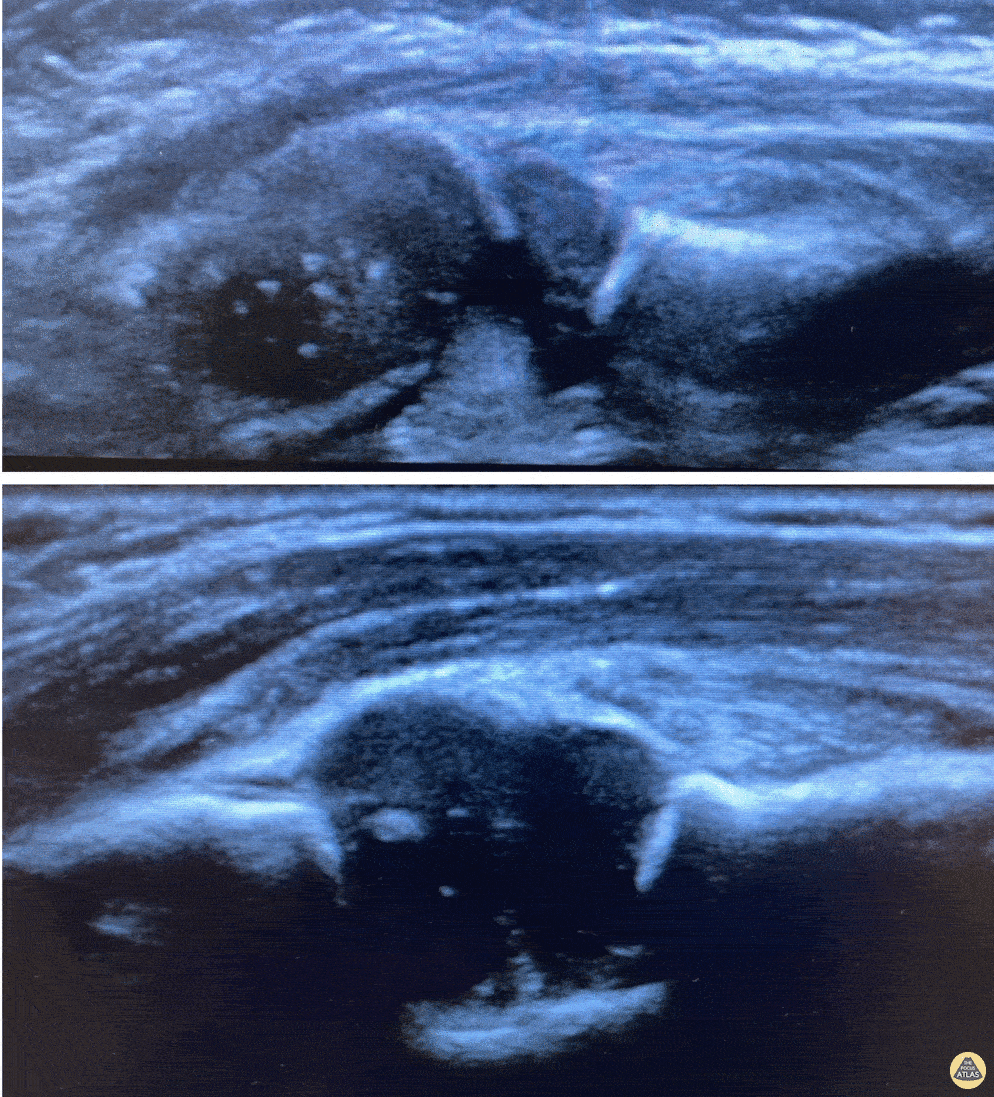
Posterior Elbow Joint Injection
92 y/o M presented with moderate to severe osteoarthritis on elbow x-ray who was treated with ultrasound-guided corticosteroid joint injection.
Video shows transverse view of the posterior elbow as corticosteroid is injected with a posterolateral approach deep to the posterior elbow fat pad located in the olecranon fossa. This area is continuous with the elbow joint capsule. Posterolateral approach is advantageous due to decreased risk of disrupting neurovascular structures or the articular cartilage from other approaches to the joint space. Posterior approach is also advantageous compared to lateral approach in moderate to severe arthritis due to limited access to the radiocapitellar joint space.
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
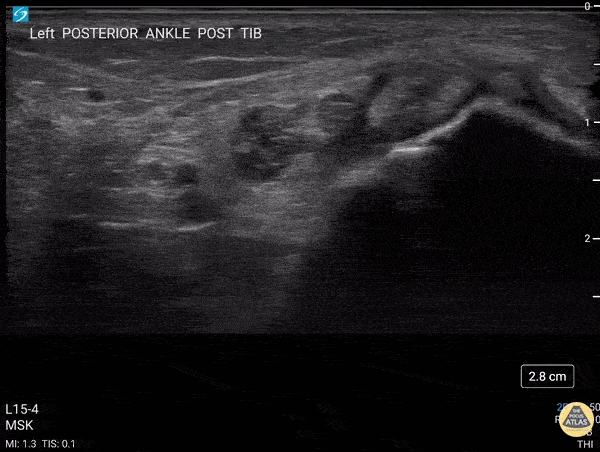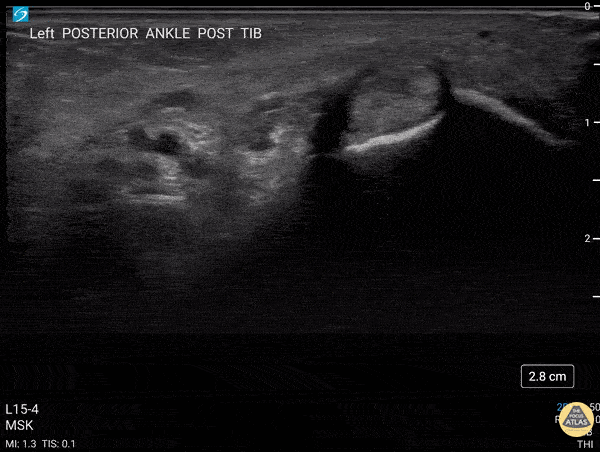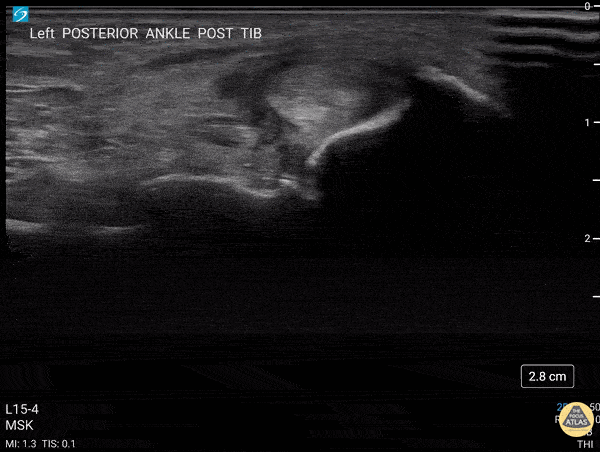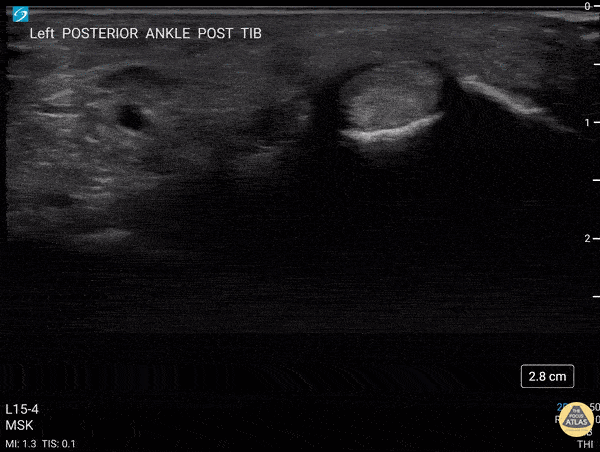
Transverse view scanning Proximal to Distal at the Posteromedial Ankle
40 y/o F presented with 9 month history insidious onset L medial ankle pain and was found to have tibialis posterior tendon partial tear.
Video shows transverse view scanning proximal to distal at the posteromedial ankle (left is posterior). There is thickening of the posterior tibialis tendon with an anechoic tendon sheath effusion. At the level of the medial malleolus there are two moderate interstitial tears extending distally. Flexor digitorum and hallicus longus appear unaffected.
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
Metacarpal Head Fracture
34 y/o M presented with fall while skiing injuring closed fist against ice and was found to have a displaced/impact fracture of his third metacarpal head.
Video shows sagittal view scanning in the ulnar to radial direction at the third metacarpophalangeal joint (right is proximal). There is diffuse disruption of the cortex of the radial aspect of the metacarpal head and displaced/impaction fracture of the metacarpal head. Usually this surface should appear smooth. Articular cartilage can be seen as anechoic at the interface between the two bones. This defect was not visualized on initial or 2 week post x-ray, so ultrasound was able to guide the clinical team to appropriately splint and manage as a fracture.
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
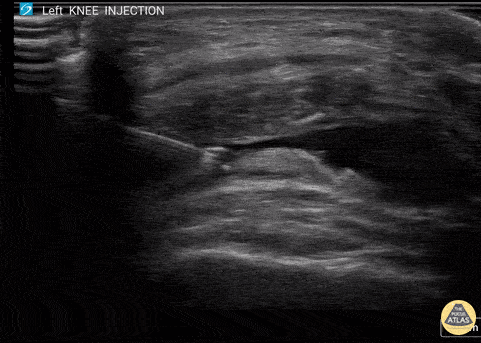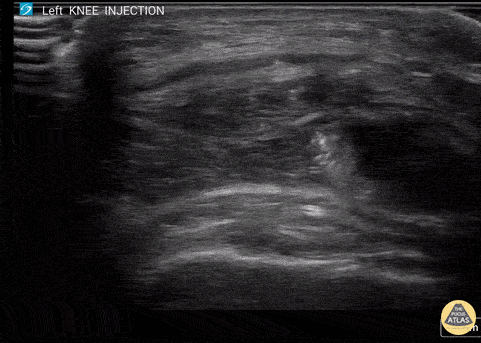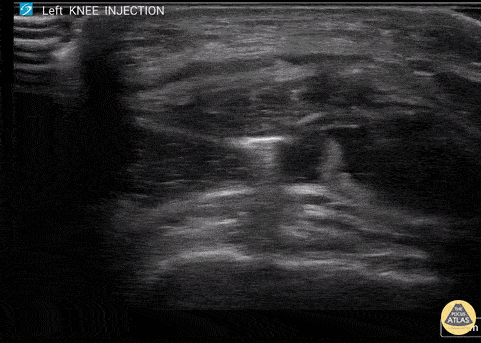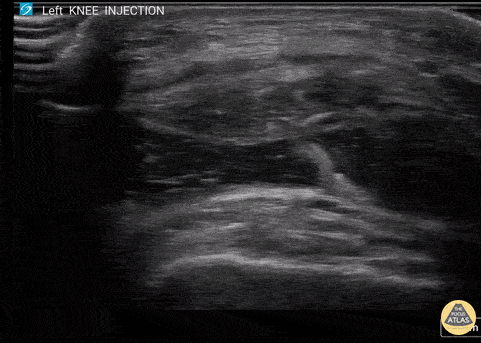
Corticosteroid Joint injection in Suprapatellar Recess
60 y/o F with knee arthritis getting corticosteroid joint injection in left suprapatellar recess.
Ultrasound probe in transverse axis just superior to the patella. Needle approach lateral to medial. Infiltrate seen injected into anechoic suprapatellar recess. The suprapatellar recess is continuous with the tibiofemoral joint. Deep to suprapellar recess in this video is the prefemoral fat pad. Just superior to the suprapatellar recess in this image is the quadriceps tendon in short axis appearing as a fibrillar structure.
Contributors:
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
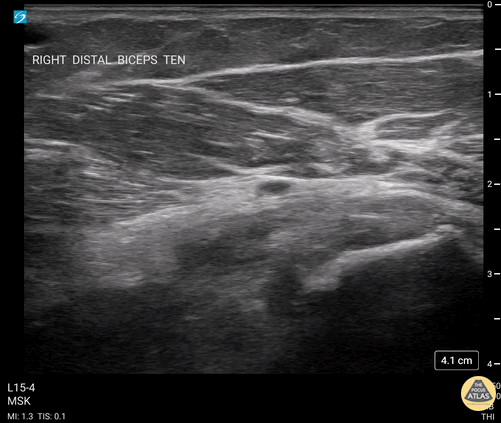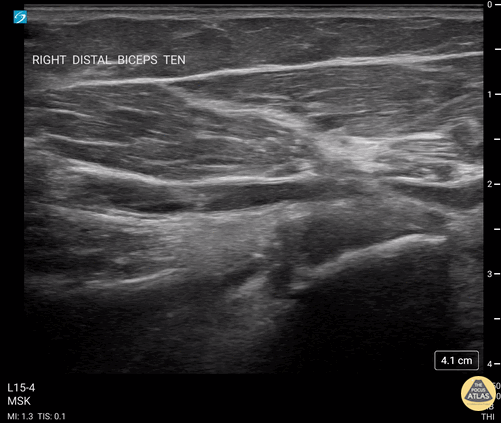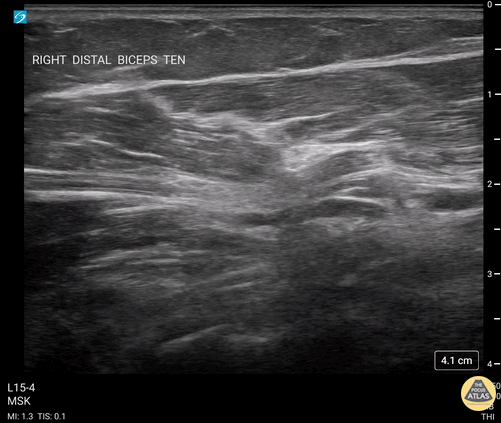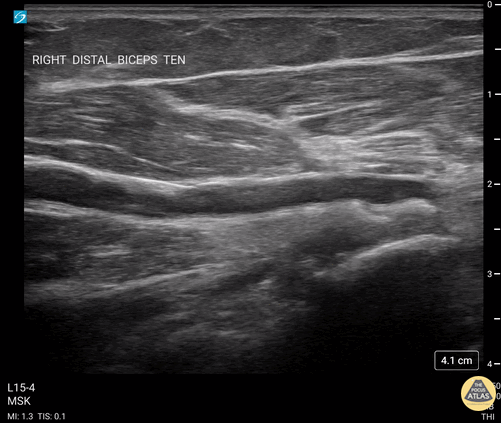
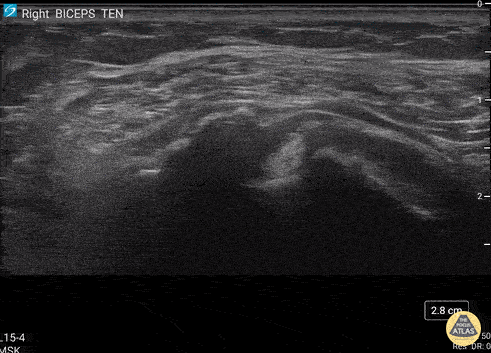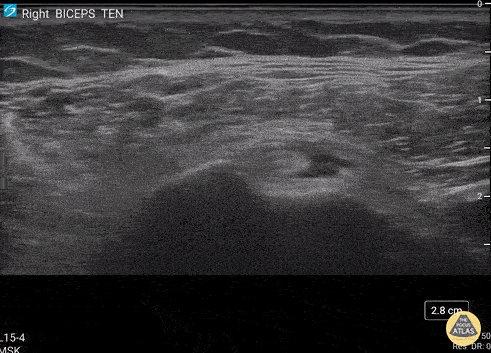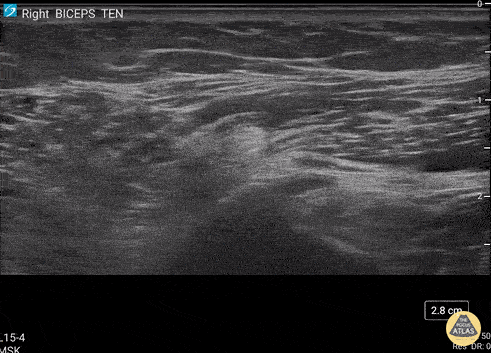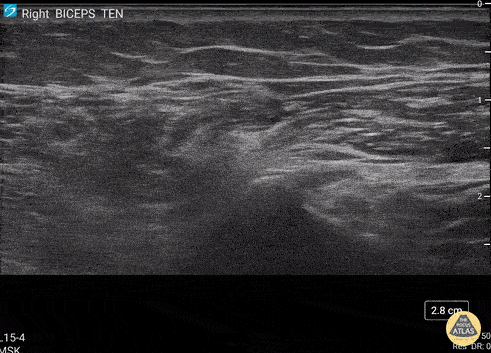
Biceps Tendinosis
60 y/o F w/R elbow pain for 8 months found to have distal biceps tendinosis.
L=proximal; R=distal. Medial long-axis view of distal biceps tendon. Radial artery seen pulsating directly superficial to biceps tendon. Distal biceps tendon diffusely thickened with decreased echogenicity at its attachment site.
Contributor:
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
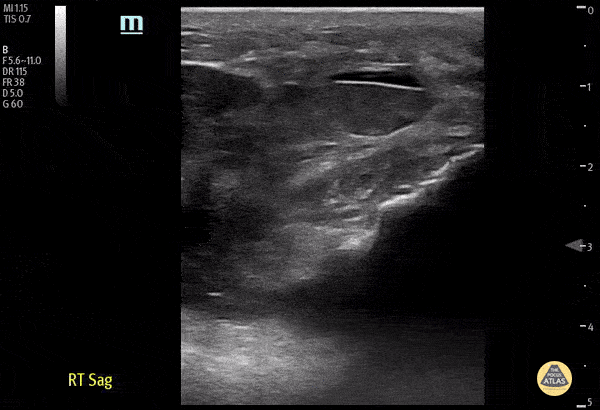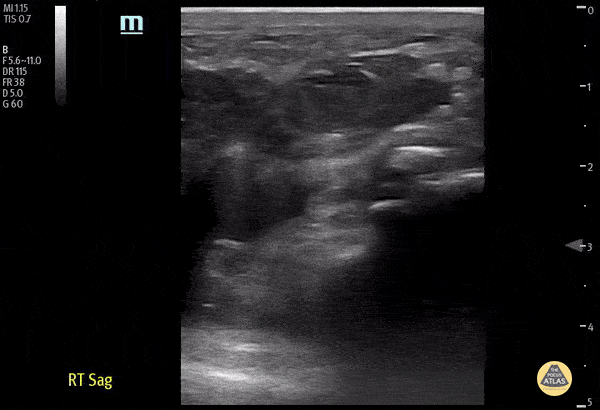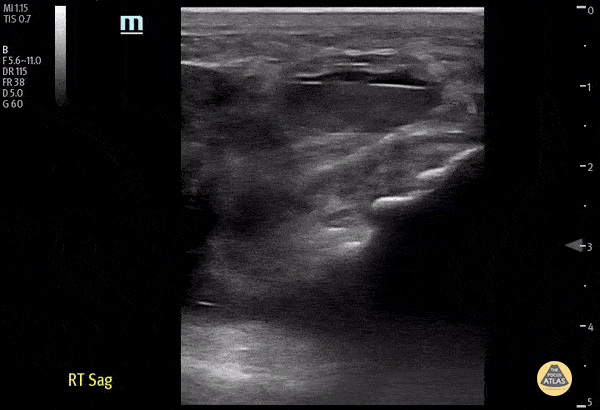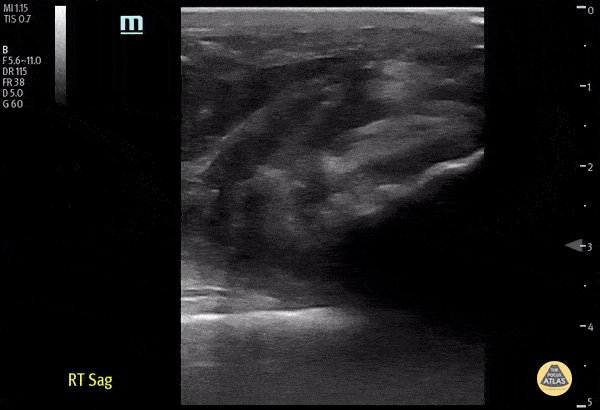
Distal Quadriceps Muscle Rupture
70 y/o male fell onto his right knee presented with visible deformity of the distal quadriceps muscle. Physical exam demonstrated weakness to active extension of the right knee. POCUS with a linear transducer demonstrated complete loss of tendon architecture of the right knee, including a hypoechoic defect between the tendon fibers. When compared to normal knee radiographs, the patient has significant displacement of the patella distally. Radiologists interpreted this as possible quadriceps tendon rupture. During operative repair, a complete rupture of the quadriceps was discovered and repaired.
Justin Morin, DO PGY-1 @justinjmorin; Alex Schlangen, DO PGY-1; Lauren Lowes, DO PGY-3; EM Residents at Central Michigan University
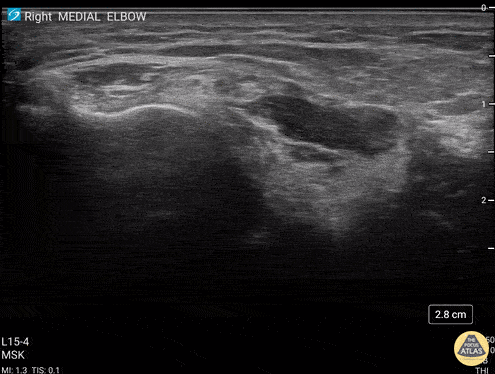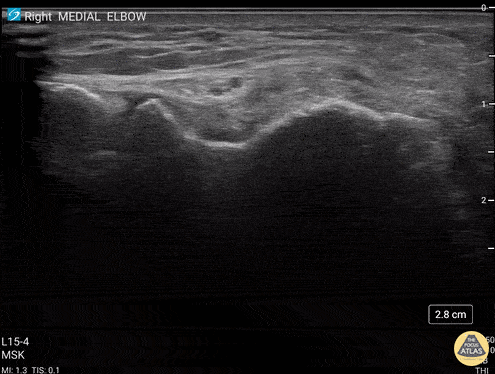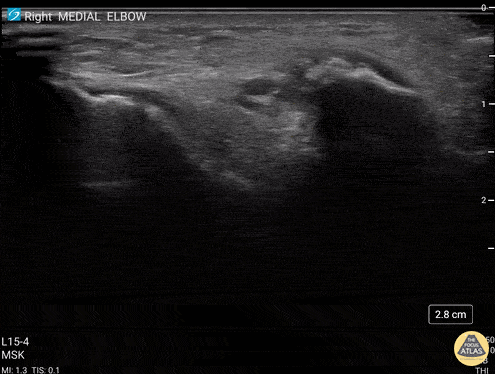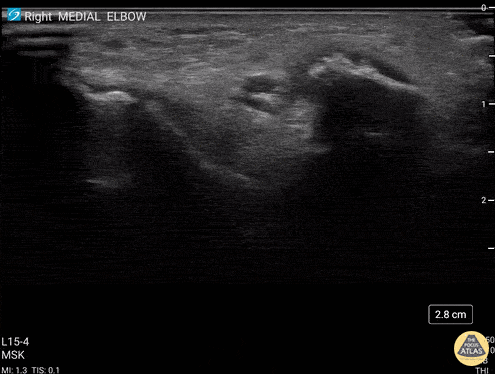
Common Flexor Tendon Tear At Elbow
59 y/o M presented with 1 year history of insidious onset R medial elbow pain especially worse with playing golf and was found to have a high grade tear of the common flexor tendon.
Video shows coronal view scanning posterior to anterior at the medial epicondyle (right is proximal). There is decreased echogenicity throughout the entire length of the tendon, but normal fibrillar tendon appreciated at deep aspect of tendon. There is an enthesophyte noted at the insertion site.
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
Biceps Tendon Sheath Effusion
55 y/o F presented 2 months after a FOOSH with adhesive capsulitis and a biceps tendon sheath effusion.
Ultrasound scanning transverse axis proximal to distal along humeral shaft (left screen is lateral). Anechoic space around hyperechoic biceps tendon (center of screen) represents fluid that is continuous with the glenohumeral joint space. Inflammation from the adhesive capsulitis is drawing in fluid into the joint that is extending into biceps tendon sheath.
Contributor:
Eben Alexander, DO
Devesh Patel, MD
Eastern Virginia Medical School
Comminuted Proximal Phalanx Fracture of Great Toe
Comminuted, dorsally angulated fracture of the proximal phalanx of the left great toe.
