Soft Tissue
Soft tissue ultrasound, abscess, abscesses, infections, cellulitis, emphysema, tumors, and glands all POCUS point of care ultrasound.

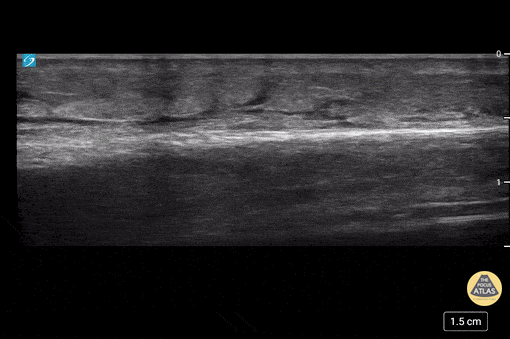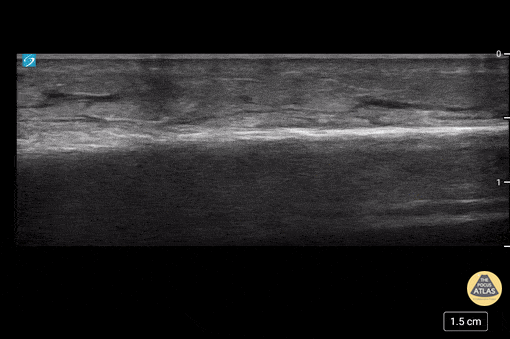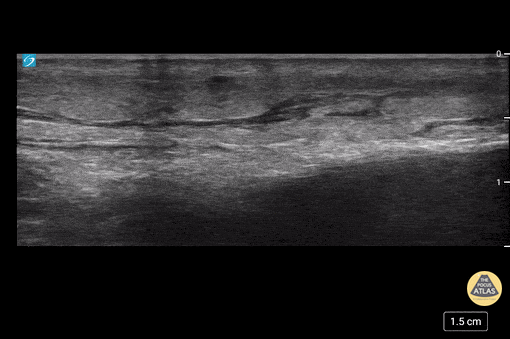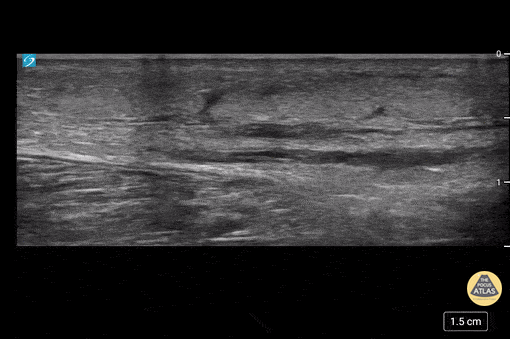
Cobblestoning in Cellulitis
This is an example of “cobblestoning”. This patient initially presented to the emergency department with lower anterior leg pain, especially with walking. Physical exam revealed minor erythema but also exquisite tenderness to palpation as well as with plantar flexion. Although cellulitis is clinically diagnosed, point of care ultrasound can be used to support it. The cobblestone presence is a result of edema between subcutaneous fat.
Dr. Carlo Zamora, DO, PGY-1
Riverside Regional Medical Center Emergency Medicine Residency (Newport News, VA)
Foreign Body - Wooden Cocktail Stick