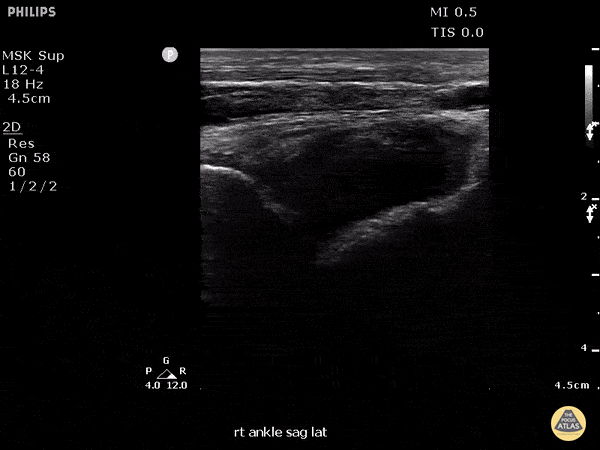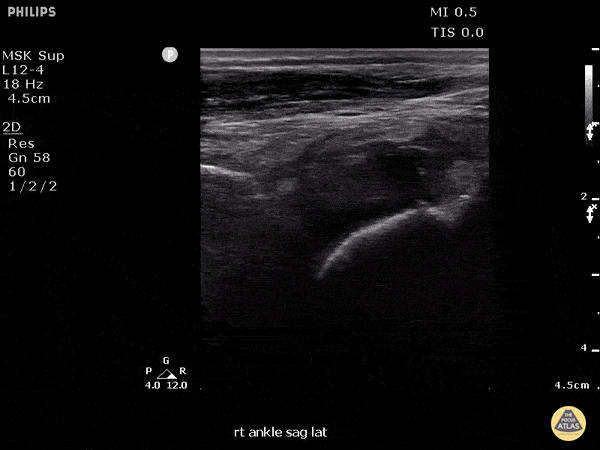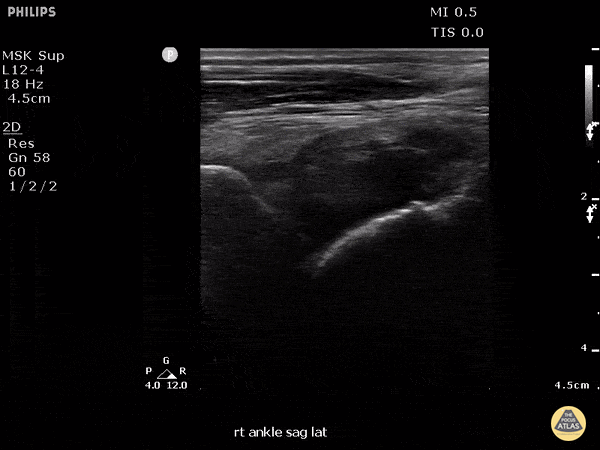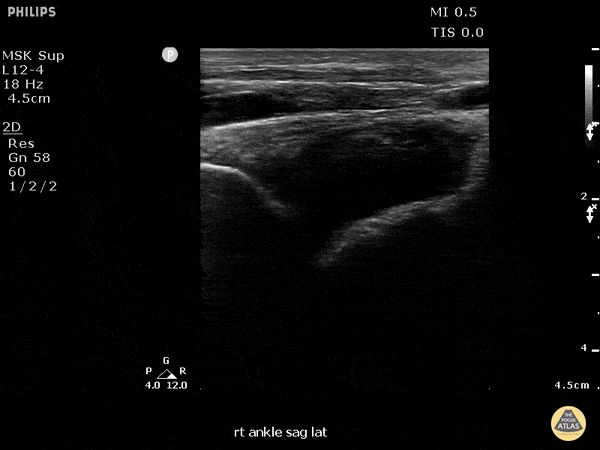
Fusobacterium Septic Joint
This patient presented to the emergency department for several days of ankle pain. Ultrasound of the joint revealed anechoic fluid within the joint, which normally suggests a non-exudative cause. However, this patient’s joint was eventually tapped which revealed thick purulent fluid that grew Fusobacterium, and a rare cause of septic joint.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
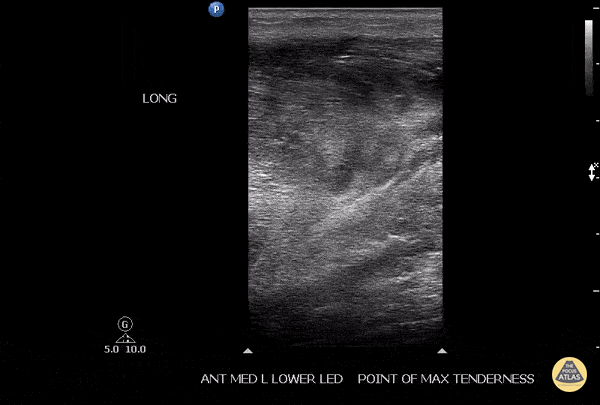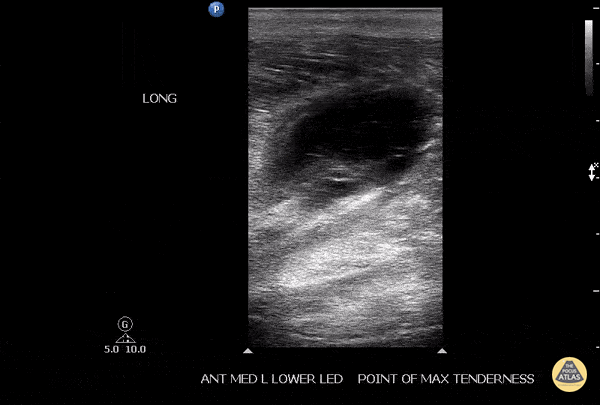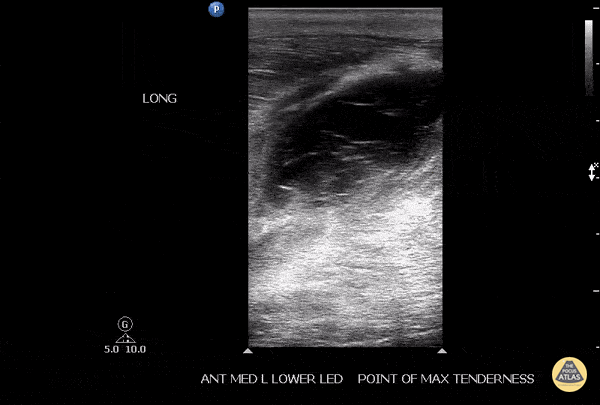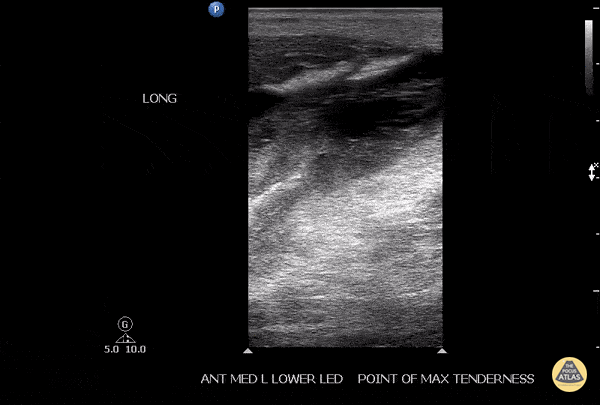
Soleus Hematoma
This is a patient who presented to the emergency department with left calf pain, swelling, previous history of DVT and currently on Xarelto. A patient with such a presentation would cause concern for ruling out a new DVT however a subsequent DVT scan proved to be negative. The key approach for this patient was to evaluated the area of maximal tenderness with ultrasound, which in this case, revealed a hematoma within their soleus muscle!
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
Biceps long head tendon rupture, transverse view
The patient presented with sudden onset right shoulder pain. On physical examination, there was tenderness to palpation anteriorly over the humeral head. POCUS demonstrated a heterogeneous structure within the bicipital groove representing a tendon stump surrounded by a developing anechoic haematoma. This study is in keeping with a complete rupture of the biceps long head tendon. This case illustrates the utility of POCUS as a diagnostic tool for the rapid identification of MSK injuries in the ED.
Contributors: Andrew Namespetra(@AndrewNamespet1), MB BCh BAO MSc; Nava Kendall, MD
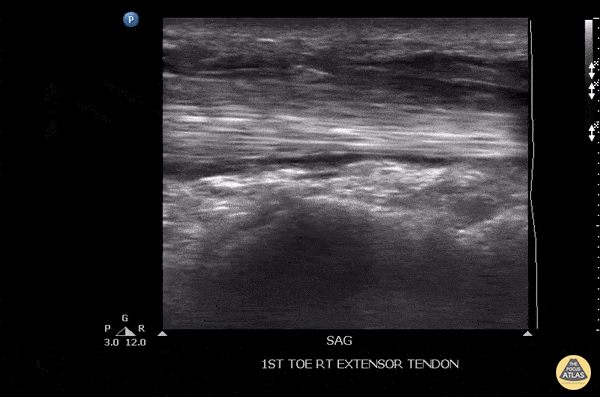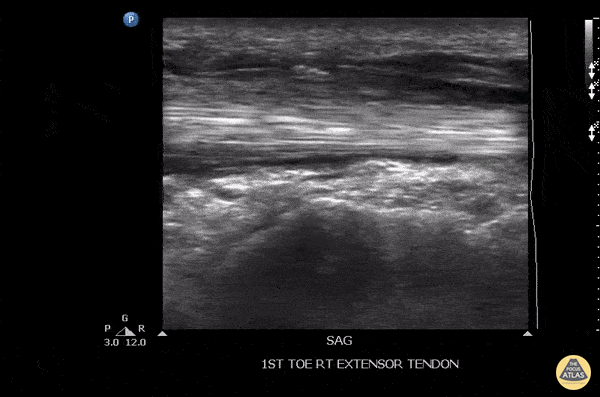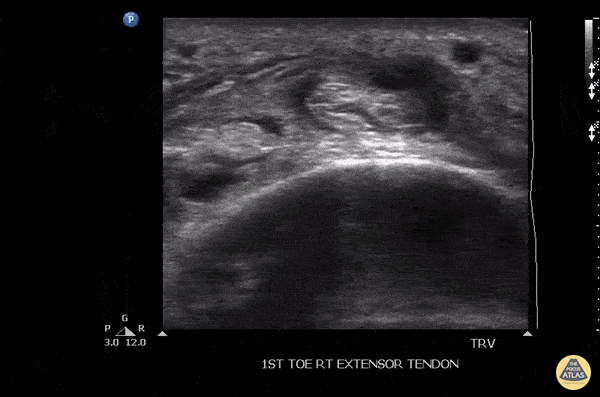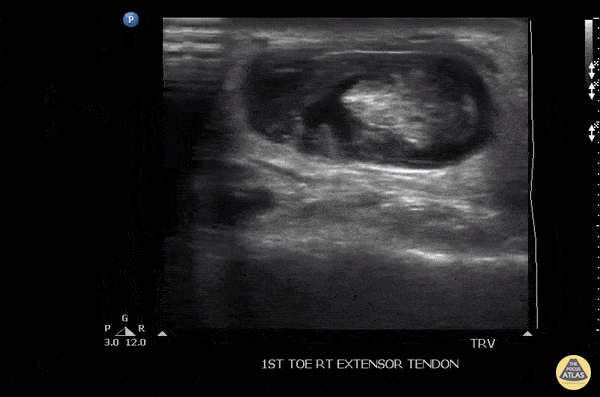
Tenosynovitis Of The Extensor Hallucis Longus Tendon
Patient initially suffered a puncture wound 8 days ago to the top of the foot. He presented a week later with pain in the toe, especially with flexion. US imaging showed extensive fluid surrounding the extensor hallucis longus tendon consistent with infectious tenosynovitis. The patient was taken to OR for debridement with good outcome.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
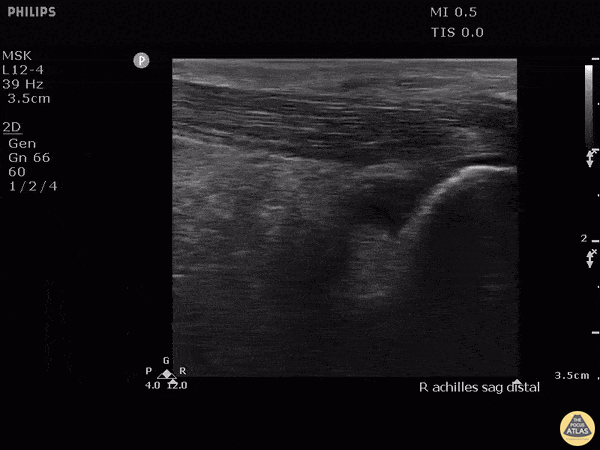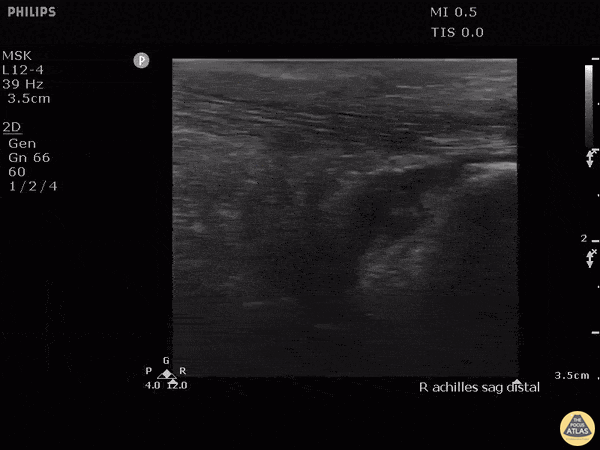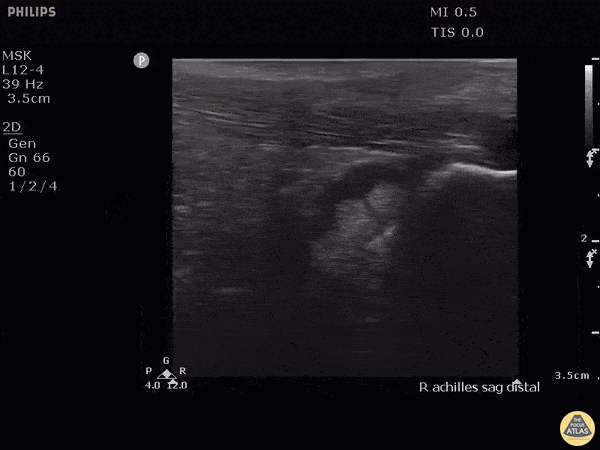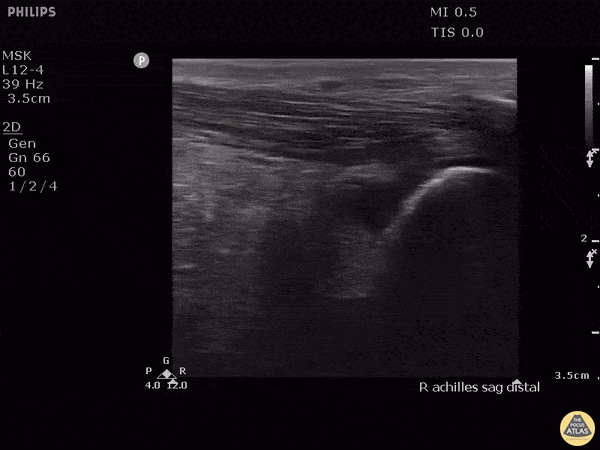
Retrocalcaneal Bursitis
Hockey player with progressive posterior ankle/heel pain. Felt sudden worsening while skating. Clip shown reveals retrocalcaneal bursitis along with insertional Achilles tendinopathy.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
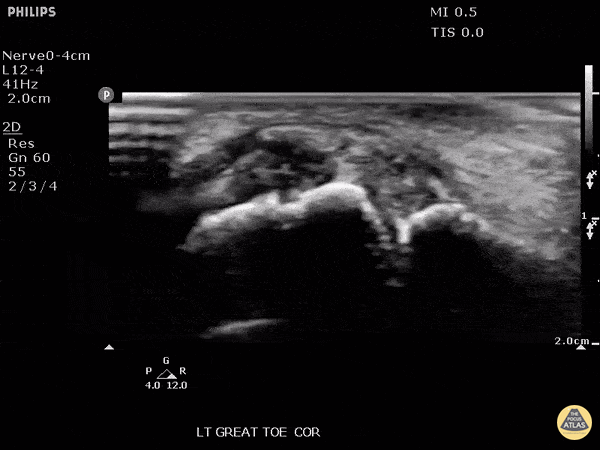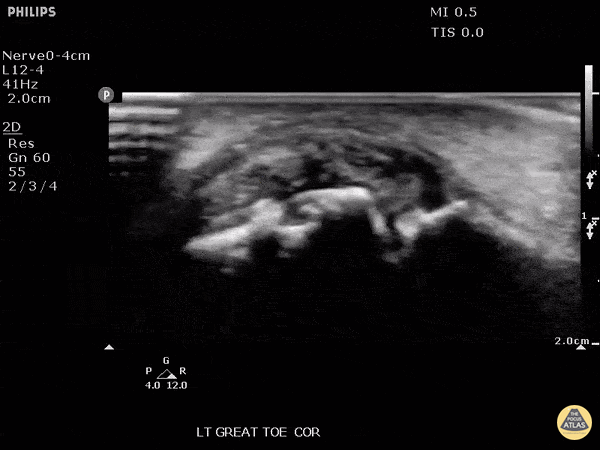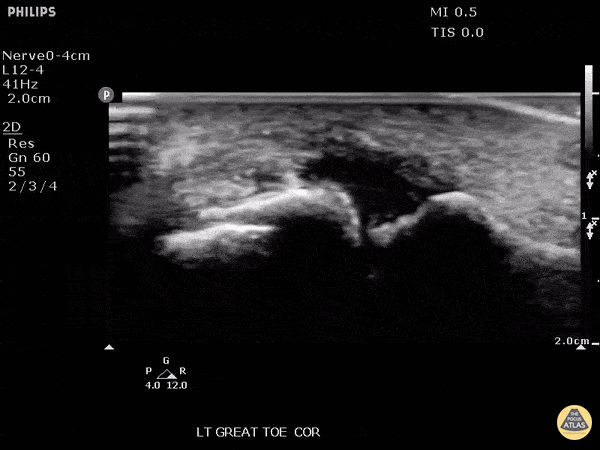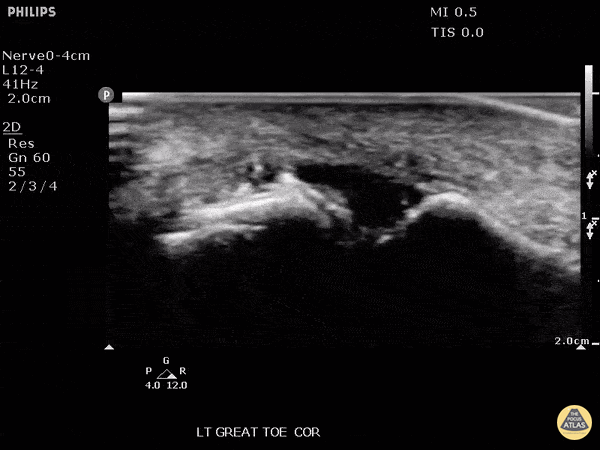
Monosodium urate crystals
Patient presented with great toe pain. POCUS performed and detected effusion in first metatarsophalangeal joint. Eventually determined to be monosodium urate crystals as seen in gout.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
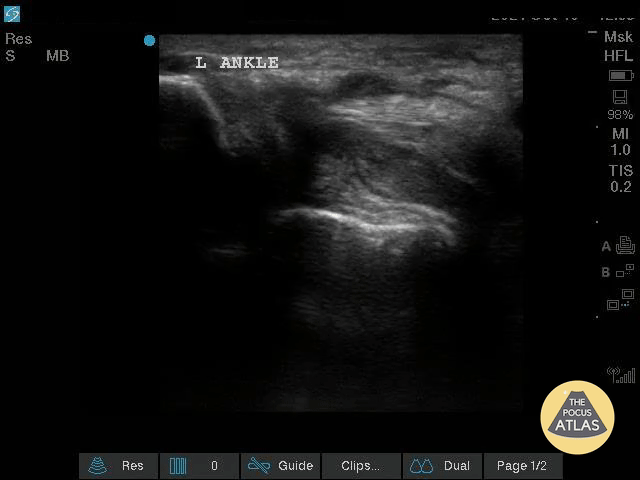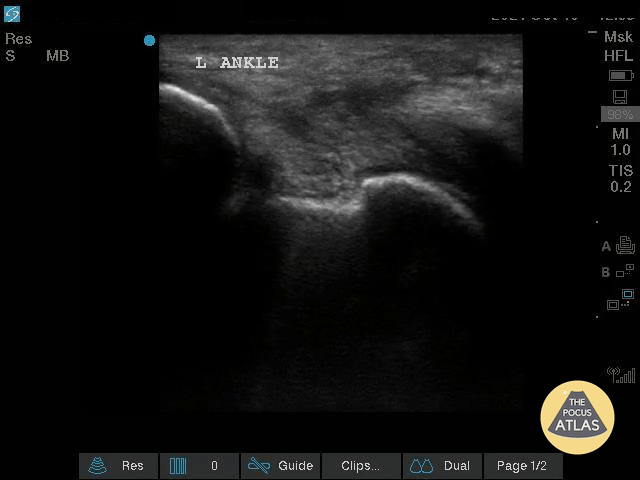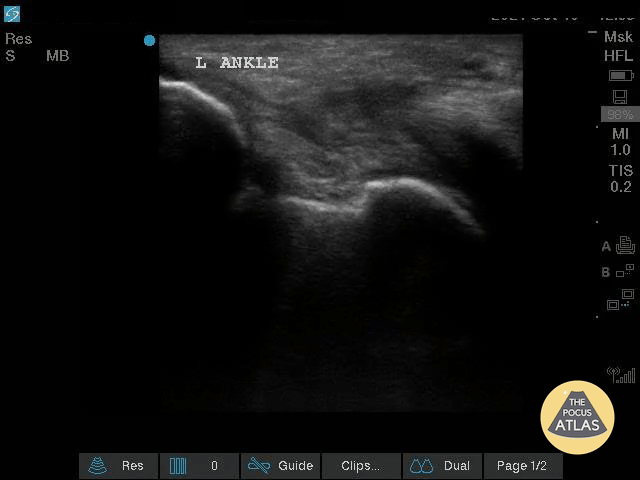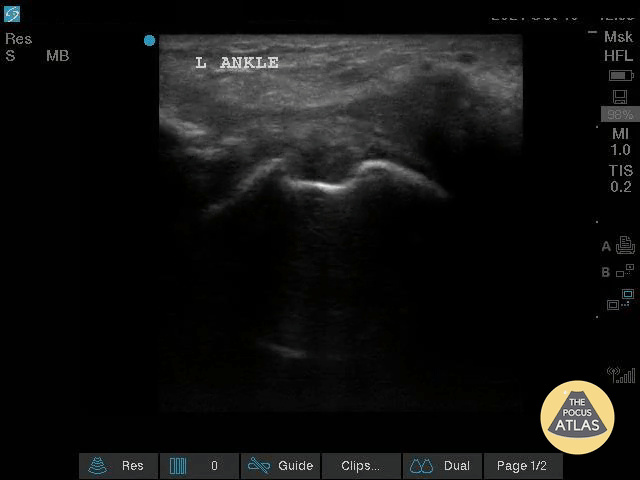
Complex Left Ankle Effusion
This is an image of a left ankle demonstrating a complex effusion in a patient presenting with ankle pain and swelling. Arthrocentesis was performed confirming septic arthritis.
Michael Macias
Intra-Articular Air
This is an ultrasound clip from a patient who presented to the ED after sustaining a laceration near the knee. There was concern for violation of the knee joint so ultrasound was used to evaluate.
The probe is held in an sagittal orientation, just proximal to the patella, overlying the quadriceps tendon. A hyperechoic line with shadowing (similar in appearance to an A-line seen on lung US) can be seen deep to the quadriceps tendon confirming intra-articular air and therefore violation of the knee joint from the laceration. A small joint effusion can also be appreciated.
Clip courtesy of Dr. Daniel Mantuani and Highland Ultrasound
Twitter: @HGHED
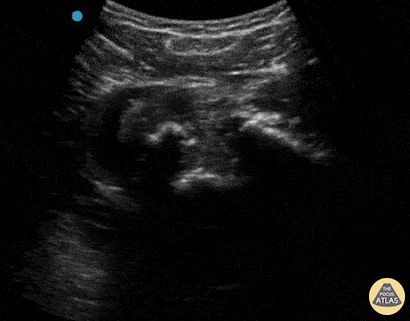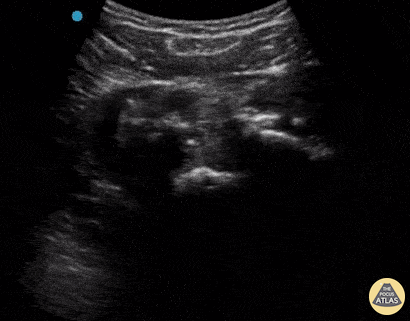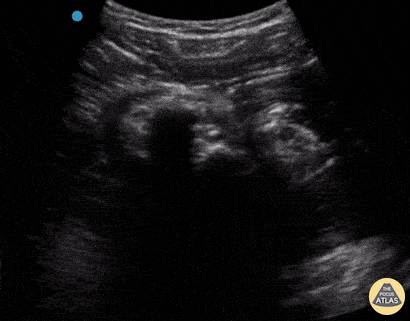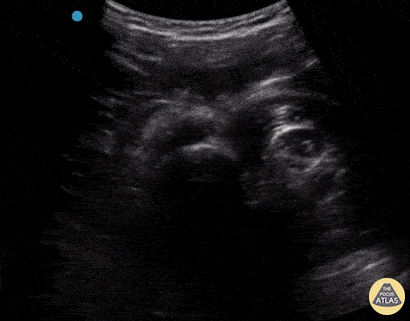
Inferior Shoulder Dislocation
A 30-year-old male presented to the emergency department with an inferior shoulder dislocation (luxatio erecta). Studies have shown that ultrasound has a very high sensitivity and specificity nearing 100% each (Secko 2020) in identification of the same. On ultrasound, the humeral head is shown dislocated anterior to the glenoid fossa, similar to typical anterior shoulder dislocations. This patient's shoulder was reduced with simple traction/countertraction under procedural sedation without any complications.
Mark Zhang
Secko MA, Reardon L, Gottlieb M, et al. Musculoskeletal ultrasonography to diagnose dislocated shoulders: a prospective cohort. Annals of Emergency Medicine. 2020;76(2):119-128.
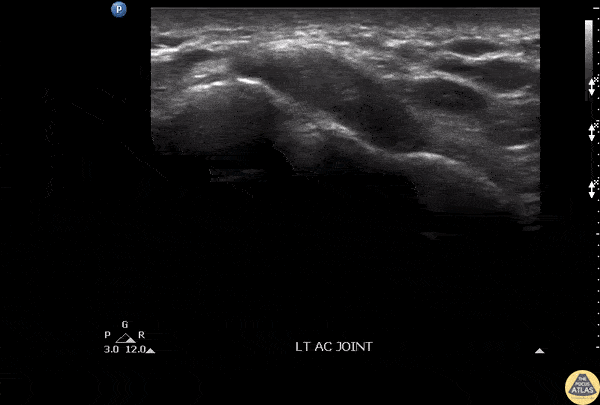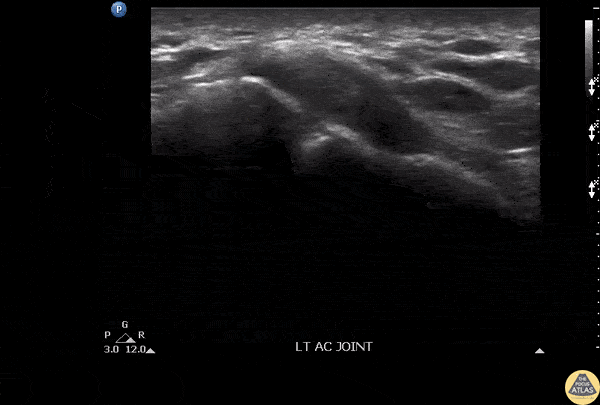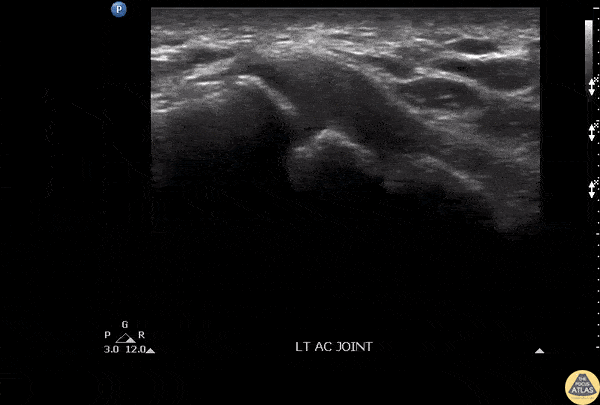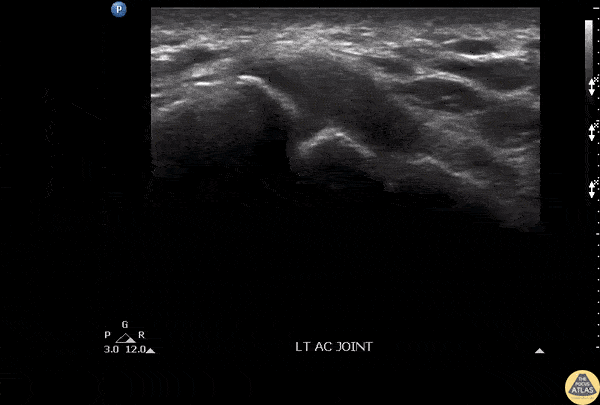
Septic AC Joint
Patient presenting with shoulder pain and AC joint tenderness. Febrile to 102. POCUS revealed an AC joint effusion.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
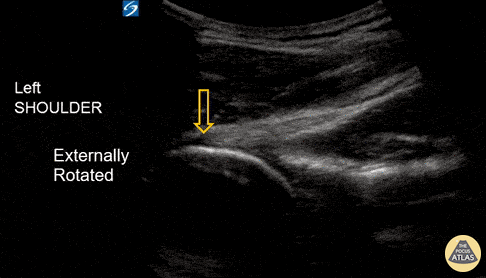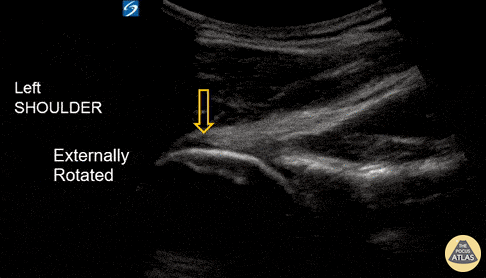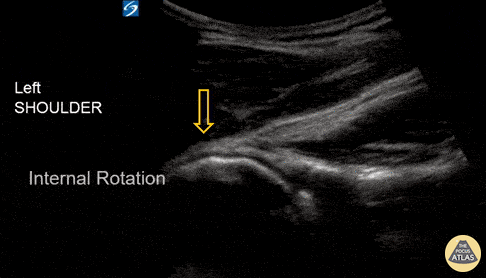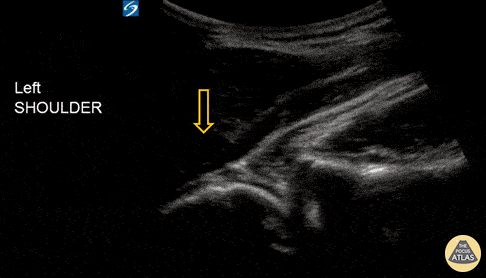
Shoulder Subluxation
An 18-year-old male with acute left shoulder pain after a physical altercation in which his left arm was pulled. Video clip reveals the left humeral head sliding in and out of the glenoid fossa with internal and external rotation, confirming the diagnosis of shoulder subluxation.
Read more about the case and shoulder POCUS on: https://www.aliem.com/ultrasound-for-win-acute-shoulder-injury-us4tw/
Mark Rivera-Morales, MD, PGY-3
Fernando Rivera, MD, PGY-3
Javier Rosario, MD, FACEP @javimedsimus
UCF/HCA Emergency Medicine Residency Program of Greater Orlando. Osceola Regional Medical Center @UCFEMOrlando
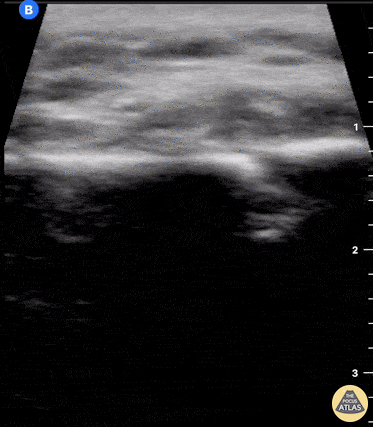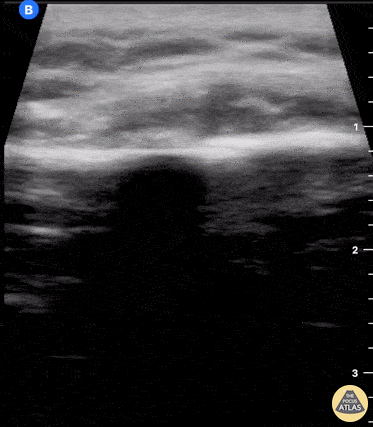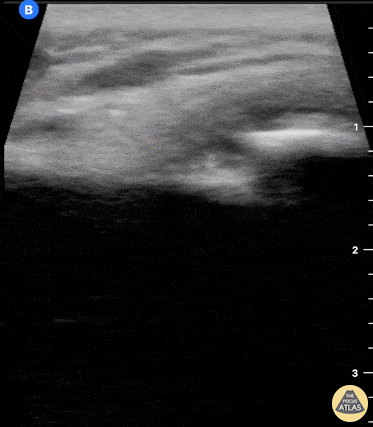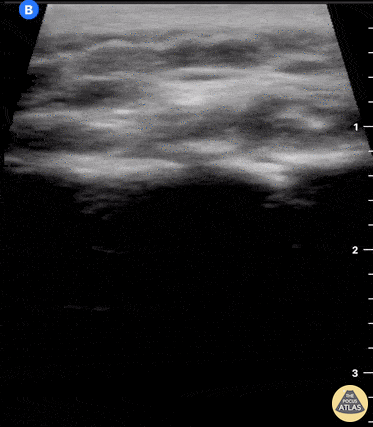
Clavicle fracture with hematoma
60 year old female with a subacute left clavicular fracture (occurred 2 weeks ago) presented with worsening pain at fracture site of onset while working with occupational therapy. Seen here is the left clavicle (hyperechoic structure) with noted fracture and mild heterogeneous (concern for bloody accumulation) edema around fracture site as observed in long axis view.
Kwasi Ampomah, DO, Eben Alexander IV, DO, Tariq Niazi, MD
EVMS PM&R
Sciatic Nerve Hematoma
Patient sustained a gun shot wound through left mid thigh.
Image is long axis view of sciatic nerve mid thigh. Nerve is running distal to proximal from left to right at approximately 3cm depth. There is a hypoechoic fluid collection seen superficial to the nerve. The epineurium is intact and we can see smaller nerve fibers contained in it.
Patient had 0/5 plantar/dorsiflexion of ankle on admission, consistent with a sciatic nerve injury. The ultrasound exam on the sciatic nerve did not show any gross abnormality other than this fluid collection around the nerve. Within 7 days (4 days after this image) he regained strength in plantar/dorsiflexion in the ankle.
Mike Guju, MD @MichaelMGujuMD
Resident PM&R EVMS
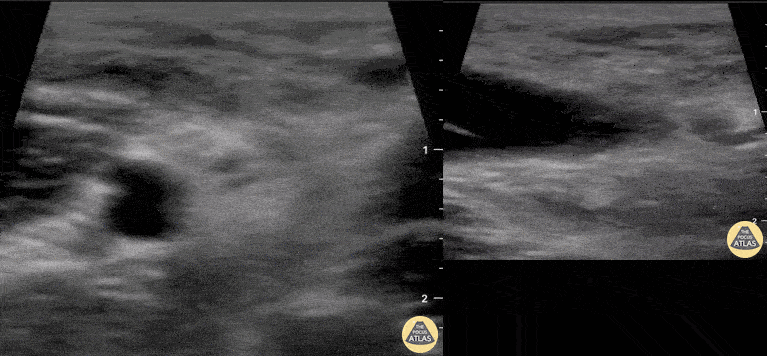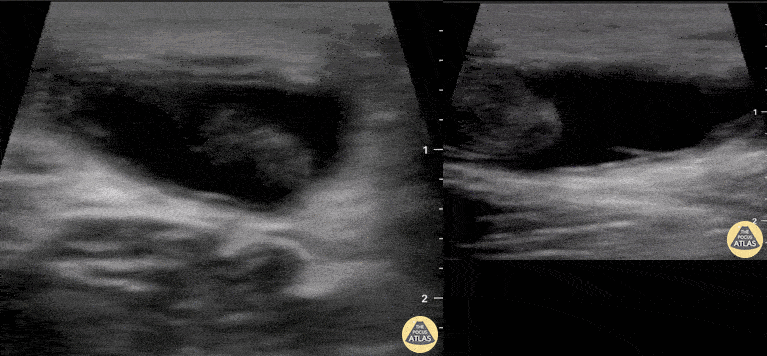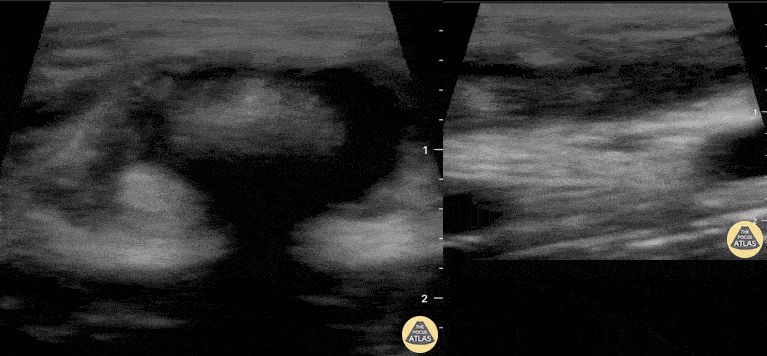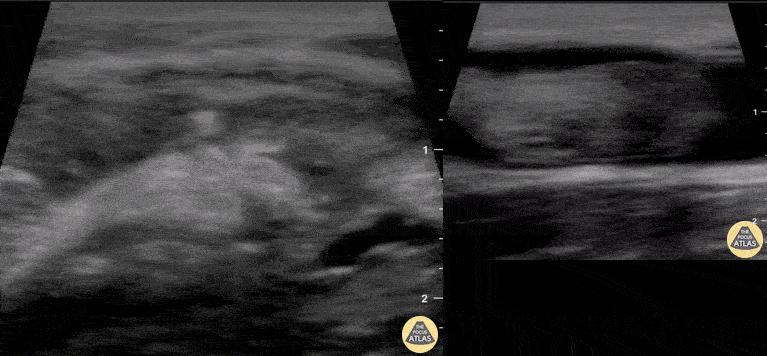
Rib Fracture
A middle aged man presented 1 week after sustaining a fall with direct injury to his left chest. He reported pain with inspiration and coughing; he localized pain to one specific area of his chest wall. Seen here is the image obtained when the linear probe was placed in the longitudinal plane to his area of point-tenderness. Notice the disruption of the hyperechoic cortex of the rib. Findings were confirmed in the transverse plan. The patient went on to have an anterior serratus nerve block for pain control related to his rib fracture.
Mandy Peach, MD @mandy_peach
Saint John Regional Hospital. NB, Canada
Distal Biceps Tendon Rupture
A 30-year-old male presented with acute-onset left anterior elbow pain after feeling a “pop” while weight-lifting. On exam, there was an obvious reverse popeye sign, swelling and mild ecchymosis. There was slight weakness in flexion and supination. Hook test was positive. A Butterfly IQ was used on an MSK soft tissue setting to assess the tendon in long and short axis via an anterior approach. Discontinuity of the tendon and surrounding anechoic fluid representing hematoma were noted. Orthopaedic surgery was consulted and reviewed ultrasound images. As a result, the patient had an urgent MRI and underwent expedited surgical repair.
Melanie Leclerc, MD CCFP(EM). @MelanieLecler19
David Lewis MB,BS FRCS FCEM CFEU PGDipSEM
Saint John Regional Hospital, New Brunswick, Canada
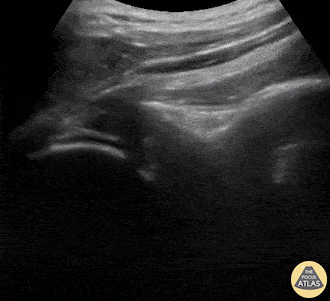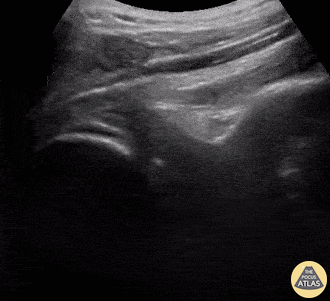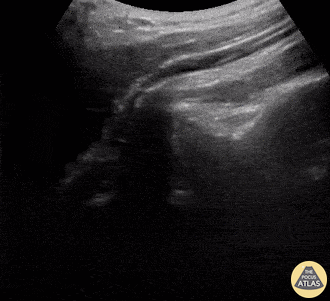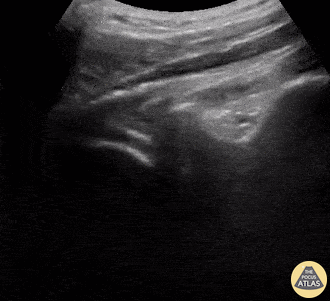
Shoulder Relocation
A 9-year-old female presented with left shoulder pain. She has a history of multiple dislocations and, as seen here on POCUS, is able to reduce the dislocation herself.
Julie Klensch, PEM Fellow & Paul Khalil, MD
University of Louisville/Norton Children's Hospital

ACL/LCL Injury
A 32-year-old male pedestrian struck by a jeep traveling at 30 mph was evaluated with POCUS for left knee injury. He sustained a left-sided rupture of ACL, LCL, and an avulsion fracture of his IT band. Pictured here is his left lateral knee US performed 10-days after the acute injury. You can appreciate the popliteus notch in the lateral femur, typically both the origin of the popliteus muscle and the plane the LCL traverses to the fibula; here only notable for diffuse edema.
Eben Alexander

Ligamentous Knee Injury
A 34-year-old male trauma patient was evaluated with POCUS for left knee swelling. He was appreciated to have multi-ligamentous injury of the left knee, with imaging notable for hypoechoic fluid within the suprapatellar plica (bursa) and evolving septation of the fluid.
Kwasi Ampomah
Normal Achilles Tendon
View of a normal Achilles tendon as seen in long axis, using a linear transducer. The relatively hyperechoic, linear fibers of the tendon are seen running from the calcaneus (right of screen, or inferior) to the gastrocnemius muscle (off screen to the left, or superior).
Achilles Tendon Injury
A 20s M presented with an ankle injury after landing a skateboard trick and feeling a painful pop in his posterior ankle. He had a positive Thompson test on exam. POCUS of the affected Achilles tendon was performed. This clip shows a long axis view of the Achilles tendon using the linear transducer, with inferior at the right of screen and superior at the left of screen. There is a relatively hypoechoic area (within red arrowheads) within the normally hyperechoic tendon, and the thickness is increased in this area as well, indicating focal injury to the tendon. Orthopedics was consulted, and the patient was placed into a splint in plantar flexion and discharged with outpatient follow up. MRI later confirmed a full thickness Achilles tendon tear and the patient was scheduled for surgery.
Jaimie Trenney, PA-C
Denver Heath Medical Center
Achilles Tendon Injury Short Ais
A 20s M presented with an ankle injury after landing a skateboard trick and feeling a painful pop in his posterior ankle. He had a positive Thompson test on exam. POCUS of the affected Achilles tendon was performed. This clip shows a short axis view of the Achilles tendon using the linear transducer. There is a relatively hypoechoic area (*) within the normally hyperechoic tendon, indicating focal injury to the tendon. Orthopedics was consulted, and the patient was placed into a short leg splint in plantar flexion and discharged with outpatient follow up. MRI later confirmed a focal full thickness Achilles tendon tear and the patient was scheduled for surgery.
Jaimie Trenney, PA-C
Denver Heath Medical Center
Nursemaid's Elbow
Nursemaid's pre and post reduction.
Nathan Jia, Orthopedic Resident
Myositis Ossificans
Patient presents to the ED with severe thigh pain following a subacute MMA injury. After proximal DVT was ruled out, POCUS revealed hypoechoic oval masses in the vastus intermedius and peripheral calcifications with shadowing adjacent to the femur.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
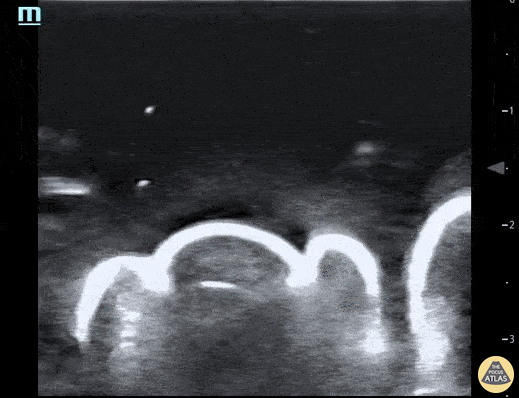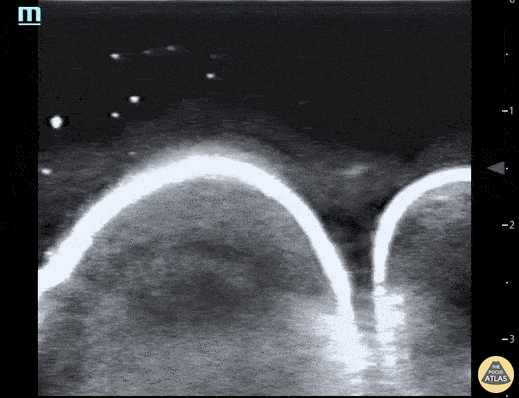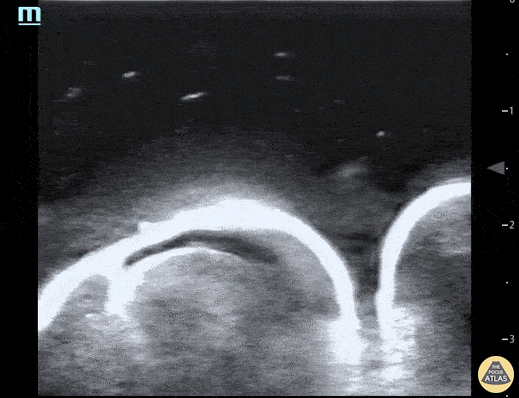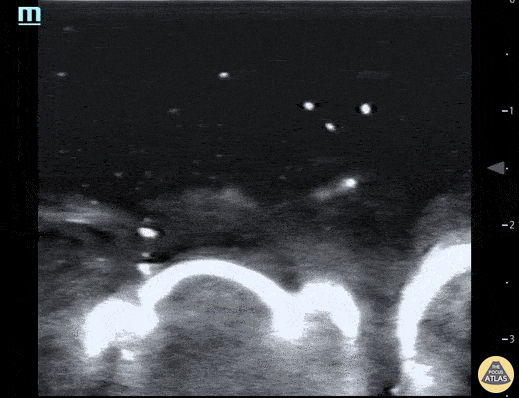
Water Bath POCUS
Pictured here is a water bath scan using a high frequency linear transducer; specifically this image visualizes the distal right great toe of a healthy young adult. Water bath scanning is a technique that augments the clarity and distinctness of structures that are otherwise challenging to visualize with POCUS including distal digital examinations. In addition to yielding higher quality images, the use of a water bath circumvents the need for direct contact with the area of interest, often resulting in less patient discomfort.
Moudi Hubeishy, MD. Rural Medicine PGY1. California, USA
@Hubeishy_MD
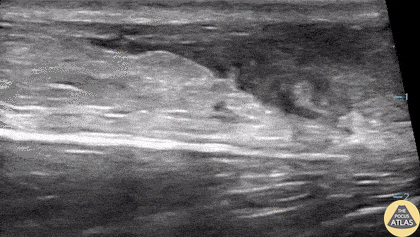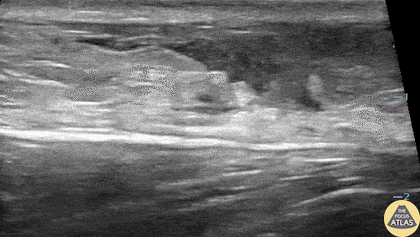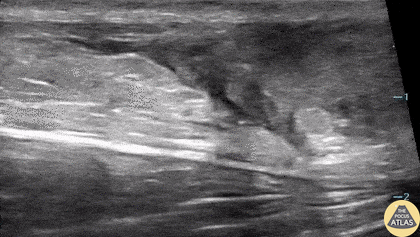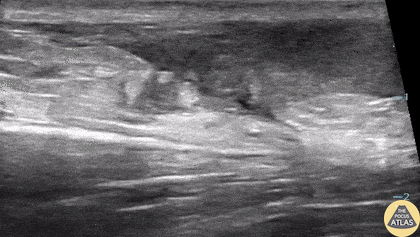
Ruptured Achilles Tendon
16-year-old male presented with acute onset sharp pain to his LE and inability to bare weight after having landed oddly while playing basketball. POCUS revealed a near-complete disruption of his Achilles Tendon.
Paul Khalil, MD. Assistant PEM POCUS director at University of Louisville/Norton Children’s
@Khalil3Paul
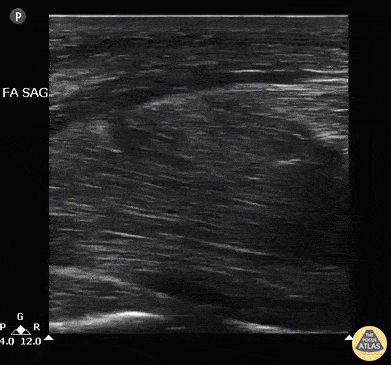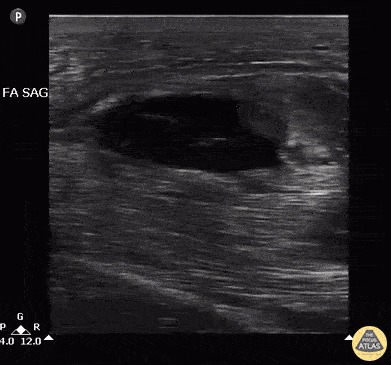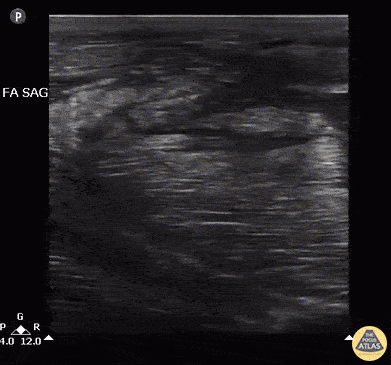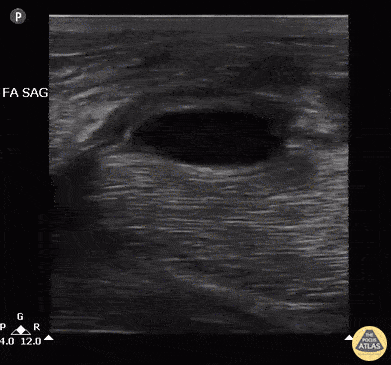
US-Guided MTP Arthrocentesis
Patient with no history of crystallopathy presented with first metatarsophalangeal pain and swelling.
Longitudinal view of the MTP joint revealed an anechoic effusion containing echogenic debris. Dynamic US guided aspiration was performed using an in-plane approach. Synovial fluid analysis showed monosodium urate crystals. Gram stain and fluid culture were negative.
Learning point: Consider US guidance for arthrocentesis to increase success rate and maximize fluid yield especially in the case of a small effusion.
Michael Cover, MD
@michaelc0ver
Intramuscular Abscess after IVDU injection
Male with LUE swelling after attempted IV drug use. Ultrasound of bicep reveals intramuscular abscess created from missed injection. Abscess was drained, and pt was admitted and given IV Abx.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
Myonecrosis of Deltoid
A patient with past medical history of diabetes presented with atraumatic right shoulder pain. Physical exam revealed decreased range of motion without obvious superficial abnormality. The patient was noted to be febrile and tachycardic. A curvilinear ultrasound reveals extensive air (scattered punctate hyperechoic areas) throughout the deltoid muscle indicative of infectious myonecrosis.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
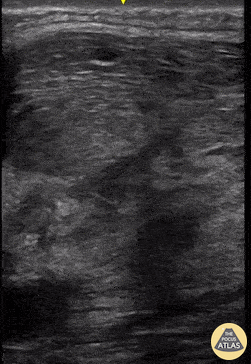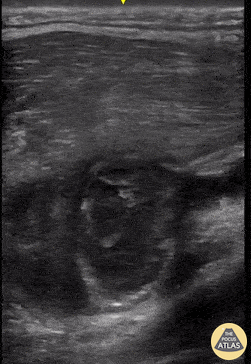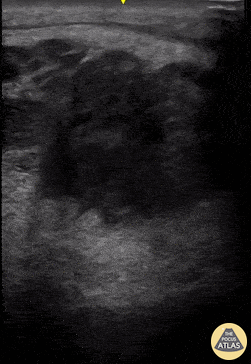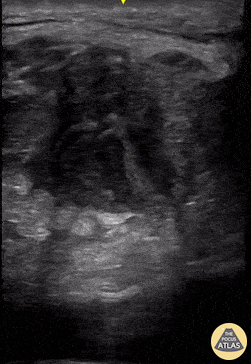
Pyomyositis
A 35 year-old-male presented with neck pain and a history of recurrent neck abscesses. Prior treatment had included I&D. Soft-tissue POCUS was notable for appearance of muscle inflammation without focal fluid collection; subsequent operative findings confirmed pyomyositis of the right neck including sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Brian Toston, Internist. Aventura, FL
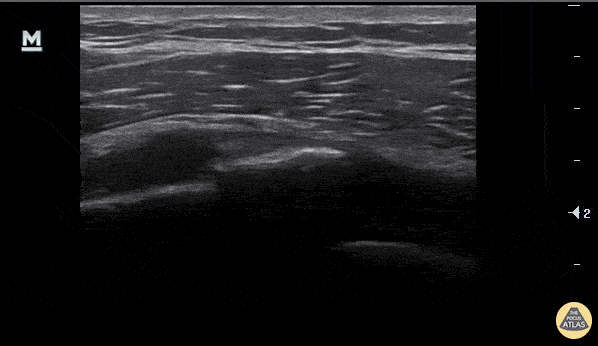
Rib Fracture
A rib fracture is seen here as disruption in the hyperechoic line or bony cortex. Also note the associated hypoechoic hematoma formation.
Aaron Inouye, PA-C, North Canyon Medical Center
@PAintheED
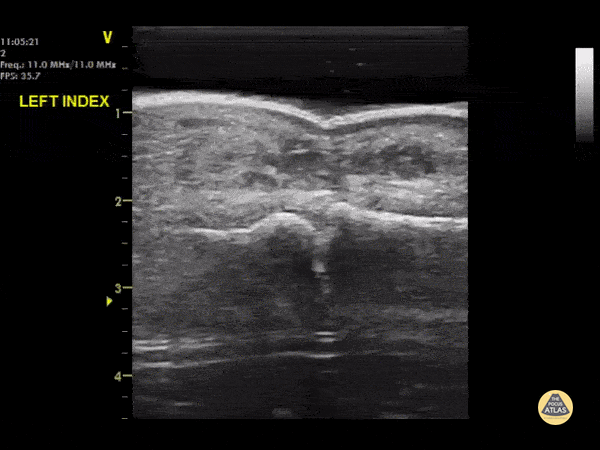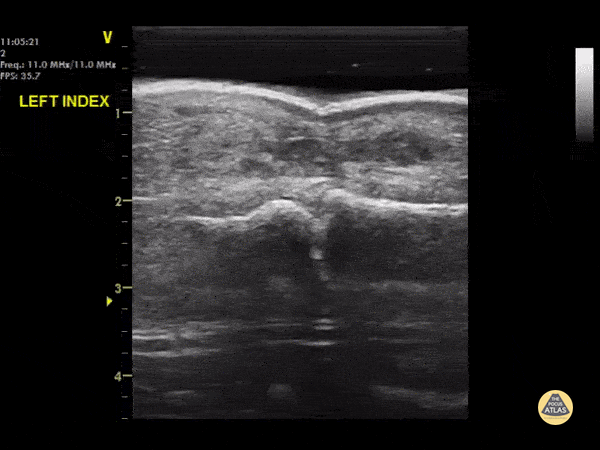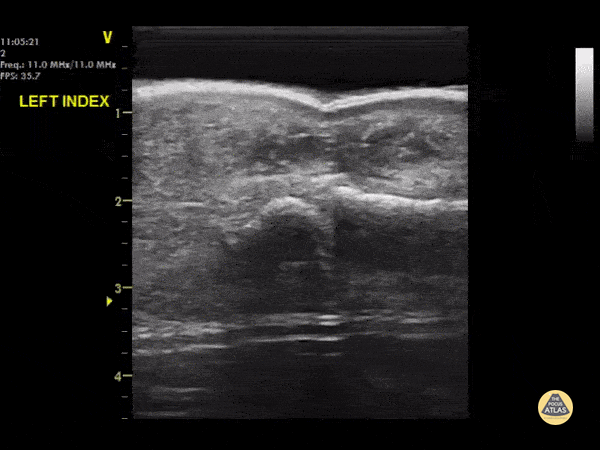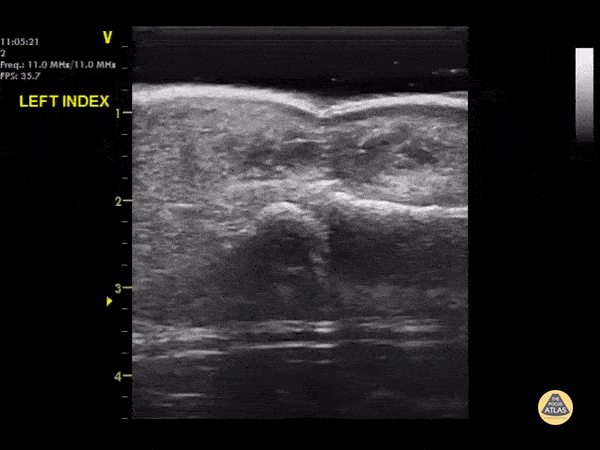
DIPJ Abscess
A waterbath-augmented soft-tissue ultrasound of the LEFT index finger was used to diagnose an abscess at the level of the DIPJ
Note a hypoechoic collection in the soft tissues sitting on top of the flexor tendon sheath
Learning point : Immerse the hand in a waterbath to increase image quality for distal extremities - the water allows improved sound wave transmission
Dr Cian McDermott, Mater University Hospital, Dublin, Ireland
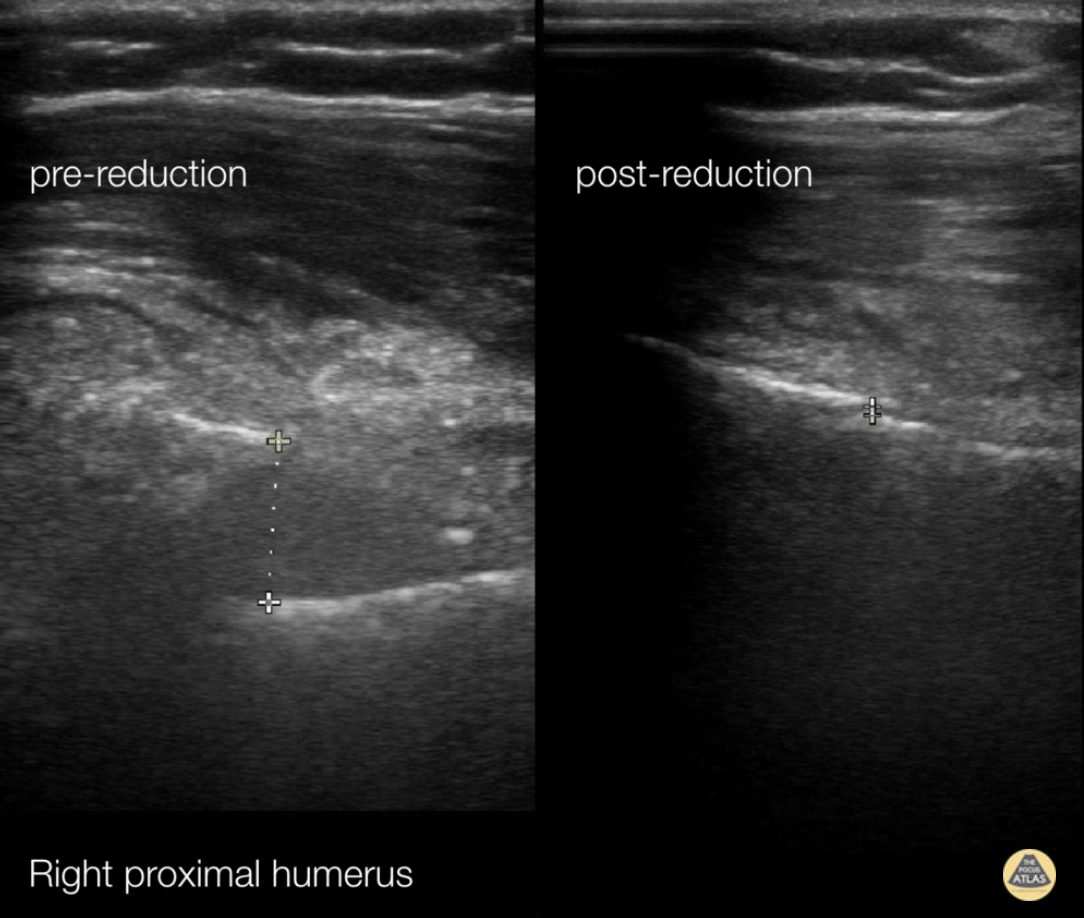
Fracture Reduction Monitoring
72 y/o female presents with right upper arm pain after a mechanical fall from standing.
A longitudinal coronal image was obtained at the right proximal humerus. Imaging showed displacement of bone fragments with hyperechoic lines 1.17cm apart. Pictures were obtained intermittently throughout reduction until displacement was reduced to 0.06cm.
This case demonstrates the utility of ultrasound in fracture reduction. Traditionally, care teams perform repeat X-rays until the fracture is reduced. In comparison, ultrasound can be quicker and reduce exposure to ionizing radiation.
Crozer Chester EM
Arthur Strzepka (MS4), Damarcus Ingram (MS4), Dr. Max Cooper
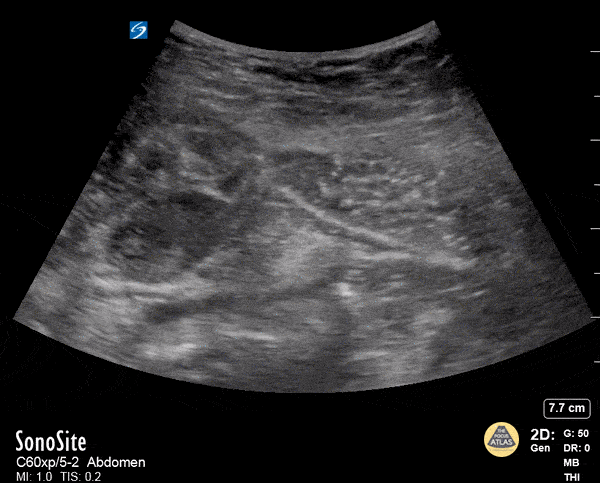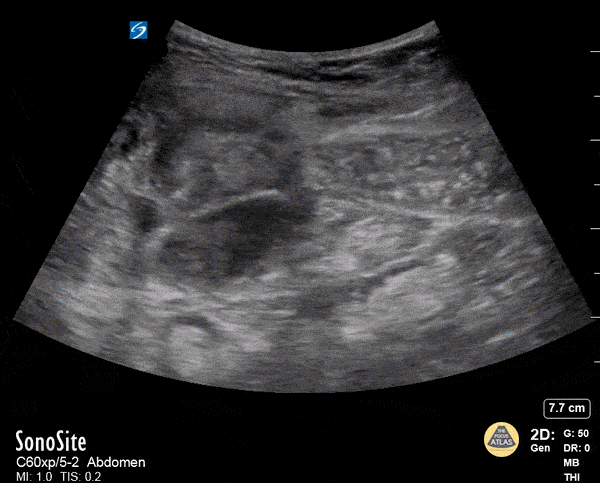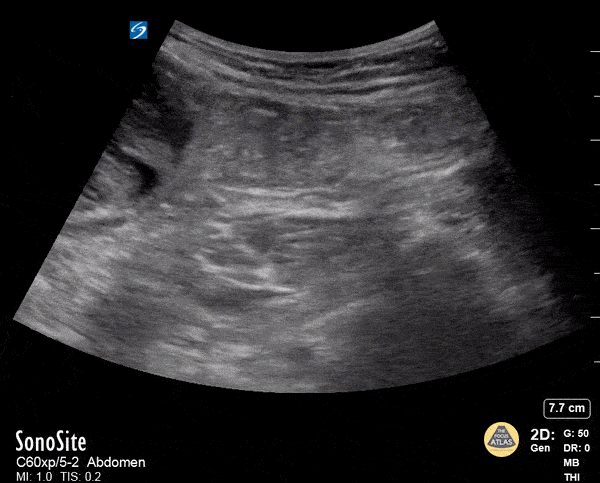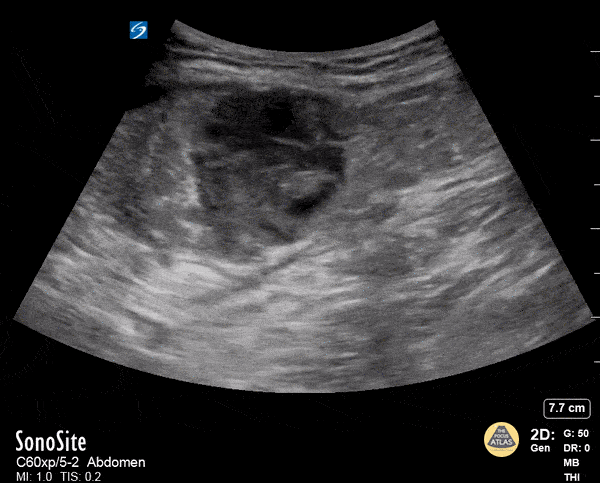
Rectus Abdominis Hematoma
A 41 year old male presented to the ED with a painful right sided abdominal mass. On examination the area of swelling was tender to palpation and initially suspected to be a hernia. Patient had engaged in strenuous exercise the day before. Using the abdominal probe, a bedside ultrasound demonstrated a hypoechoic 4.9 x 4.7 cm hematoma within the right lower rectus muscle with active extravasation. This patient underwent successful interventional radiology embolization and had unremarkable hospital course. POCUS for abdominal masses can quickly narrow the differential for such patients, which can expedite decision making particularly in those who are hemodynamically unstable and on anti-coagulation.
Max Cooper, MD Ultrasound Fellowship Director Crozer-Chester Medical Center
Kevin Conor Welch, DO Ultrasound Fellow Crozer-Chester Medical Center
Elena Grill, MD EM Resident Physician Crozer-Chester Medical Center
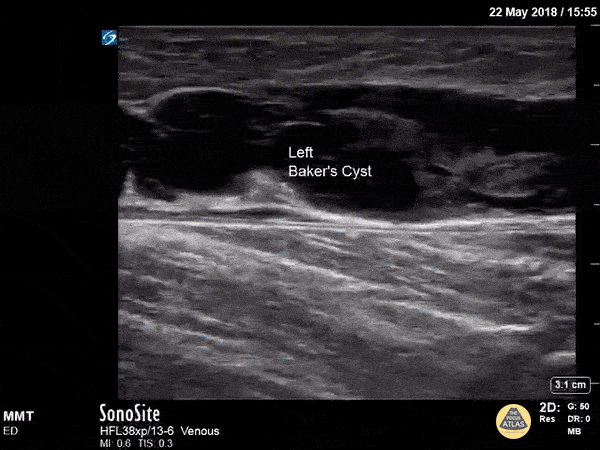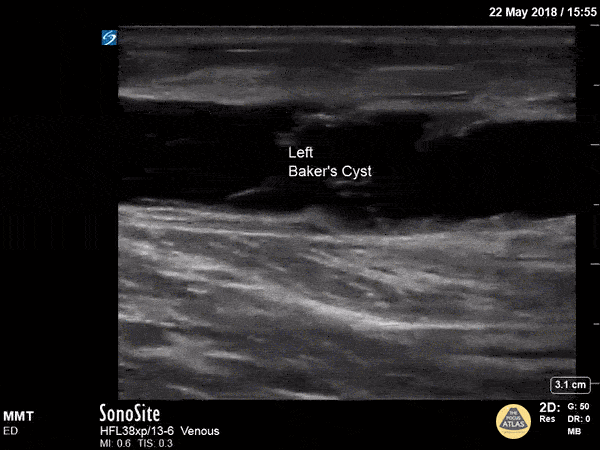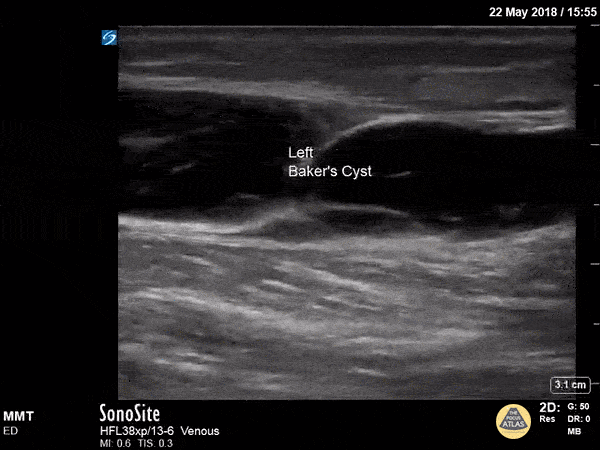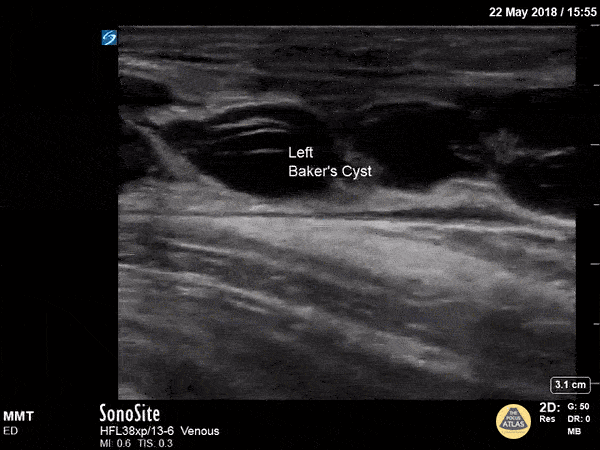
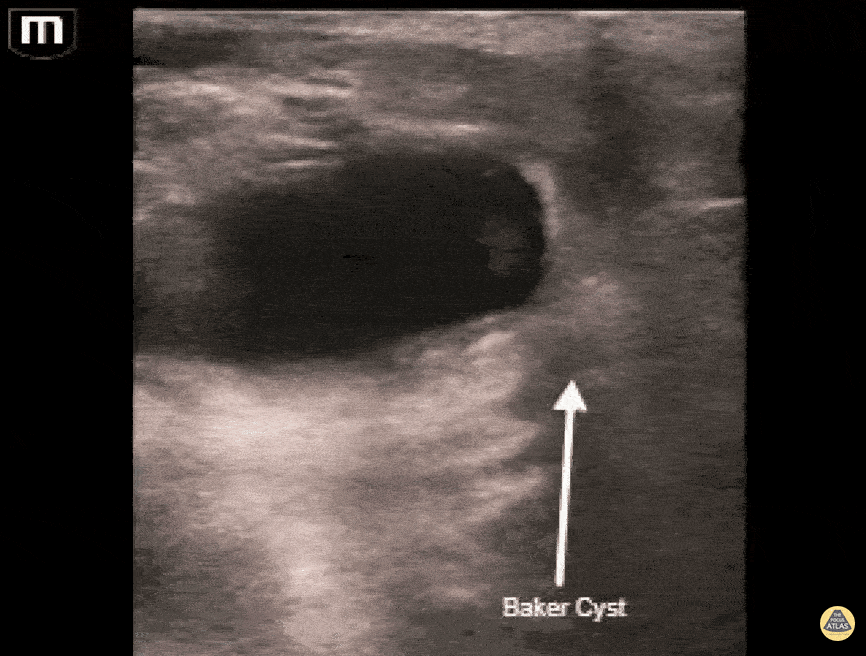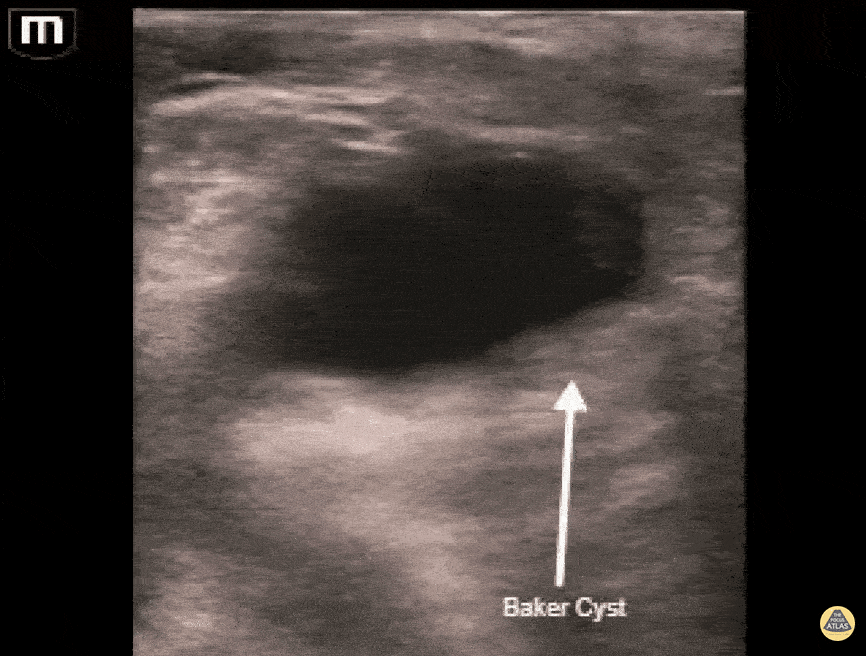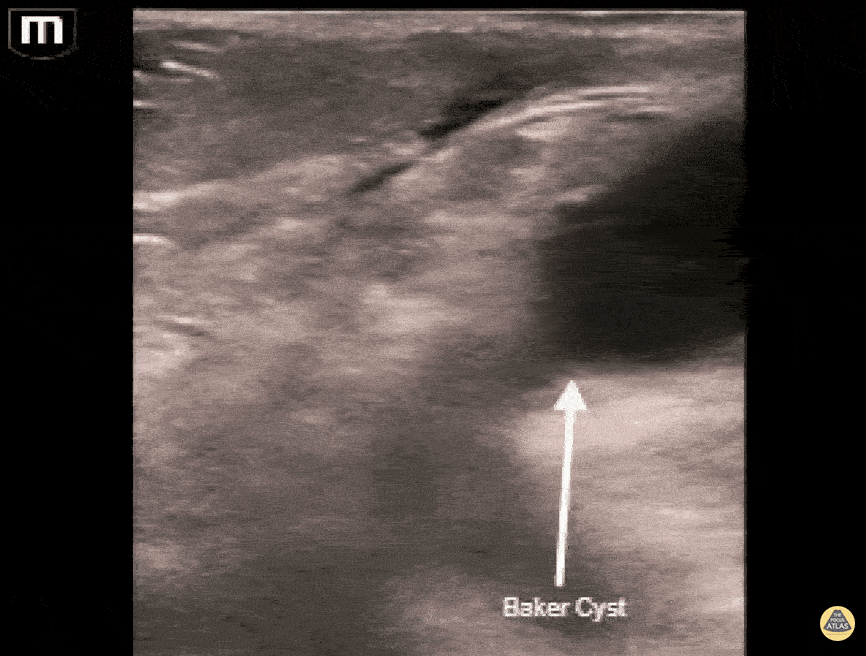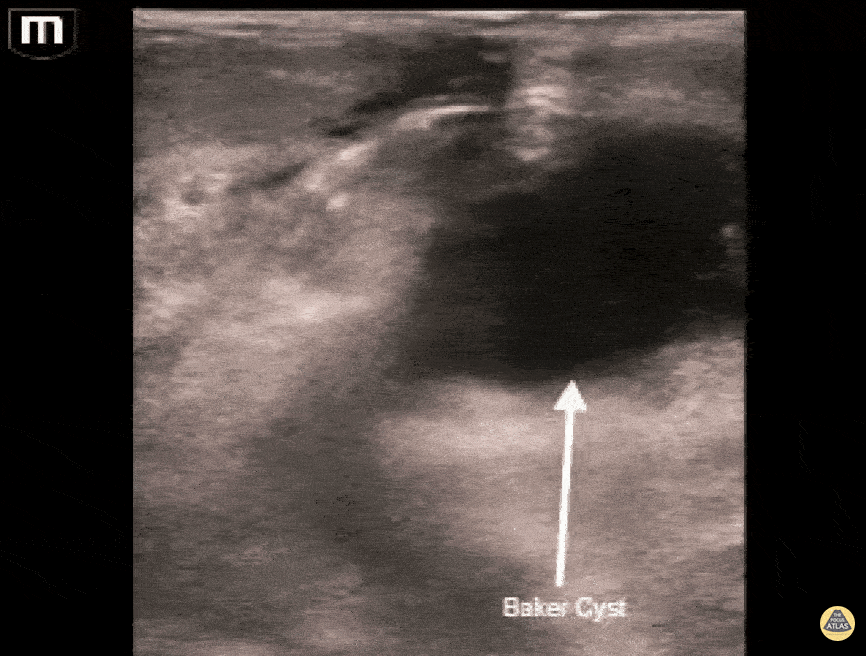
Baker's Cyst
A longitudinal view of a ruptured Baker's cyst. When performing a DVT scan, always look out for incidental findings that may explain the patient's presentation!
Dr. Michael Trauer
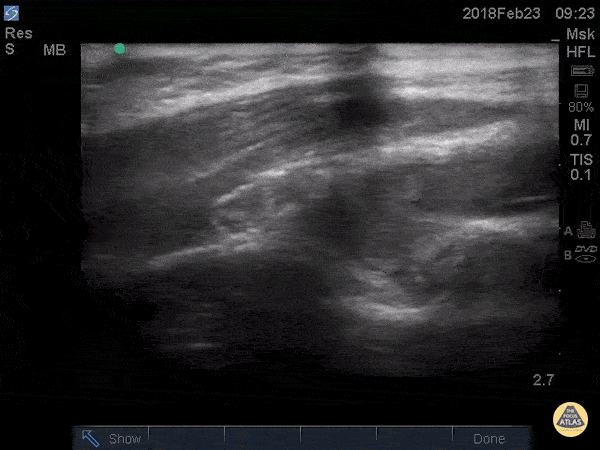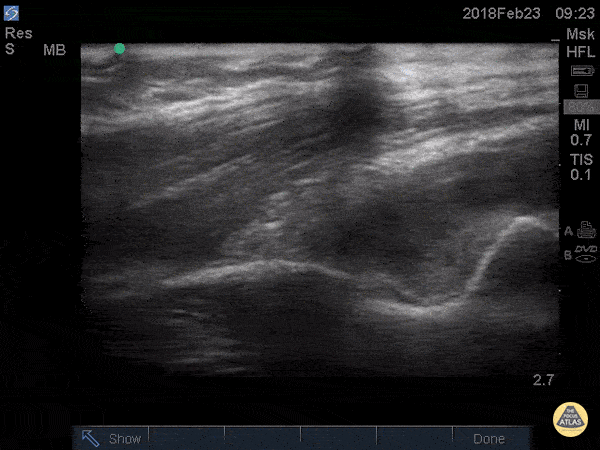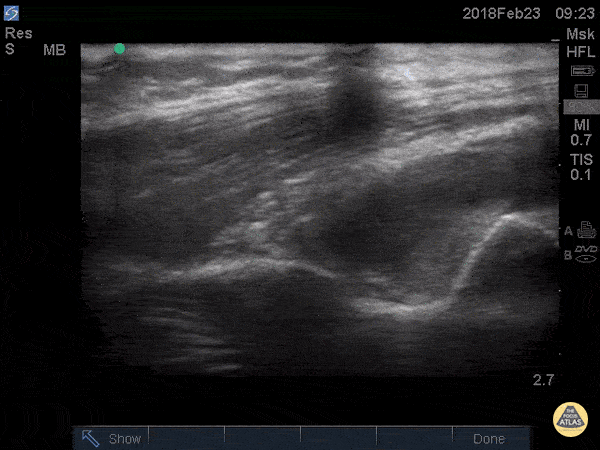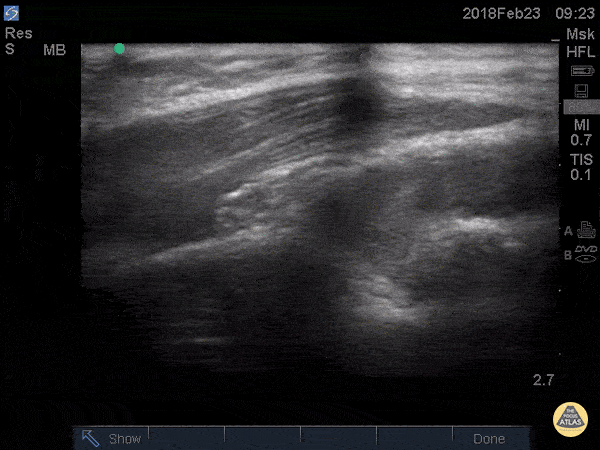
Posterior Fat Pad
Posterior fat pad aka Sail sign, is one of the common findings that we look for after a traumatic elbow injury that can indicate an underlying fracture. It represents hemarthrosis pushing the fat pad superiorly causing the triceps tendon to tilt. Plain films has been used as the initial modality of choice to look for sail sign but POCUS has been shown to be highly sensitive (97%) and specific (88%). It can be seen as anechoic fluid between the olecranon, humerus and fat pad. Source: Avci et. al. (PMID: 27645809). Also note the broken crystal on this image causing a dark artifact anteriorly.
Dr. Maan Al Dubayan, Steven Greenstein, and Matthew Riscinti - Kings County Emergency Medicine
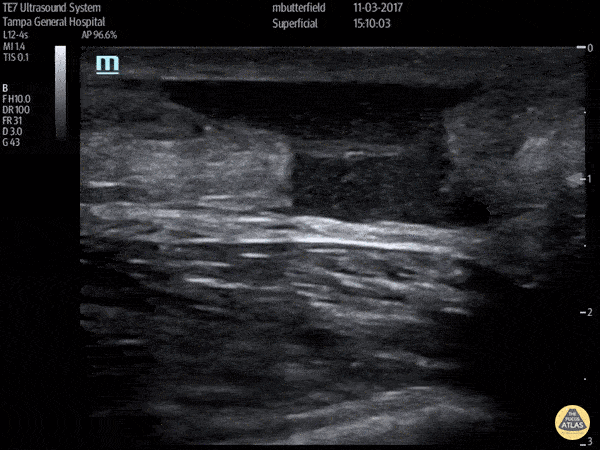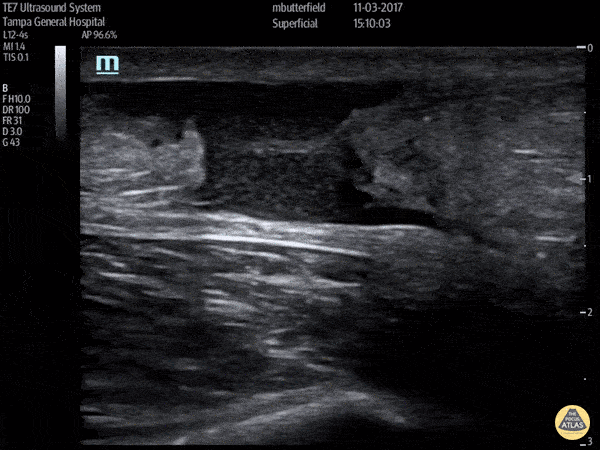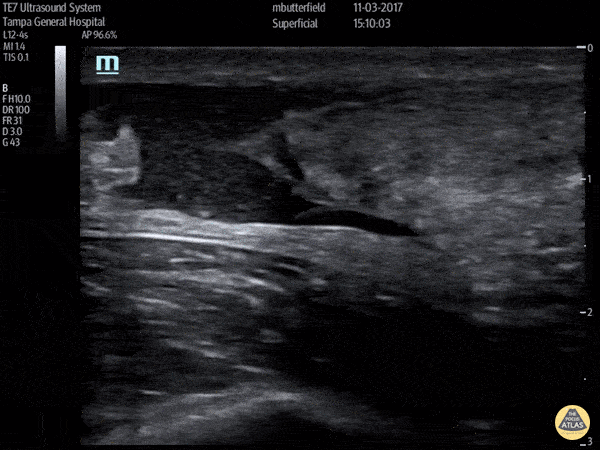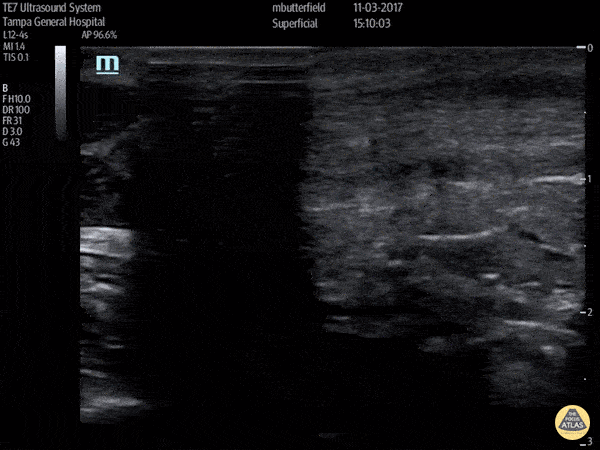
Achilles Rupture (Long Axis)
Full thickness tear of right achilles tendon after a skateboarding accident. (Long Axis)
Dr. Mike Butterfield
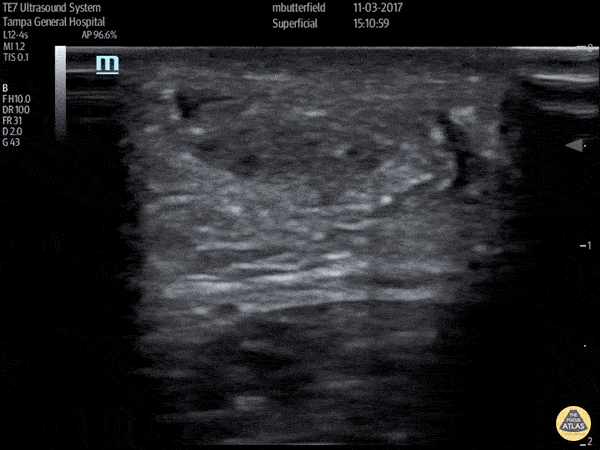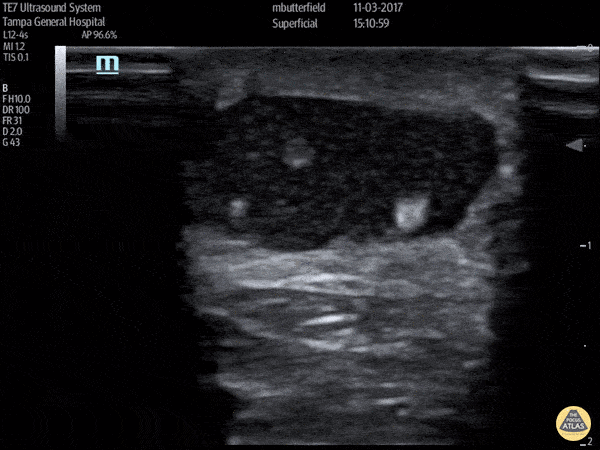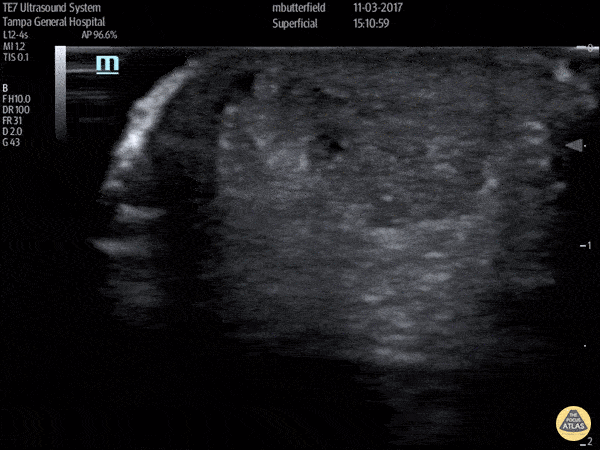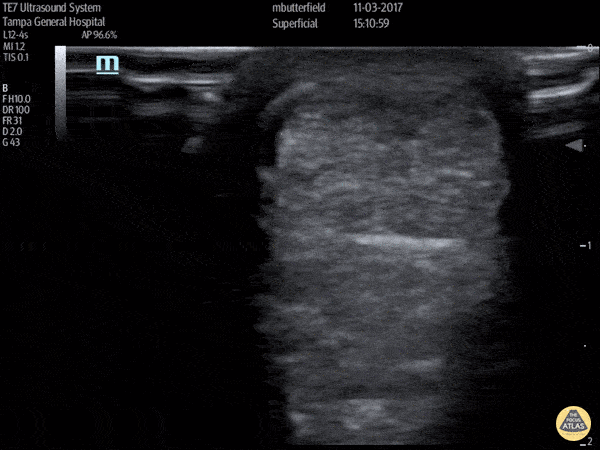
Achilles Tendon Rupture (Short Axis)
Full thickness achilles tendon rupture of the right leg after a skateboard accident. (Short Axis)
Dr. Mike Butterfield
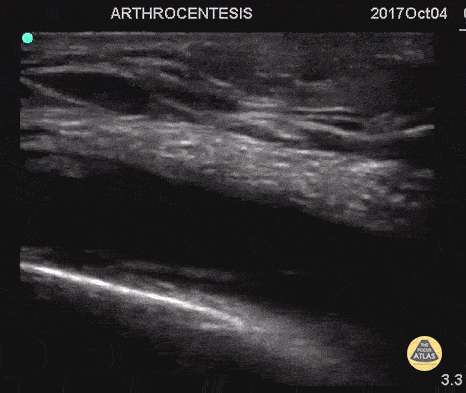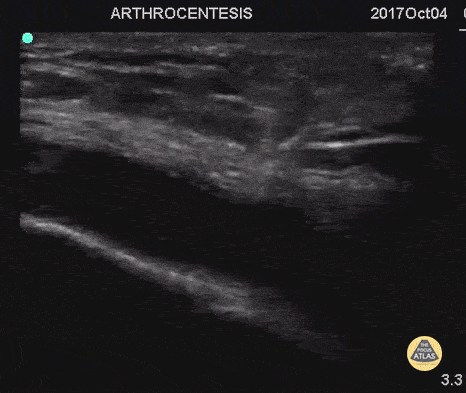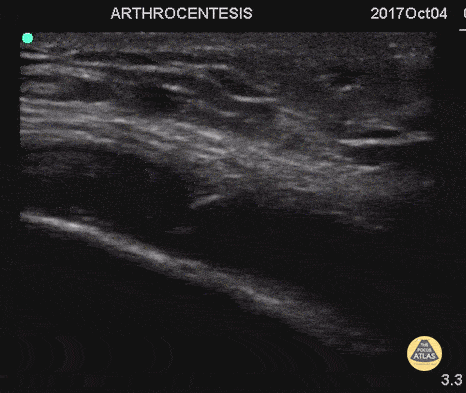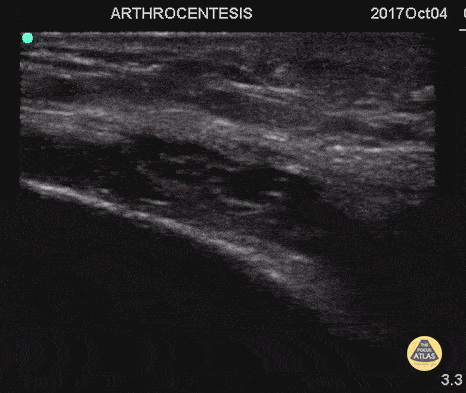
Arthrocentesis and Joint Injection
55 y/o with history of gout and osteoarthritis with an effusion. Join tapped and triamcinalone injected at the end.
Going to tap a joint and unsure of the best spot? Grab POCUS to find the biggest fluid pocket. Many prefer the in-place US guidance technique for big targets such as a joint and watching the needle enter the whole way.
Matthew Riscinti, MD - Kings County Emergency Medicine
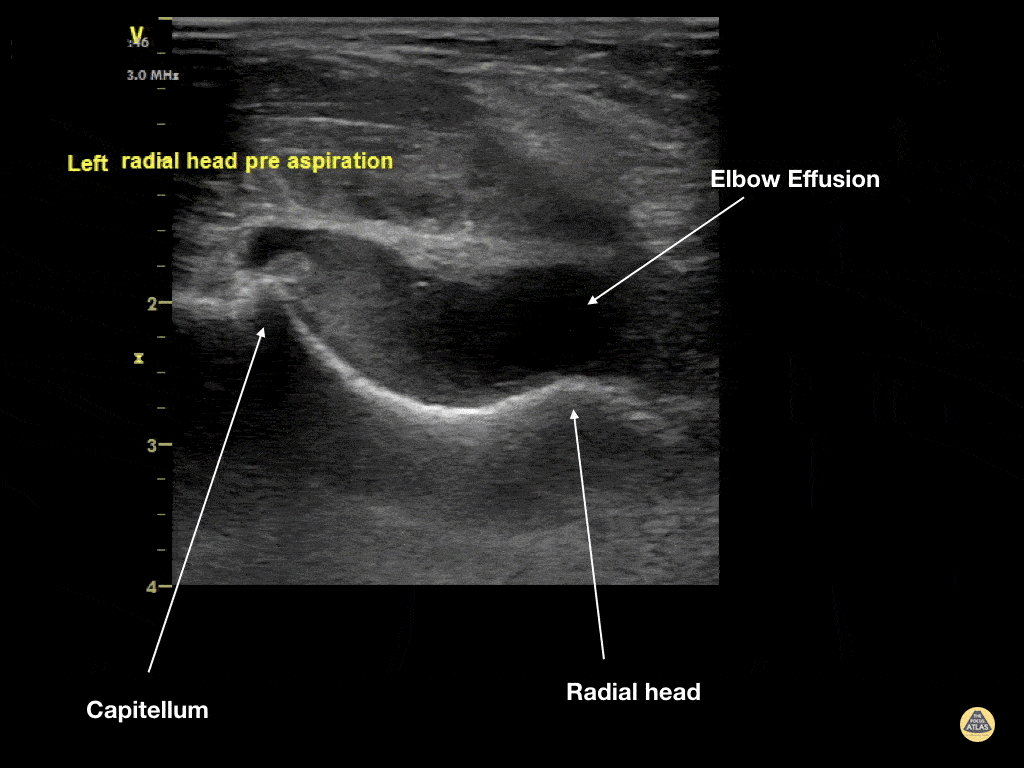
Elbow Effusion (Traumatic)
Aspiration of traumatic elbow effusions may be considered in the management of radial head fracture. Slide a linear transducer along the forearm towards the elbow until the radial head, effusion and capitellum are seen. Using an out of plane approach, insert a needle into the effusion. The syringe will fill itself under intrinsic pressure. Relief is often instantaneous and prolonged and the range of motion of the elbow will increase dramatically
Dr Cian McDermott, Emergency Physician, Mater University Hospital, Dublin, Ireland
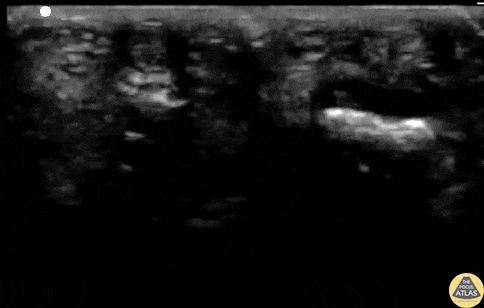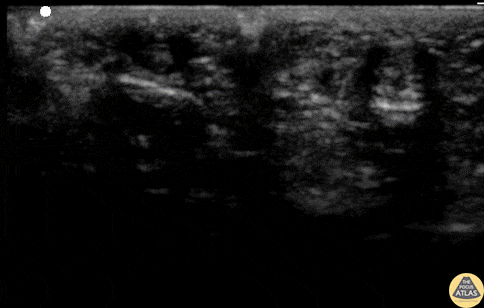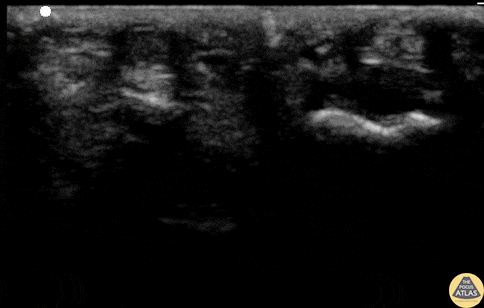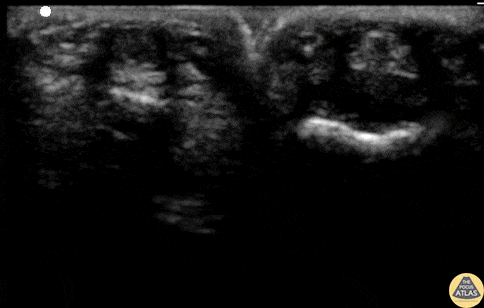
Flexortenosynovitis (FTS)
21 y/o F with 1 day of pointer finger pain. 4/4 Kanavel's signs - pain with passive extension, percussion tenderness, sausage digit, flexion posture of finger. Consultant is "unimpressed" and wants the patient on observation.
Waterbath POCUS performed and demonstrates a fluid collection between the tendon and the bone (digit on left). Normal digit is on right. POCUS changed management and the patient went to the OR with confirmed FTS.
Matthew Riscinti, MD - Kings County/SUNY Downstate Emergency Medicine
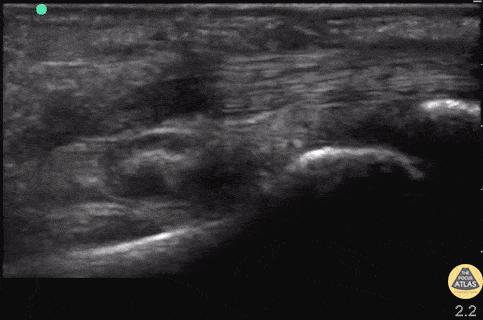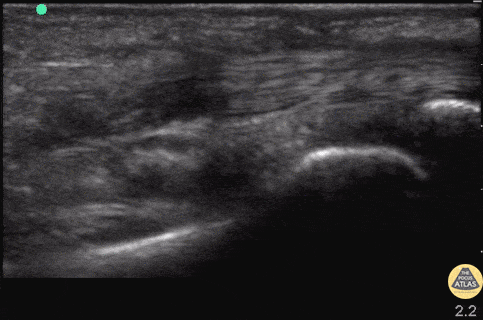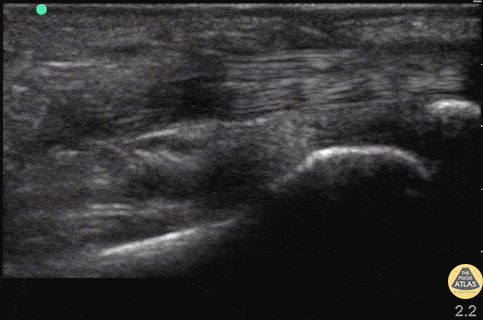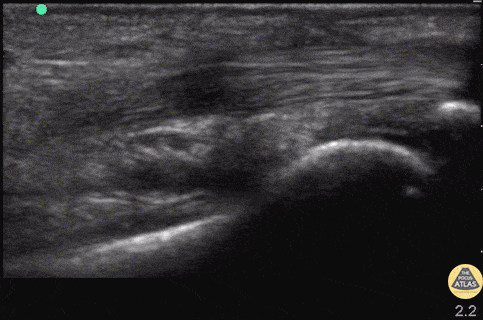
Flexor Tendons of Hand (normal)
Patient with atraumatic pain and swelling of R proximal phalanx. Flexor tenosynovitis was considered but view revealed normal flexor tendons without surrounding hypoechoic fluid or inflammation of the tendon. Keep in mind this is not a sufficient rule out test.
In this image, the tendon can be seen flexing and extending with the proximal and distal phalanges articulating on each other.
Drs. Hannah Moreira and John F Kilpatrick - Kings County/SUNY Downstate Emergency Medicine
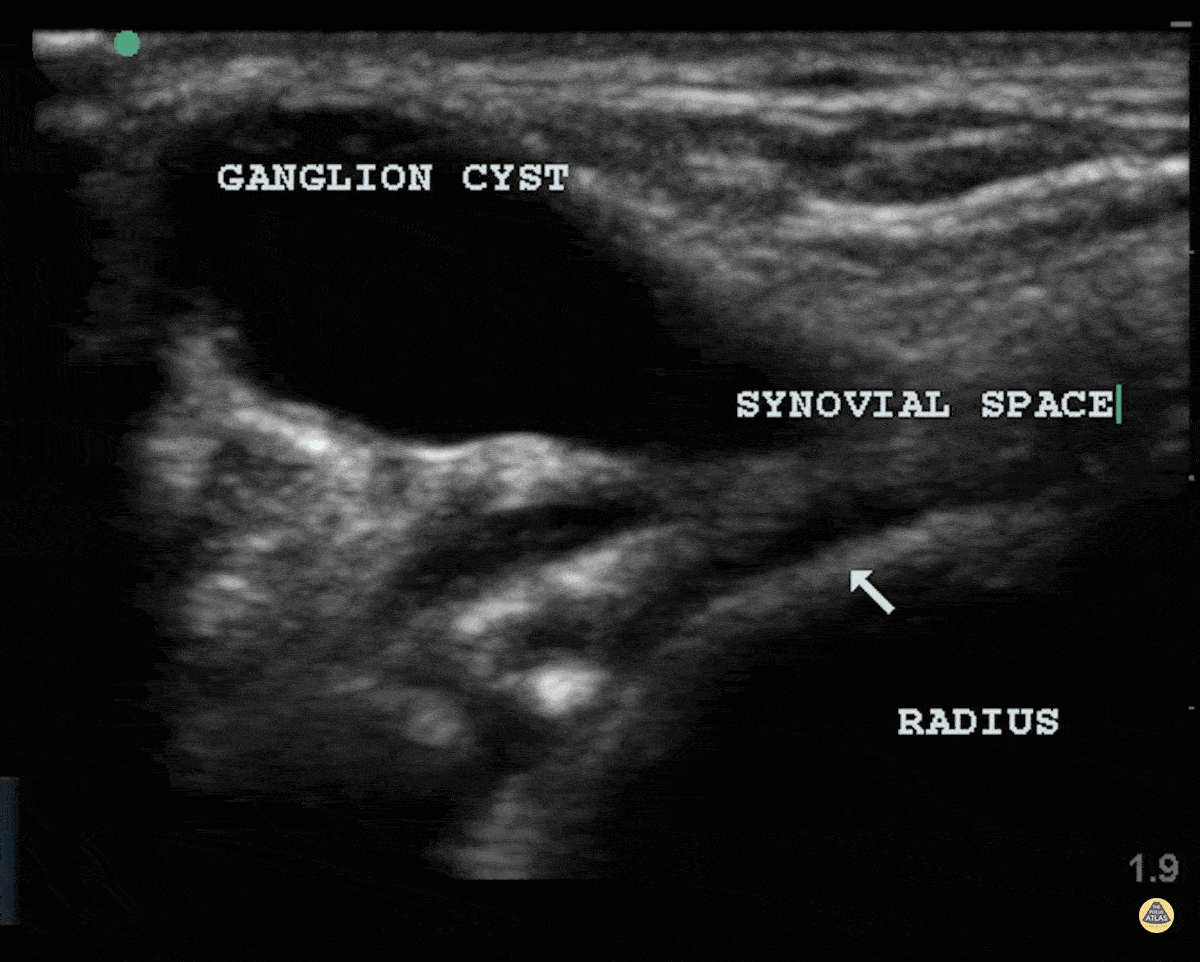
Ganglion Cyst
Patient struck his wrist several days ago and noted a deformity. There is a clear cystic structure with no doppler flow diving between the bones and involving the synovium representing a ganglion cyst.
Dr. Dustin Morrow
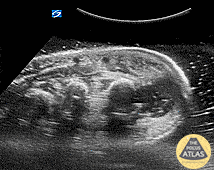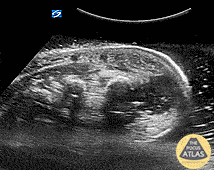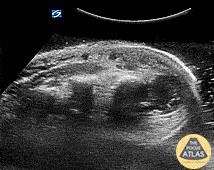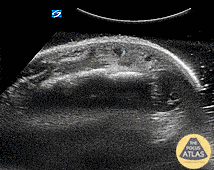
Hand Abscess (Periosteal)
Periosteal Hand Abscess
Pt is an IVDA with a recent lanced boil, total hand swelling and pain with movement. Water bath demonstrates a large collection periosteally which underwent washout and drainage in the OR for concern of early osteomyelitis.
Dr. Dustin Morrow
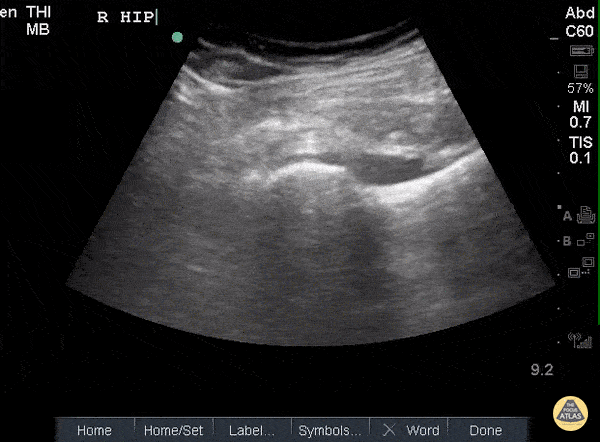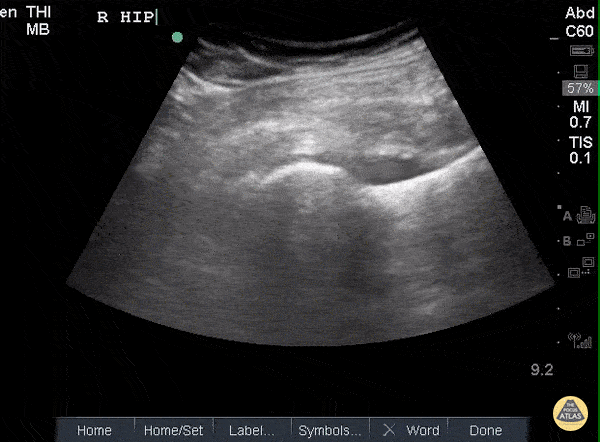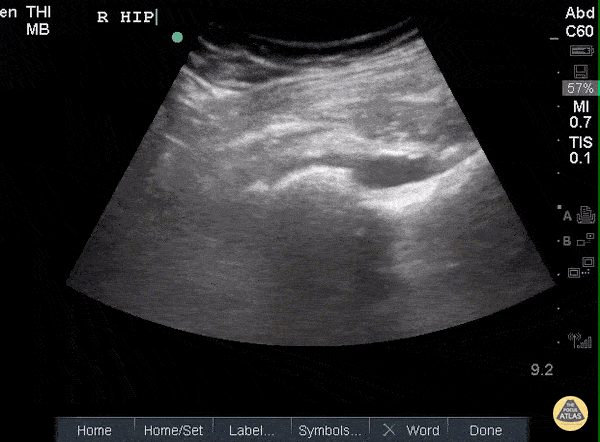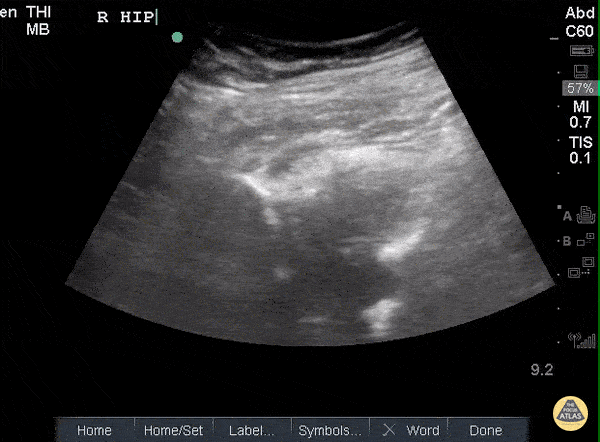
Hip Effusion
POCUS of the R hip shows an anechoic region adjacent to the femoral head and within the joint capsule consistent with an effusion.
Sukh Singh, MD
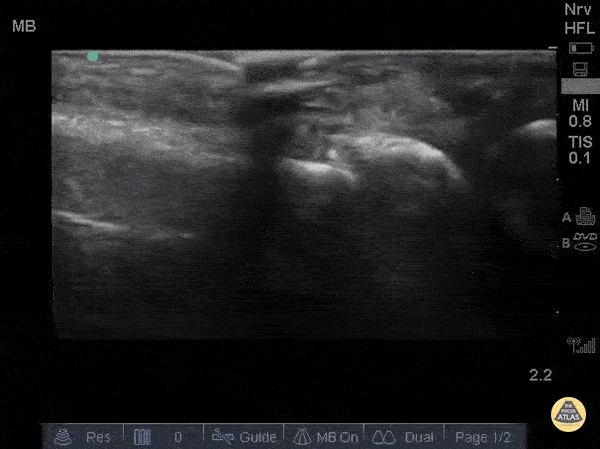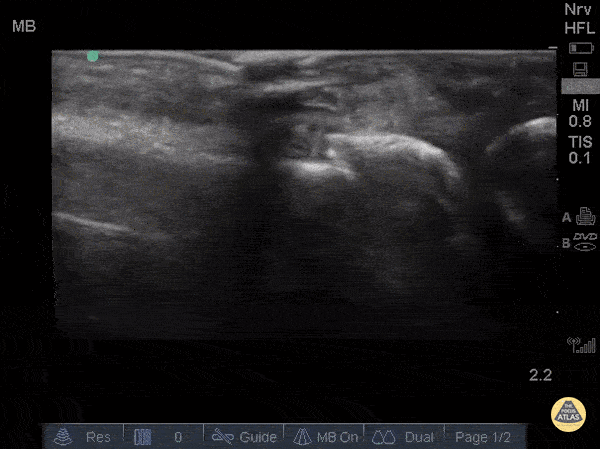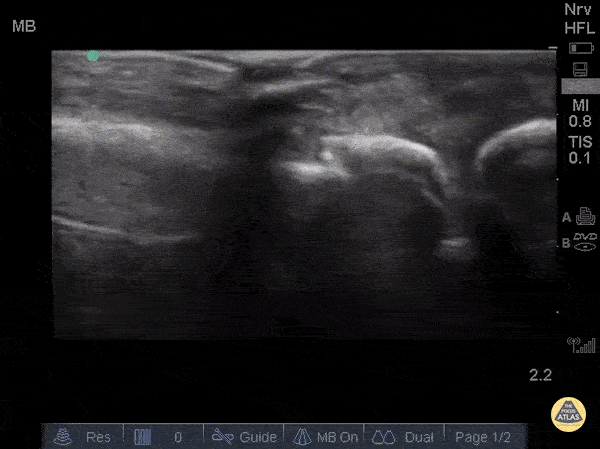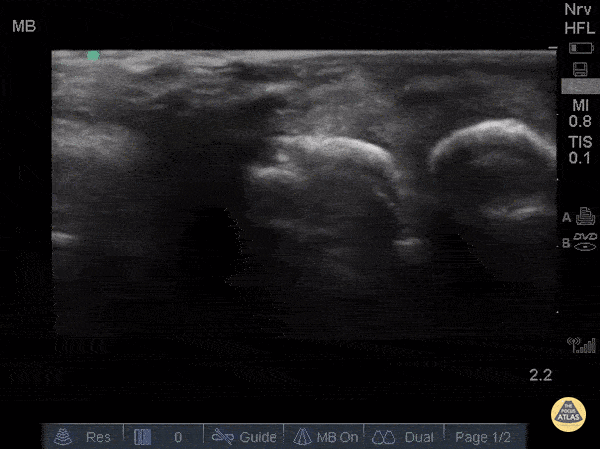
Metacarpal Fracture
Fractures can easily be diagnosed with POCUS especially in resource limited settings. Just remember... this could be painful so use A LOT of gel and try not to press hard or at all. Gently move the probe along the axis of the bones where you suspect a fracture.
The deepest and most hyperechoic horizontal line is the cortex and discontinuity in the lines represent fracture. Angulation and displacement can be measured. Two planes should be measured.
Sukh Singh, MD, Caption: Matthew Riscinti, MD
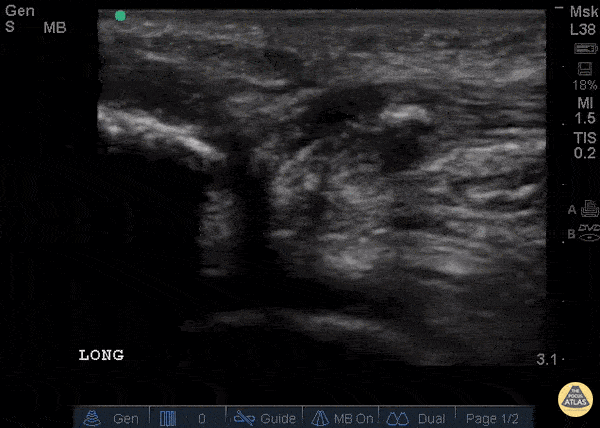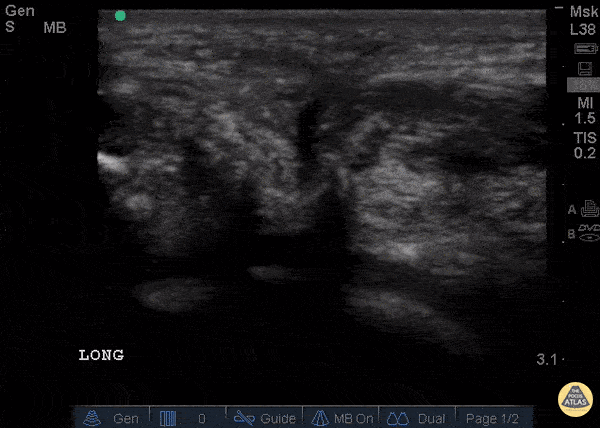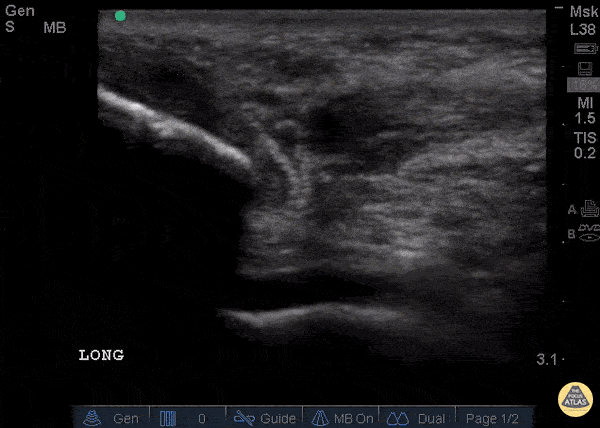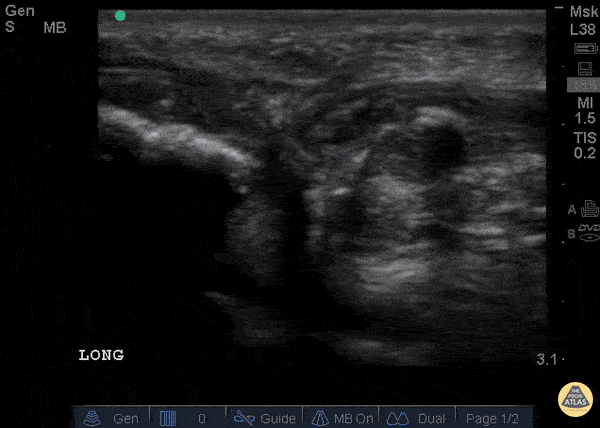
Patellar Tendon Rupture Longitudinal
34 y/o M presented with swelling and pain inferior to his knee following hearing a pop when he jumped playing basketball. Pt unable to extend leg and x-ray demonstrated a high riding patella. Longitudinal ultrasound showed a hyperechoic tendon that is not continuous between the patella and tibia, with an anechoic area of hemorrhage consistent with patellar tendon rupture.
Patellar tendon rupture can be diagnosed with H&P and POCUS can be used to confirm this diagnosis. In one study, diagnosis of tendon rupture by physical exam had a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 76%, while diagnosis by POCUS had a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 95%. Ultrasound is especially useful in patients who cannot cooperate with a physical exam, and serial ultrasound can also be used to monitor healing of a tendon rupture.
Caroline Rago - MS4, Dr’s Bryan Jarrett and Joshua Schechter - Kings County Emergency Medicine
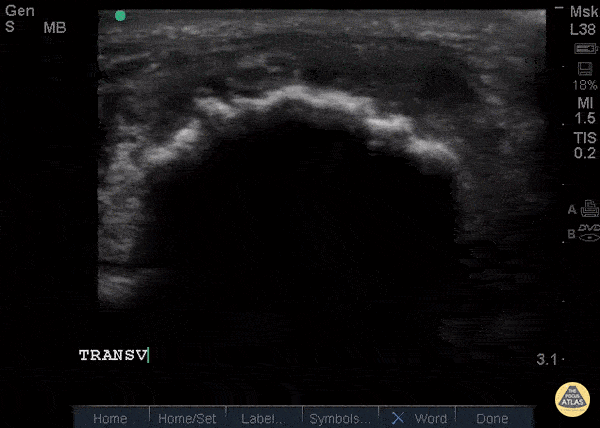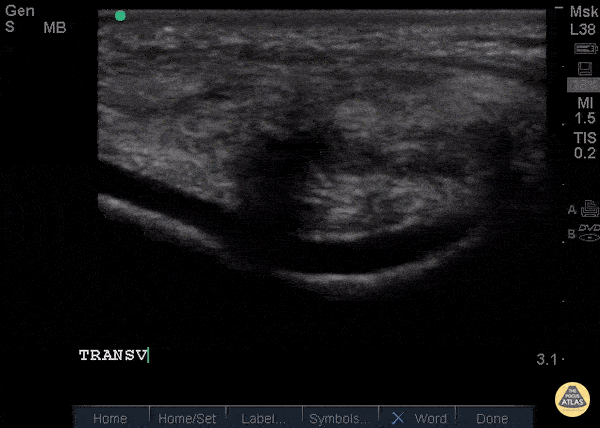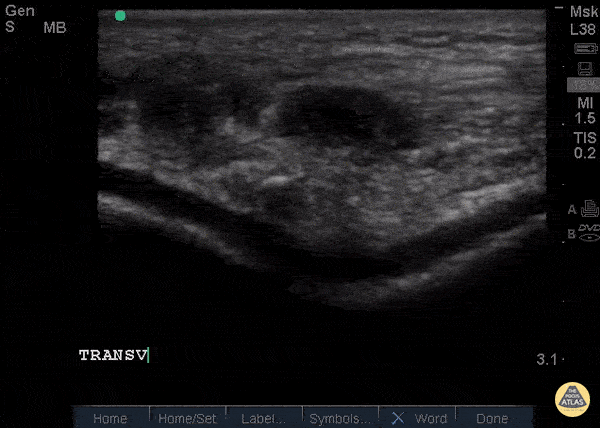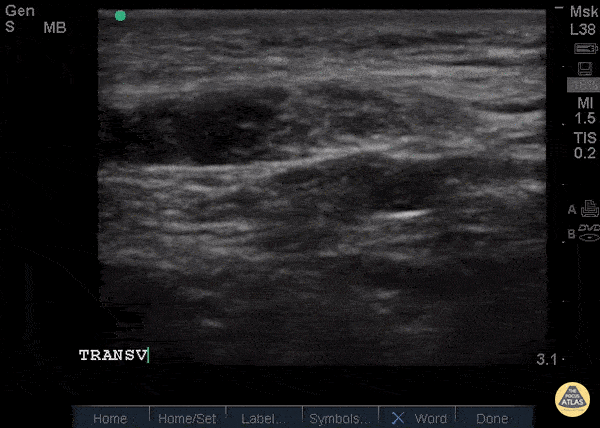
Patellar Tendon Rupture Transverse
34 y/o M presented with swelling and pain inferior to his knee following hearing a pop when he jumped playing basketball. Pt unable to extend leg and x-ray demonstrated a high riding patella. Longitudinal ultrasound showed a hyperechoic tendon that is not continuous between the patella and tibia, with an anechoic area of hemorrhage consistent with patellar tendon rupture.
Patellar tendon rupture can be diagnosed with H&P and POCUS can be used to confirm this diagnosis. In one study, diagnosis of tendon rupture by physical exam had a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 76%, while diagnosis by POCUS had a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 95%. Ultrasound is especially useful in patients who cannot cooperate with a physical exam, and serial ultrasound can also be used to monitor healing of a tendon rupture.
Caroline Rago - MS4, Dr’s Bryan Jarrett and Joshua Schechter - Kings County Emergency Medicine
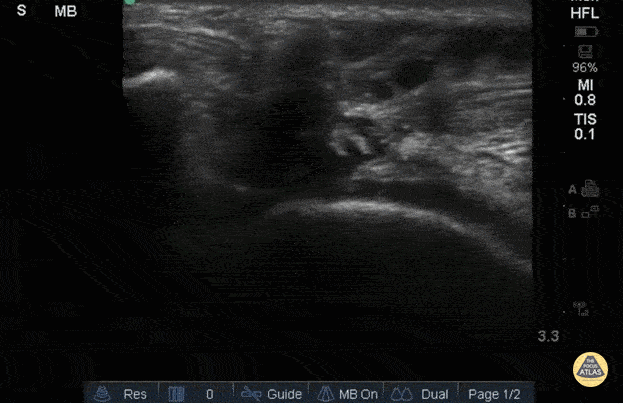
Right Patellar Tendon Rupture
56yo M with right knee swelling after getting foot stuck under a pallet and falling backwards, found to have patella alta and right patellar tendon rupture. Longitudinal image using linear 13-6MHz probe along proximal (left) and distal (right) patellar tendon with hypoechoic fluid at site of tendon rupture. Dynamic ultrasound is useful in diagnosing tendon ruptures as the site and extent of rupture can be easily visualized, which facilitates triage to surgery, if indicated.
Dr. Jasmin Harounian
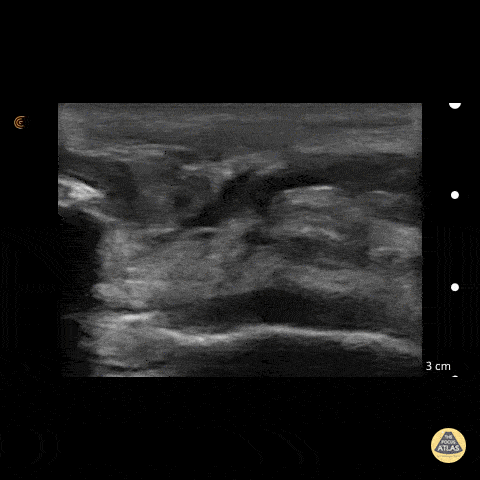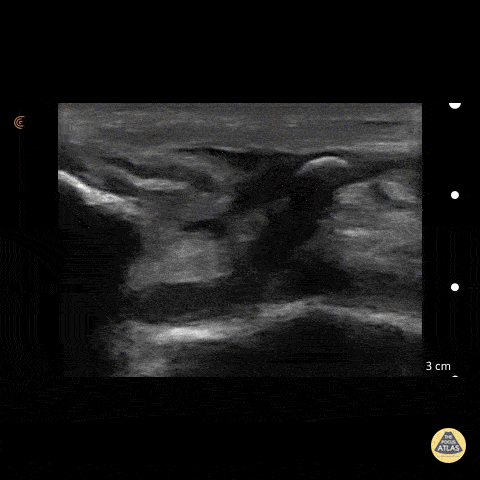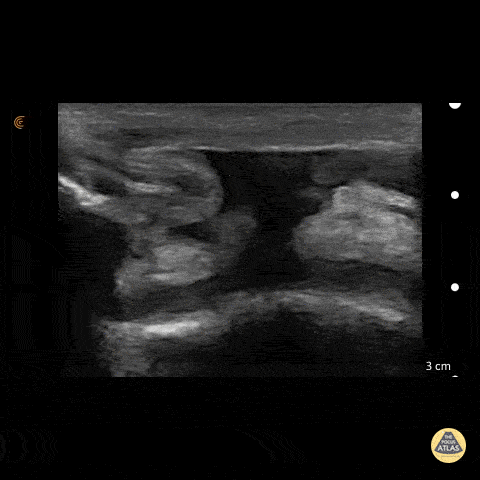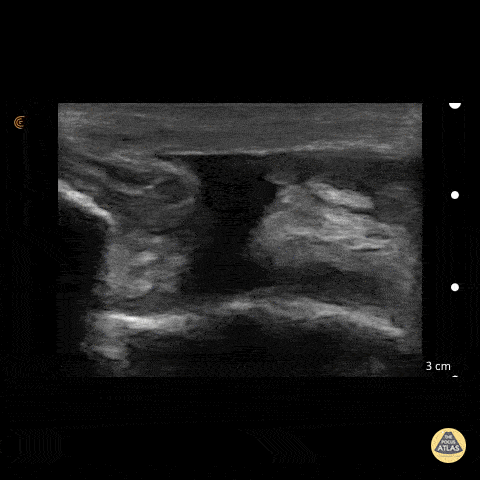
Patellar Tendon Rupture
50 y/o M presents with acute left anterior knee pain after fall. On exam, patient noted to have high riding patella.
Longitudinal sonogram of the infrapatellar region showed marked discontinuity of the normally hyperechoic linear patterned tendon. The discontinuity is replaced with an anechoic collection indicative of hemorrhage. Comparison to normal knee can be seen on the next post.
Of note, anisotropy may be encountered when utilizing ultrasound, leading to artifact. Depending on the angle of the insonating beam, a normally hyperechoic structure may be falsely viewed as hypoechoic due to poor return of echo. Ensure US probe remains perpendicular to the tendon to minimize this artifact.
Dr. Hannah Moreira, Dr. Tareq Azad, Dr. Kyle Kelson - Kings County/SUNY Downstate Emergency Medicine

Plantar Fasciitis
84 y/o F who couldn’t bear weight on her left foot. Pt usually ambulatory with no known trauma.
L side thickened plantar fascia on symptomatic side (>4.5mm) and a hypoechoic fascia compared to a normal R side.
Dr. John F Kilpatrick - Kings County/SUNY Downstate Emergency Medicine
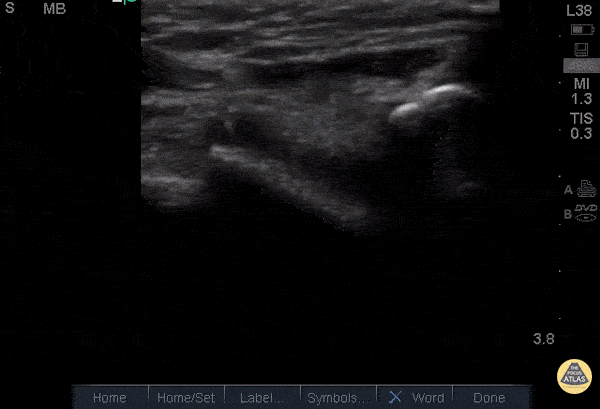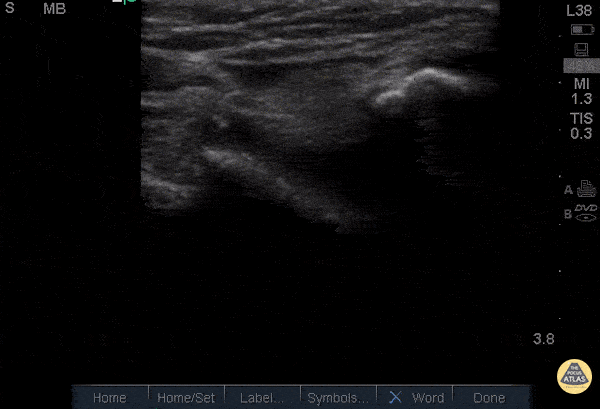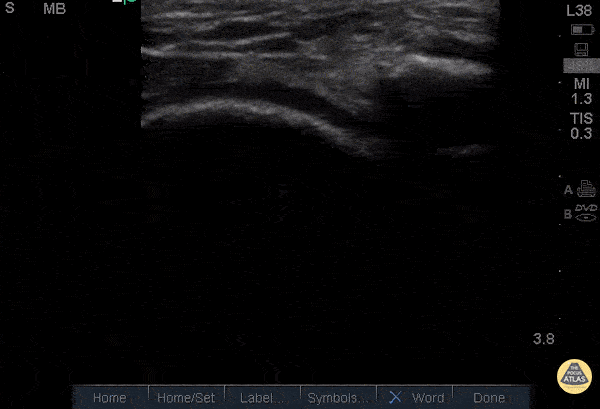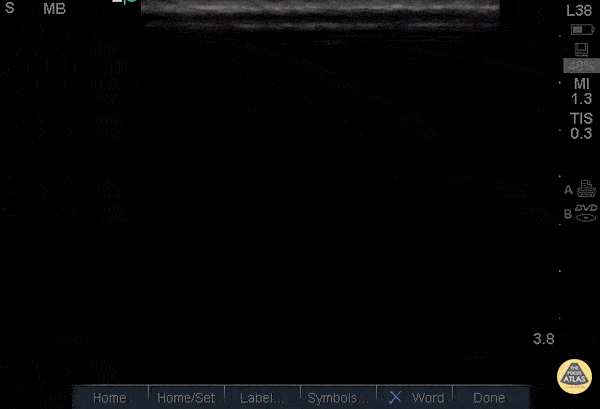
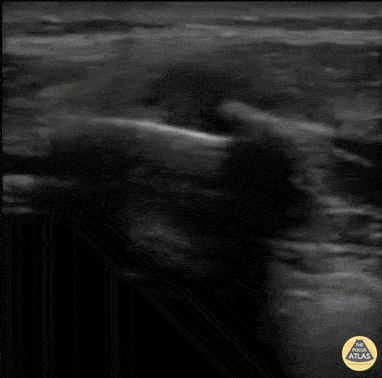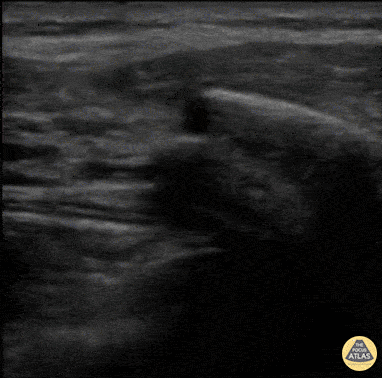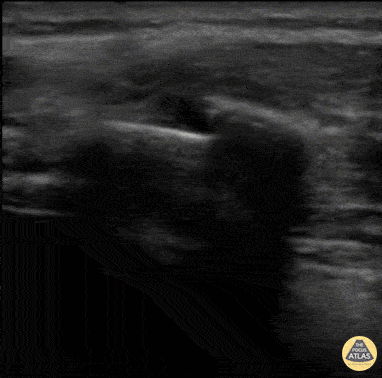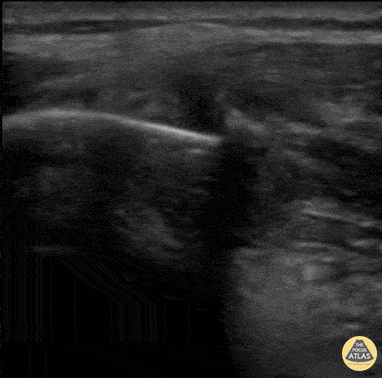
Quad Tendon Rupture (Bilateral)
40 year old M presented with bilateral knee pain and inability to extend knees after injuring knee while carrying heavy plywood boards.
POCUS confirmed the diagnosis of bilateral quadriceps tendon rupture. On ultrasound you can see the retracted tendon independent of the patella as the knee is being actively ranged. Also visible is a surrounding traumatic hematoma. One should look for discontinuity in the tendon in longitudinal view to diagnose any sort of tendon rupture. Often, there is an adjacent fluid collection reflecting hematoma. Be careful not to interpret the anisotropy of the ultrasound as discontinuity. Anisotropy is that the US looks different in cross section vs longitudinal views, any variation in the direction of the tendons and the positioning of the probe can lead to a false positive.
Dr. Nathan Frank, Dr. Benjamin Weissman, Dr. Walter Valesky - Kings County/SUNY Downstate Emergency Medicine
Rib Fracture
40 y/o M with polysubstance abuse, left-sided rib pain after a traumatic blow. Chest xray was equivocal. The patient was asked to "point to where it hurt", and the linear transducer revealed a displaced rib fracture. He complained of significant pain even after the resident gave two Percocet and was unwilling to leave the ED.
An intercostal nerve block, and that relieved the patient's pain and he went home.
Dr. Stephen Alerhand, Mt Sinai Hospital NYC
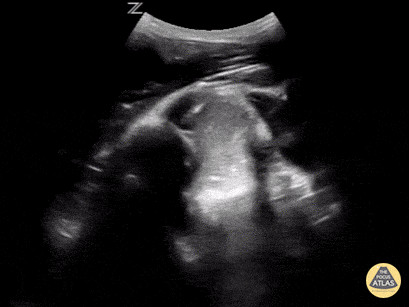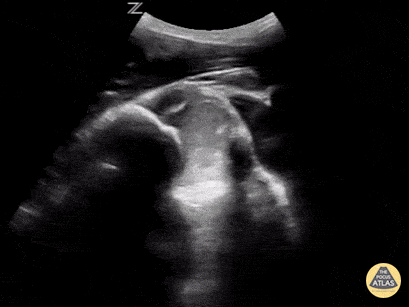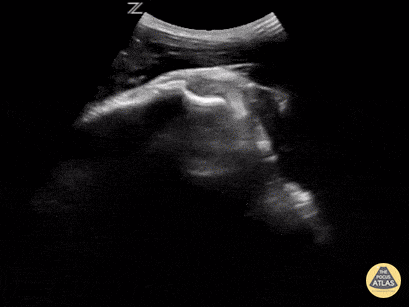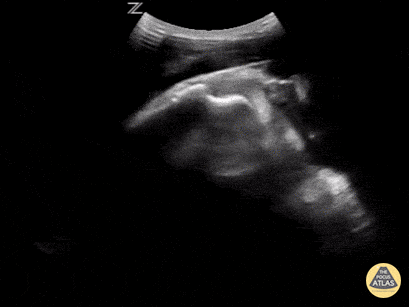
In-Vivo Shoulder Reduction
This is a posterior approach looking at the left shoulder showing an anterior dislocation. The dislocation was found before X-ray was shot. While the resident was performing the Cunningham technique to reduce the shoulder, the attending was able to, in real time, watch it go back in place. In between the humeral head and the glenoid rim is a large hematoma where I would aim my needle if I were to do an intra-articular block. It is a helpful technique in those recurrent dislocators. Saves the initial X-ray, but probably should get the post-reduction film at this point.
Matt Rutz, MD - Indiana University Department of Emergency Medicine, Ultrasound Division
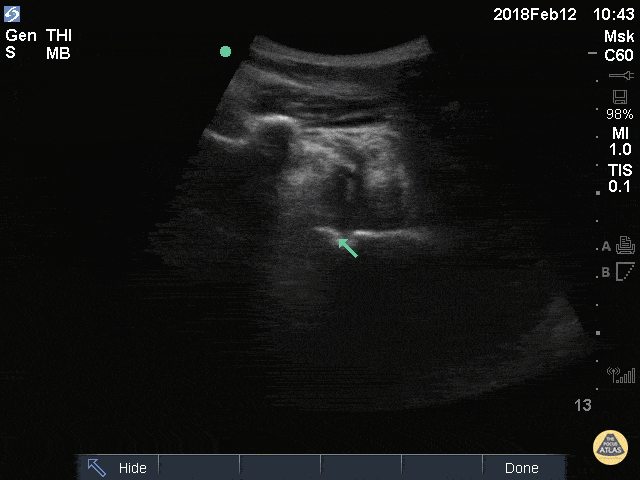
Shoulder Dislocation
50M w/ R shoulder dislocation (arrow over humeral head), also likely has blood and possible air in joint space from injection of anesthetic.
Greg Powell, MD
Subscapularis Tendinopathy
50 year-old woman with anterior left shoulder pain; severe subscapularis tendinopathy with calcification and several small tears.
Dr. Mike Butterfield
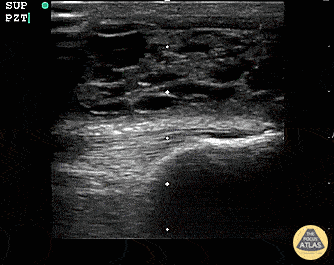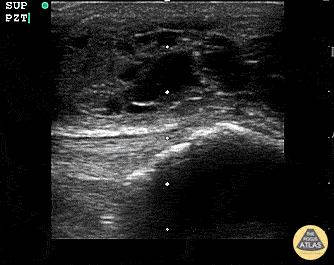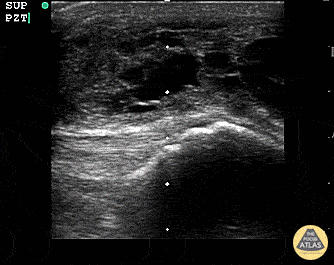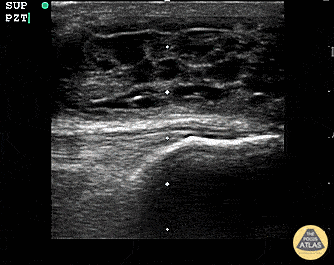
Suprapatellar Bursitis
Suprapatellar bursitis from repetitive trauma of playing on the floor with grandchildren. Presented with over a week of knee pain and swelling. Superficial involvement and septae are possible for abscess, however it is contained within the bursal space above the patella. Arthrocentesis revealed no infection, and conservative therapy yielded improvement.
Dr. Dustin Morrow
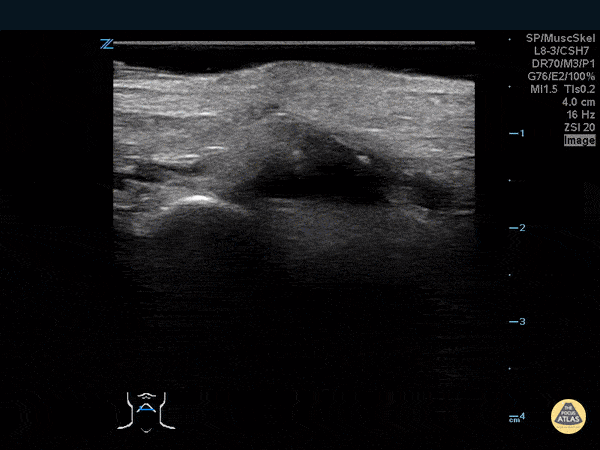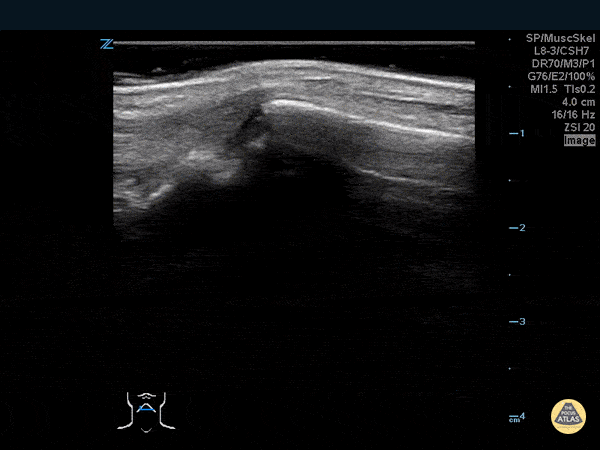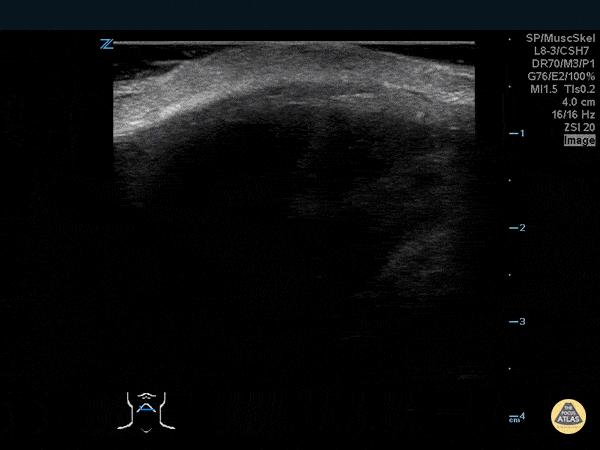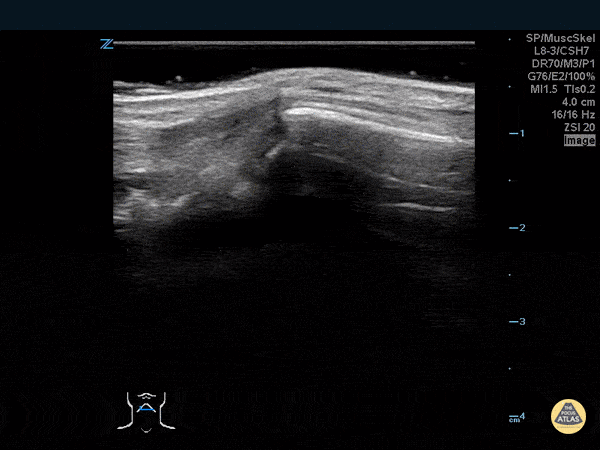
Thumb Fracture
30 year-old male ED resident who injured his thumb at some point while playing football versus the attendings in the annual flag football game. He figured the thumb had merely been sprained, and he kept playing in the game (and scoring touchdowns) while the residents dominated.
Two days later the swelling/ecchymoses seemed to worsen, he used the linear transducer in a water bath to diagnose a fracture of the base of the 1st metacarpal. An x-ray confirmed the diagnosis, and he underwent percutaneous pinning in the operation room the following week.
Dr. Stephen Alerhand, Mt Sinai Hospital, NYC
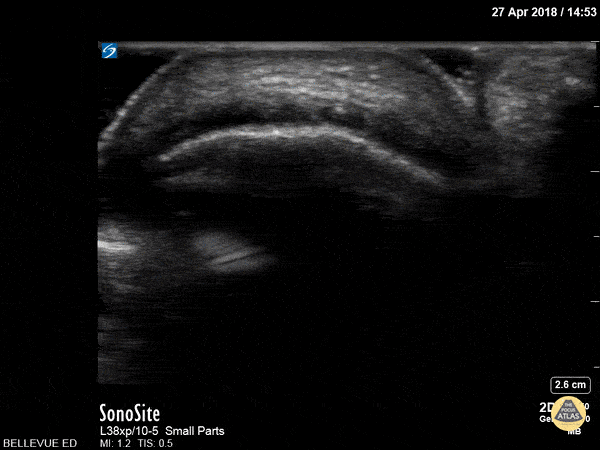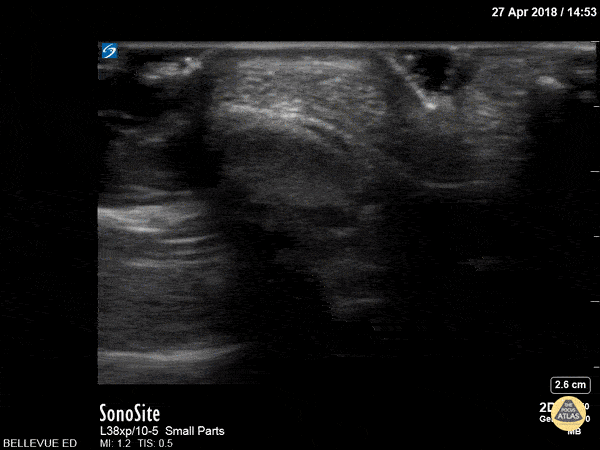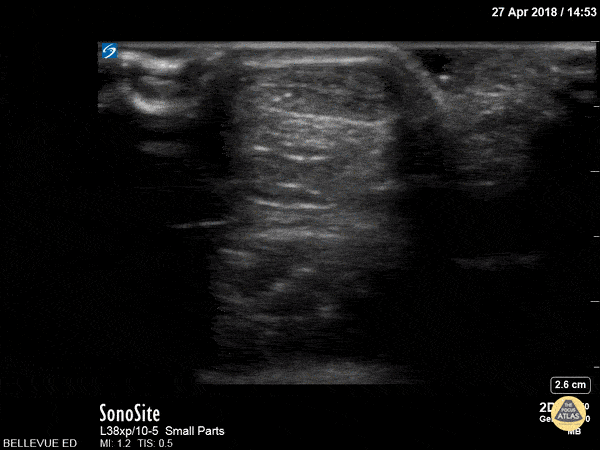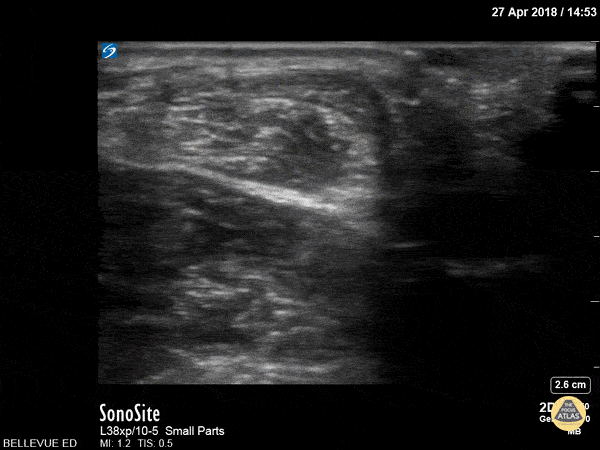
Achilles Tendon Short Axis
This clip begins with the soft tissue of the heel and calcaneus visible in short axis. As the probe moves proximally, the achilles tendon appears in transverse view as an oval with an echogenic punctate appearance beneath a bright layer of skin at the top of the screen. As we move proximally the achilles tendon tapers and the gastrocnemius/soleus muscle complex becomes more prominent.
Hannah Kopinksi and Dr. Lindsay Davis - NYU Emergency Medicine

Normal Shoulder
This clip of the shoulder is obtained by placing the probe in transverse plane on the posterior shoulder, and demonstrates the humeral head (left of screen) rotating in the glenoid. The scapular spine is to the right of the glenoid. The infraspinatus muscle is seen overlying the humeral head superficial to the infraspinatus is the deltoid muscle.
Hannah Kopinksi and Dr. Lindsay Davis - NYU Emergency Medicine
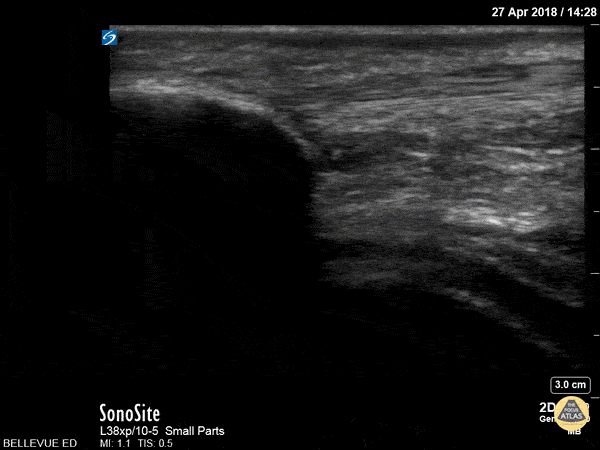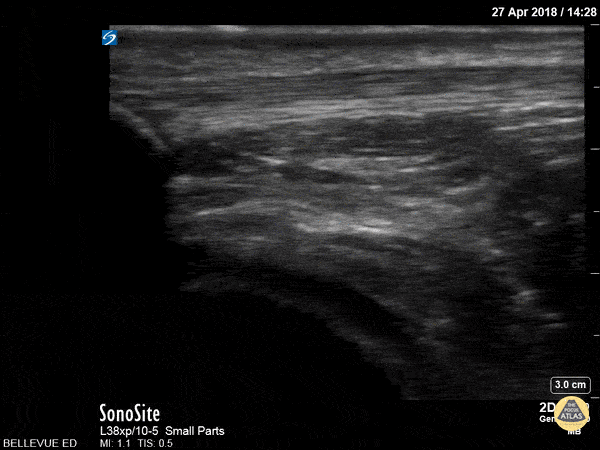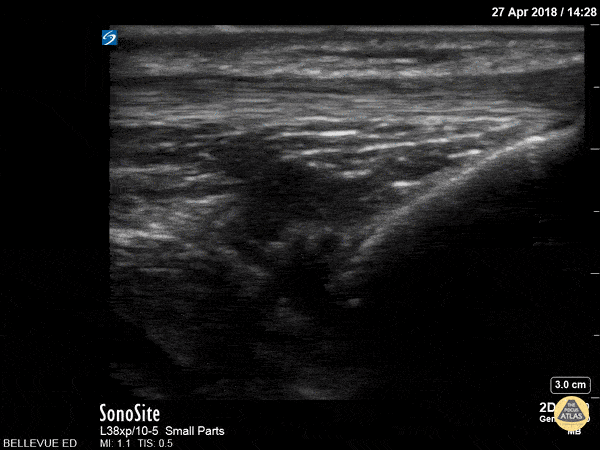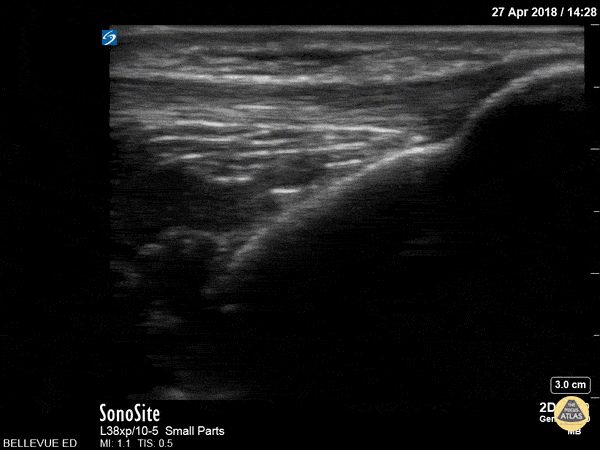
Patellar Tendon
In this clip we see the linear, fibrillar, echogenic patellar tendon in long axis tracking along the top of the screen. It starts with the insertion point at the distal patella (left side of the screen). As the probe moves distally, we see where it attaches to the proximal tibia on the right of the screen.
Hannah Kopinksi and Dr. Lindsay Davis - NYU Emergency Medicine
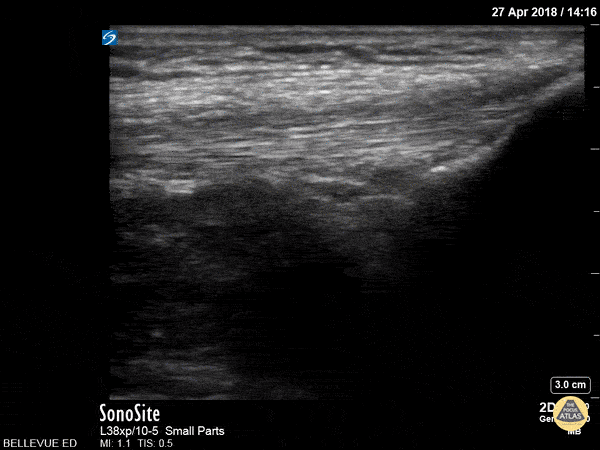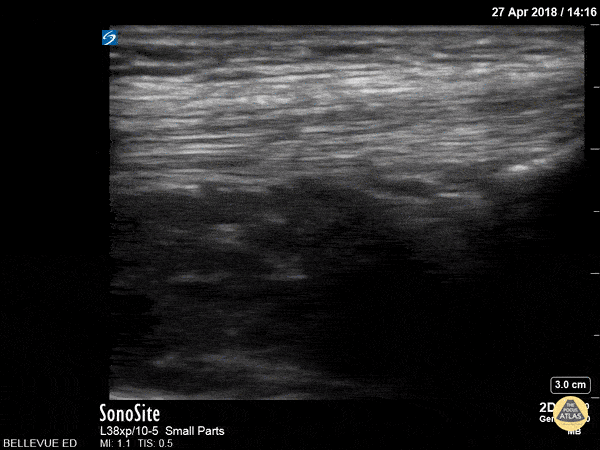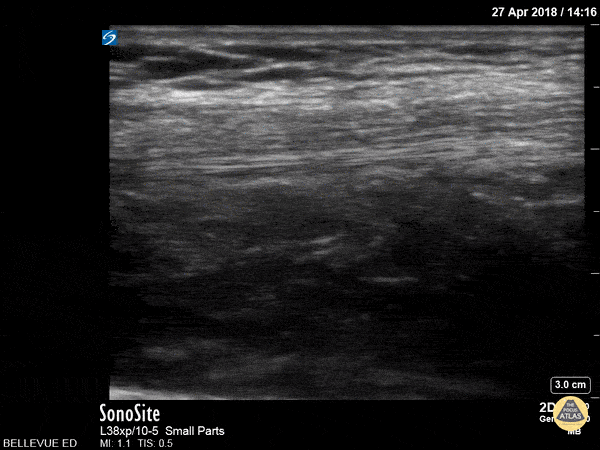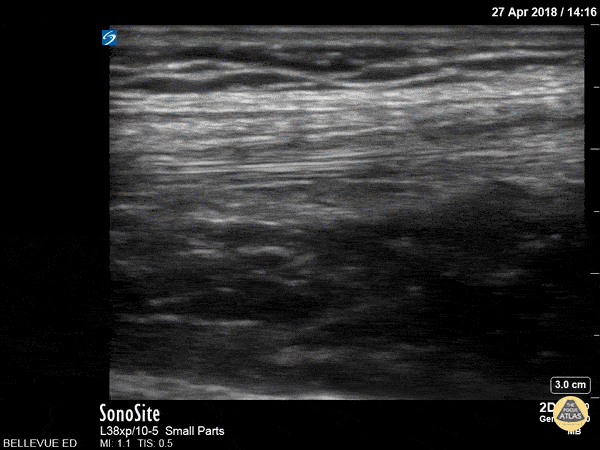
Quadriceps Tendon
This clip shows the quadriceps tendon in longitudinal axis. It is hyperechoic, linear and fibrillar in texture. The distal tendon inserts onto the proximal patella, seen on the right side of the screen at the beginning of the clip. As the probe is moved proximally, the quadriceps muscles are seen deep to the tendon.
Hannah Kopinksi and Dr. Lindsay Davis - NYU Emergency Medicine
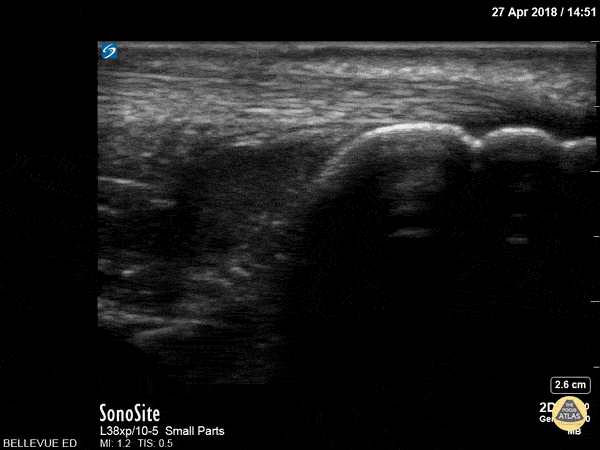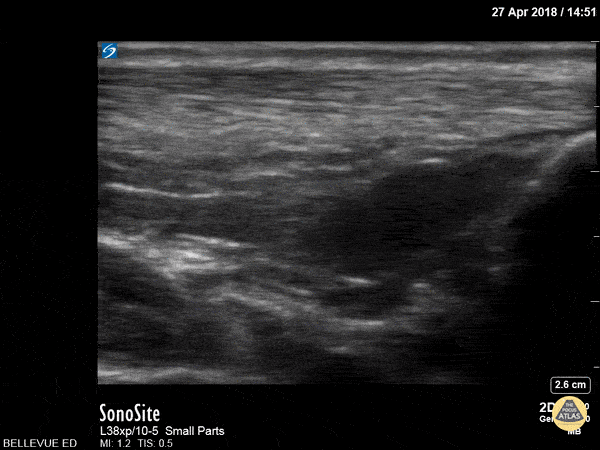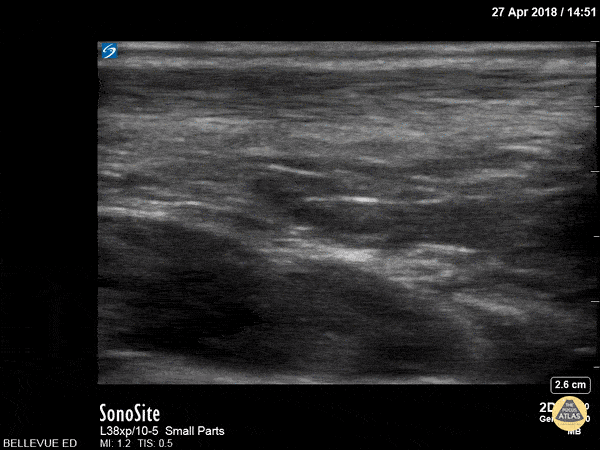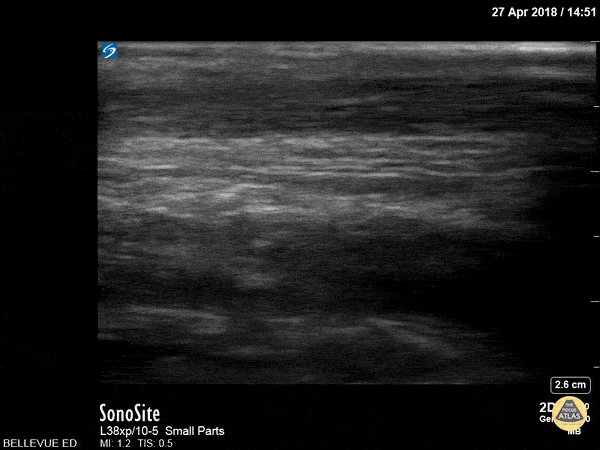
Achilles Tendon
In this clip we see the linear, fibrillar, echogenic achilles tendon in long axis along the top of the screen. The clip begins distally at the tendon’s insertion onto the calcaneus (the curved hyperechoic structure on the right of the screen). As the probe is moved proximally, the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles become visible in long axis deep to the tendon.
Hannah Kopinksi and Dr. Lindsay Davis - NYU Emergency Medicine
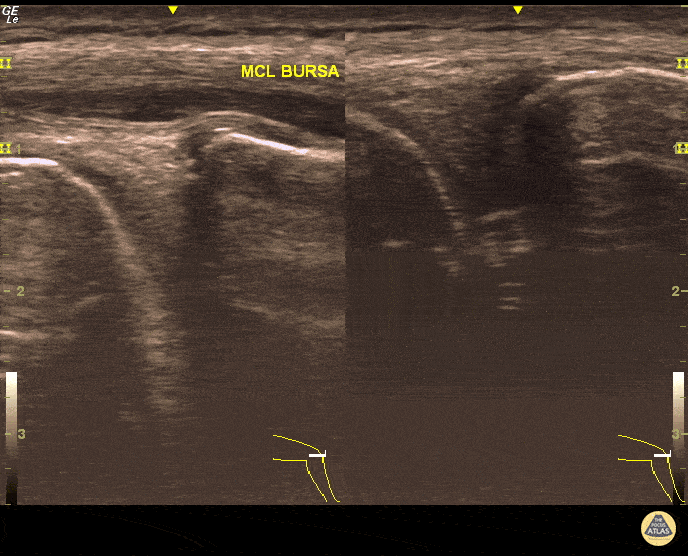
MCL Bursitis
29 year-old elite level soccer player with medial knee pain. He describes this being 'the worst episode ever', as he was having recurrent episodes of such pain. Valgus and flexion deformity due to prior surgery 15 years ago at the affected knee. Sharp, non-radiating pain 9/10 on NPRS, wakes him up at night. Palpation of medial knee and valgus stress test positive. Concomitant recent trauma. Unable to train/compete. USG of his knee revealed both MCL insertional edema (grade 1 injury) and MCL bursitis. Guided aspiration (3cc) and corticosteroid injection to MCL bursae revealed excellent outcomes. He returned to play 3 days later. Pitfall: It was not an MCL injury. Key point : Intervention was necessary and US-guidance allowed correct needle positioning without complication.
Dr. Omer Batin Gozubuyuk, Sports Medicine Specialist, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey.
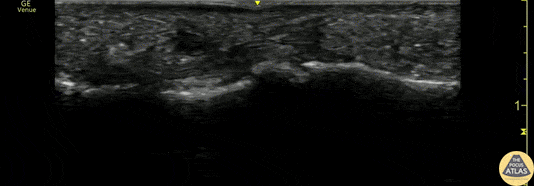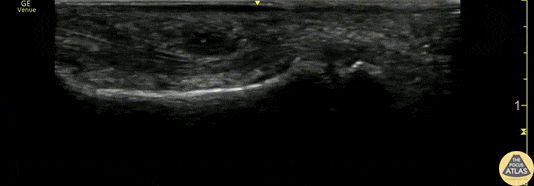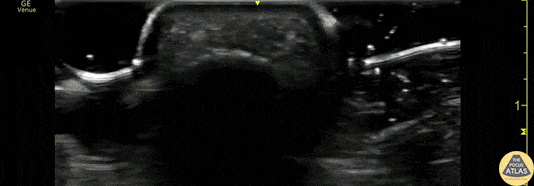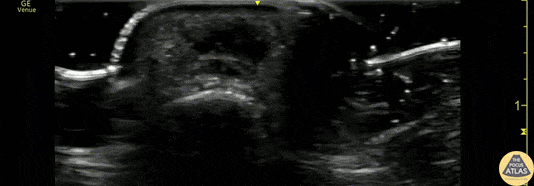
Flexor Tendonitis
A 50s M presented with atraumatic finger pain/swelling x2 weeks. On exam, he had focal swelling localized the volar aspect of the ring finger over the proximal phalanx, without fusiform edema/erythema or any limitation of ROM. POCUS showed a small fluid collection adjacent to the flexor tendon. The flexor tendon is shown in long axis, with linear fibers seen just superficial to the bone cortex, and then is seen in short axis. The hypoechoic area superficial to the tendon represents the fluid collection. As the patient had intact ROM and no signs of infection, he was splinted and will follow up for a recheck of tendonitis.
Kristy Karkula, PA and Dr. Ruth Foss
Denver Health Medical Center
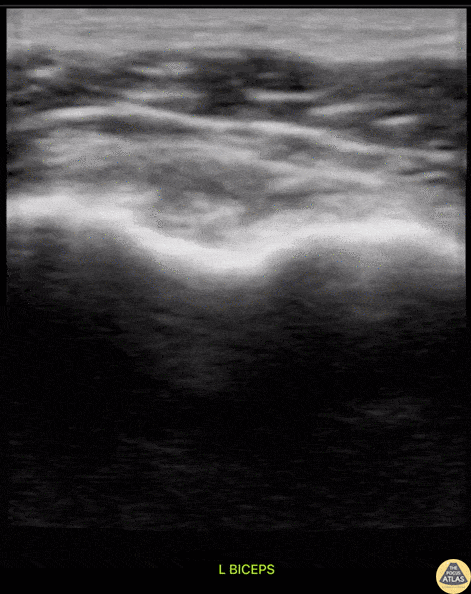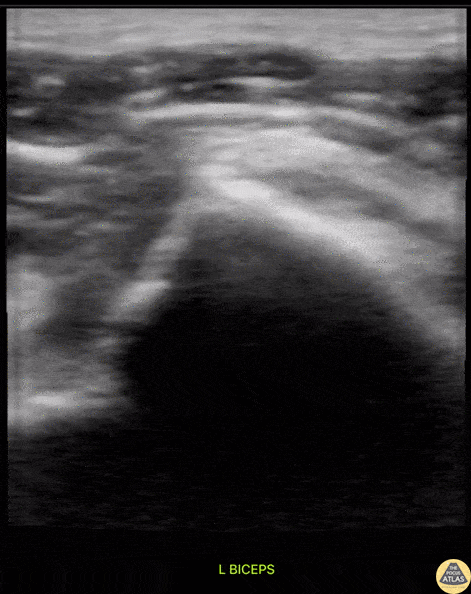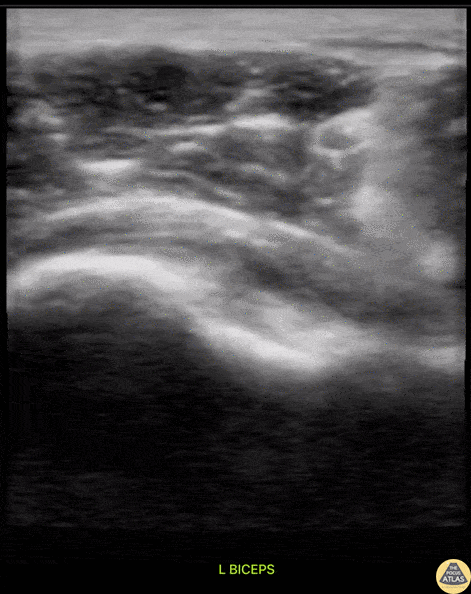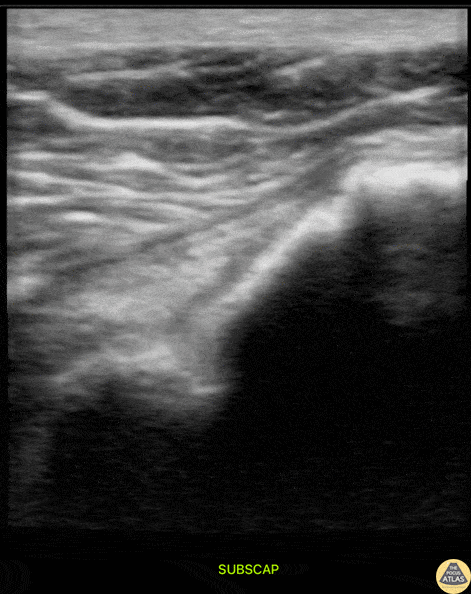
Subscapularis Tendon Tear
A middle aged male presented to the ED with shoulder pain after skiing crash. POCUS of the shoulder was performed, showing a subscapularis tendon tear. Here, the proximal humerus is shown in short axis, with the linear probe placed in transverse orientation at the anterior aspect of the shoulder. The biceps tendon is seen in the biceps groove, between the greater tuberosity (lateral or right of screen) and lesser tuberosity (medial or left of screen). The patient is asked to externally rotate the arm, which brings the subscapularis tendon into view, and a hypoechoic, thickened area is seen, indicating a tendon tear.
Dr. Matthew Riscinti
Denver Health Medical Center
Nearly Complete Achilles Tear
Healthy male in late-20s trying to do a backflip off a diving board. Still was able to plantarflex (very weak and with significant pain).
Submitted by Dr. Elias Jaffa
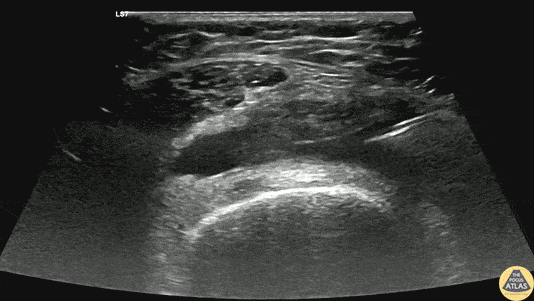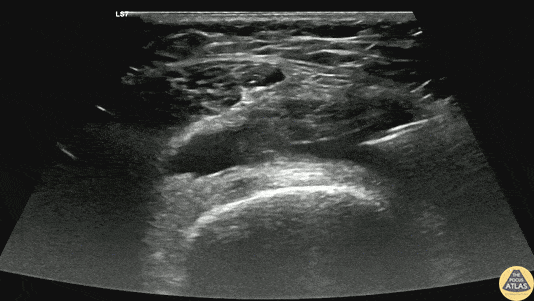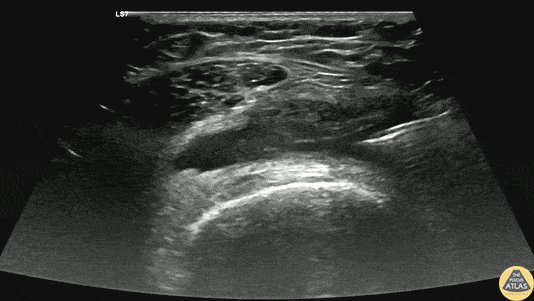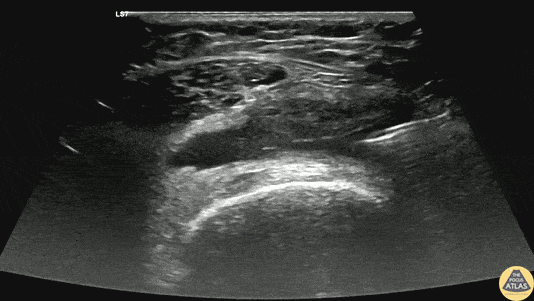
Arthrocentesis of Knee Effusion
40s F with prior history of contralateral trimalleolar ankle fracture s/p multiple surgeries presents 1 month of knee swelling and pain after starting levofloxacin. The symptomatic knee appeared swollen without warmth or erythema, ROM was preserved, and the patient was ambulatory. Point of care US demonstrated an effusion around the knee, so diagnostic and therapeutic arthrocentesis was performed as shown here. The linear probe was used in a transverse orientation just superior to the patella to view the suprapatellar bursa just deep to the quadriceps tendon. Using sterile technique, a needle was advanced under real-time, in-plane US guidance to enter the bursa and aspirate synovial fluid. Ultimately the patient did not have septic arthritis and was discharged with a compressive knee wrap with a plan for orthopedic surgery follow up.
Dr. Caleb Knight, PGY-2
Denver Health Residency in Emergency Medicine
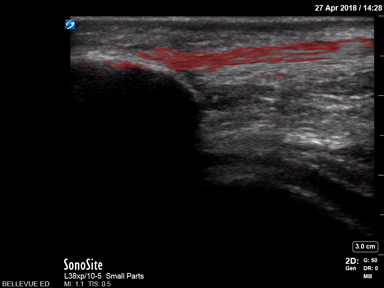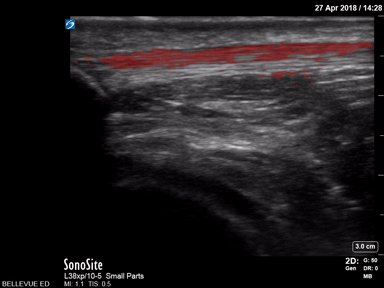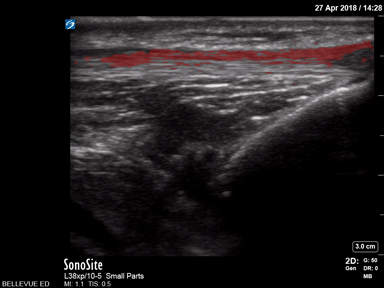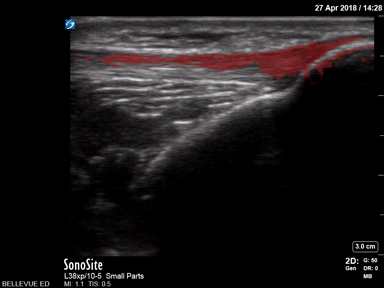
Patellar Tendon - Colorized
Patellar Tendon
Red: Patellar tendon
Images: Dr. Lindsay Davis, Dr. Hannah Kopinski. Image Editing: Michael Amador and Dr. Matthew Riscinti
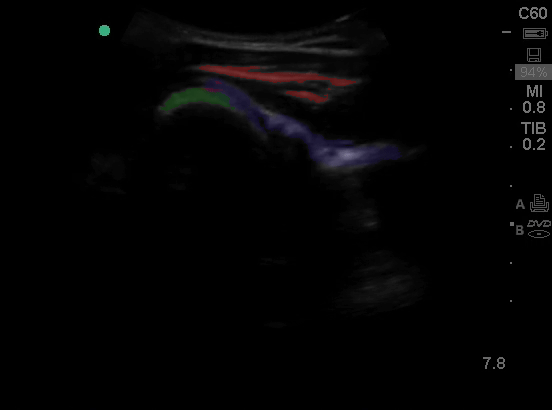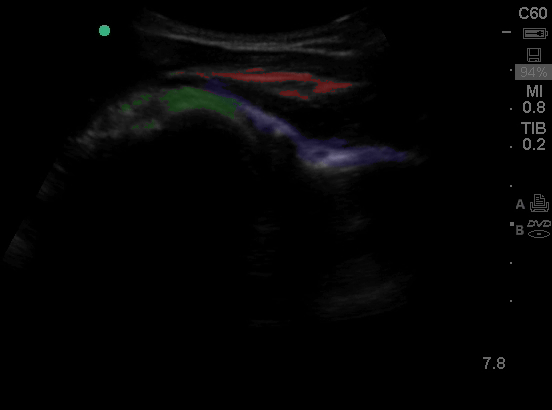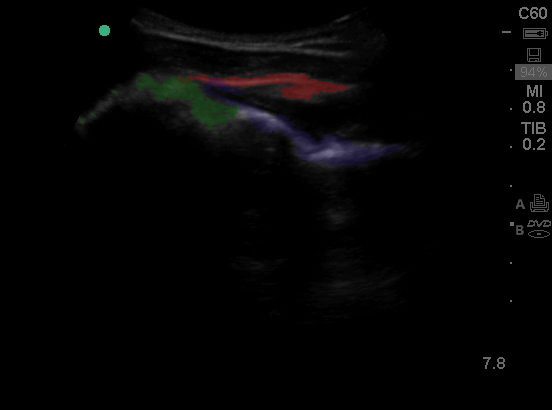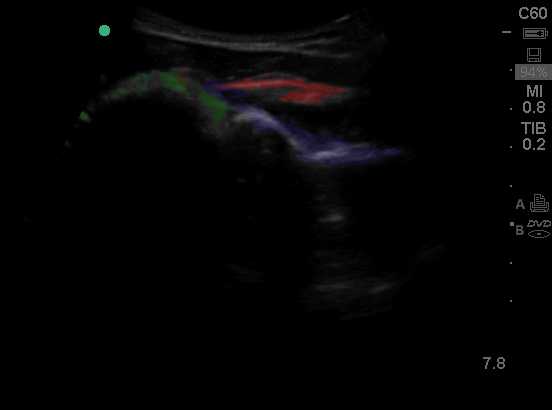
Shoulder - Colorized
Shoulder
Green: Humeral head, Blue: Infraspinatus, Red: Rotator Cuff
Images: Dr. Lindsay Davis, Dr. Hannah Kopinski. Image Editing: Michael Amador and Dr. Matthew Riscinti
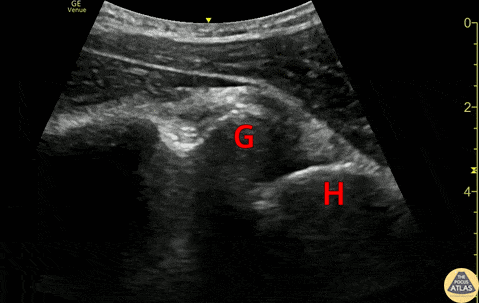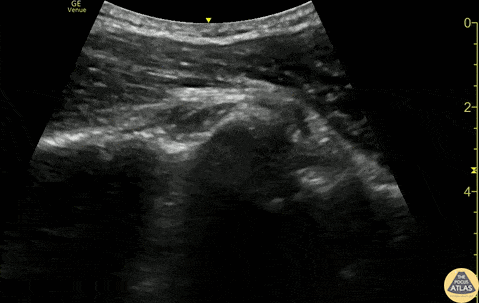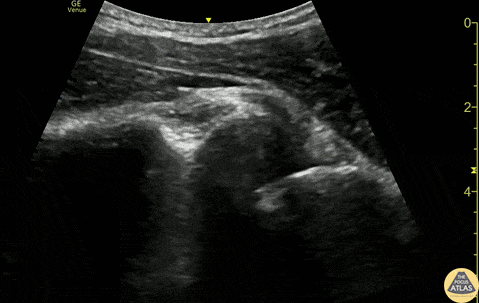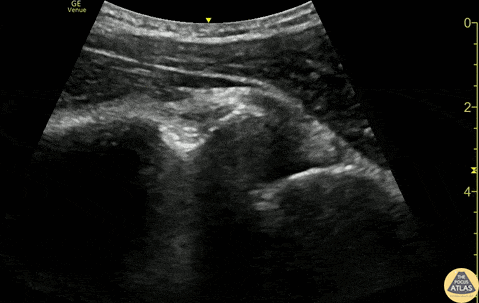
Anterior Shoulder Dislocation
20s M with history of recurrent shoulder dislocations presented with pain and a deformity after being transferred from an urgent care after multiple failed attempts at closed reduction. POCUS confirmed dislocation at the bedside. The clip shown here is a posterior view of glenohumeral joint, illustrating the anterior displacement of the humeral head (H) in relation to the glenoid rim (G). A humeral head which is more than 1 to 1.5 cm anterior to the glenoid rim should be concerning for anterior dislocation (PMID 32111508). In this case, it is easy to see that the humeral head is almost 2cm anterior to the glenoid rim.
After placement of an US guided interscalene nerve block, this patient was able to be reduced without difficulty.
Dr. Anthony Rodriguez, PGY1
Denver Health Residency in Emergency Medicine
Dr. Nimish Bhatt, Fellow
Denver Health Ultrasound Fellowship
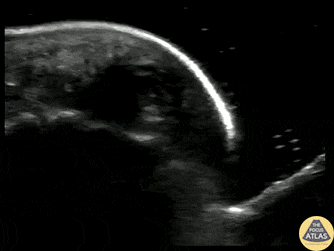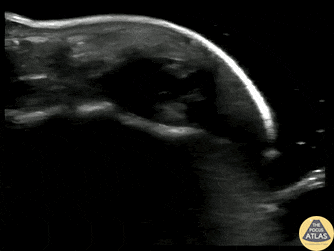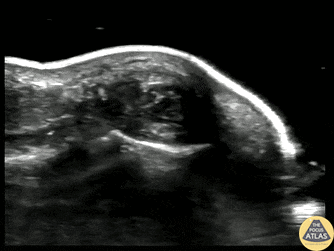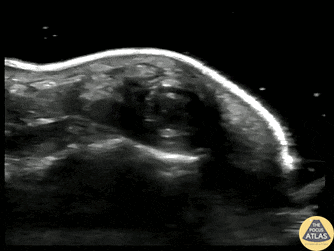
Fingertip Felon
40s M who works as a carpenter presented with finger pain and swelling 10 days after he injured his finger when a heavy object fell on it. He sought medical care on the day of the injury and had radiographs which were negative for fracture, and there was no visible wound initially. On this visit, he was noted to have focal erythema and edema to his distal phalanx. POCUS was performed to evaluate for abscess and flexor tenosynovitis. To improve visualization, a water bath was used. The finger tip is shown here, with a small circumscribed area of hypoechoic fluid at the distal phalanx, indicative of a felon. Incision and drainage was performed and the patient was discharged on oral antibiotics and with plan for PCP follow up.
Nayun Lee, MS3
Dr. Molly Thiessen
Denver Health Medical Center
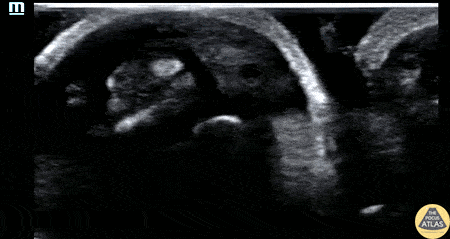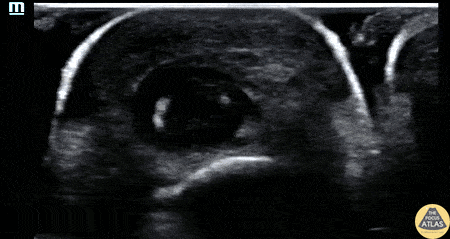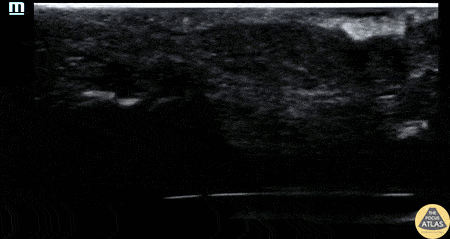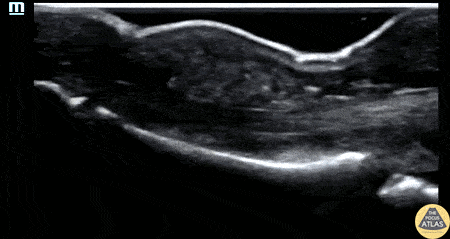
Flexor Tenosynovitis
30s M with PMH IVDU presented with worsening swelling over his middle finger and hand. His clinical exam was concerning for flexor tenosynovitis, so a water bath POCUS was performed to evaluate his flexor tendon sheath. The study is shown here, where the middle finger is shown first in short axis and then in long axis. The flexor tendon is seen as the relatively hyperechoic structure just superficial to the bony cortex, and has a fibrillar appearance when seen in long axis. This clip demonstrates anechoic fluid within the sheath surrounding the flexor tendon, which in this clinical context is diagnostic of flexor tenosynovitis, a surgical emergency. This patient was given IV antibiotics and was taken to the operating room for I&D and washout of his hand.
Dr. Brigit Noon, PGY3
Denver Health Residency in Emergency Medicine

Achilles Tendon Rupture
20s M presented with calf/heel pain after skateboarding, found to have a positive Thompson test. POCUS confirmed a full thickness tear of the achilles tendon. The patient was splinted and referred to orthopedic surgery for repair.
Alexandrea Netto PA, Denver Health and Hospital Authority
Lois Isaksen MD, Attending Physician, Denver Health Residency in Emergency Medicine



















































