35 year female presented to the Emergncy Department with a self harm retained foreign body in the left forearm. The foreign body was a wooden cocktail stick not seen on x-ray. POCUS easily identified the cocktail stick by it's acoustic shadowing which allowed removal under local anaesthetic. Repeat POCUS scan showed no other foreign bodies.
Dr Pete Hulme @Dr_Pete_EmMed
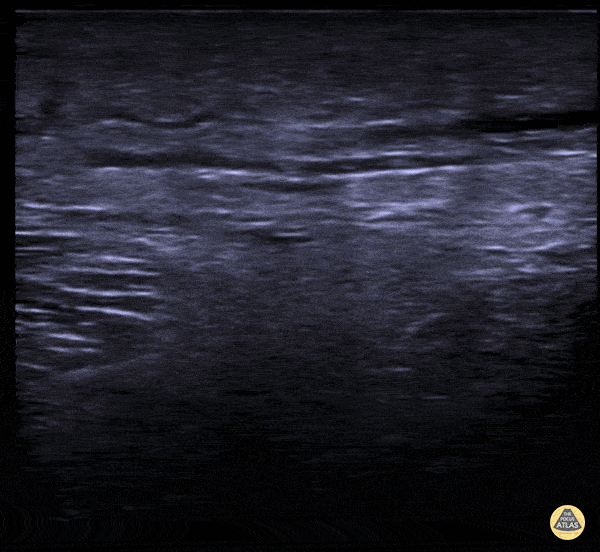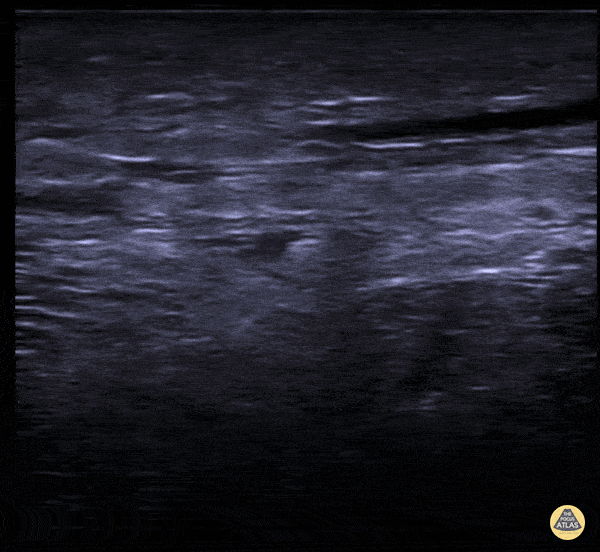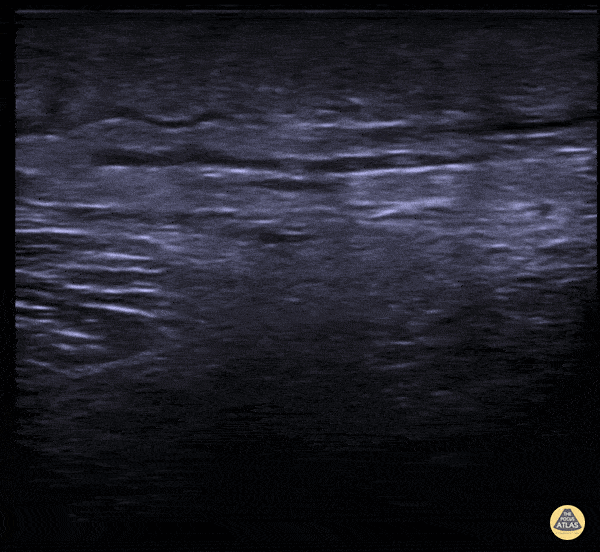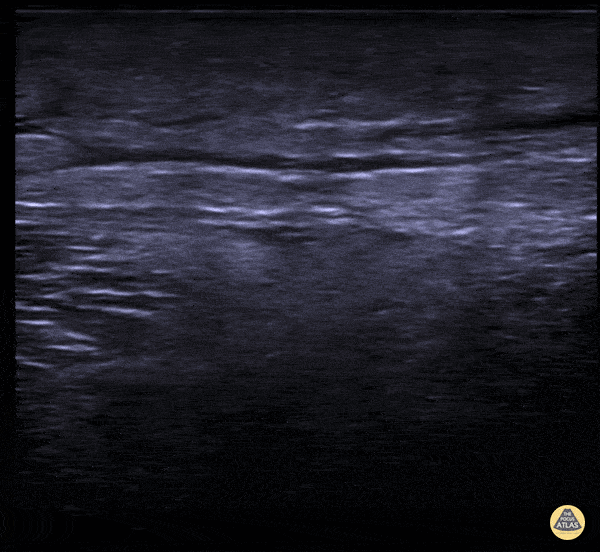
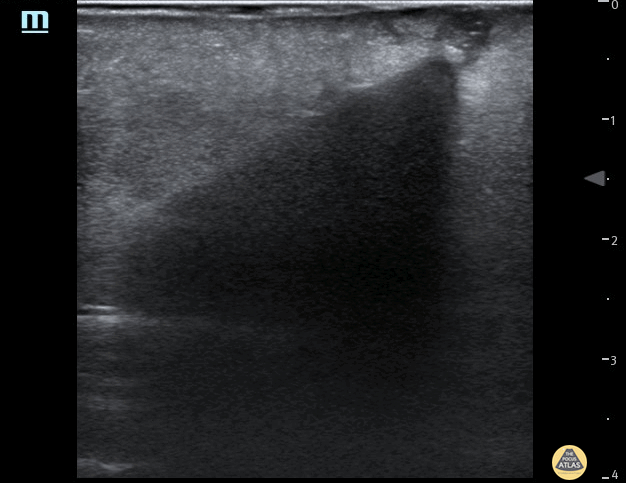
Subcutaneous Air in Necrotizing Fasciitis
A middle aged male presented to the ED for left leg pain after sustaining puncture wound to the foot 4 hours prior arrival. The ultrasound image demonstrates free air causing dirty shadowing seen deep to the fascial plane obscuring the normal muscle architecture in the middle of the screen.
Nicmarie Maldonado, MD PGY-2; Eddie G. Rodriguez, MD; Miguel Agrait, MD; Michelle Surillo, MD - Division of Emergency Ultrasound, St. Luke's Medical Center/PHSU, Ponce, PR
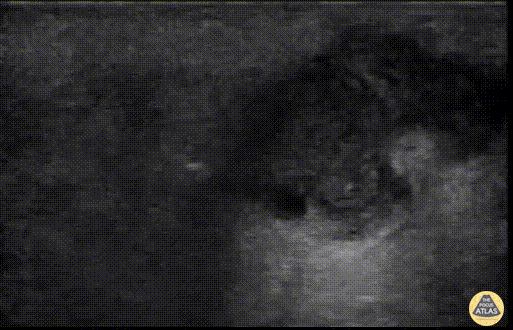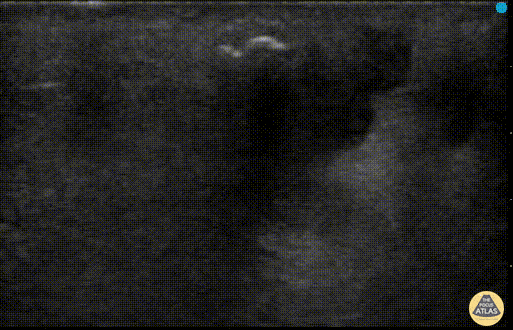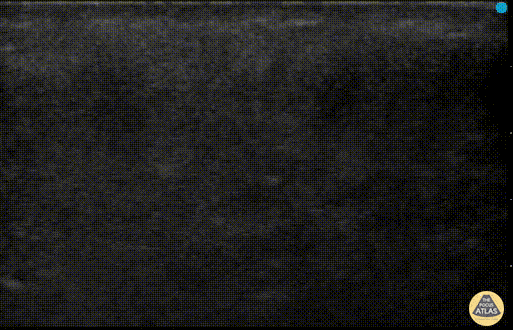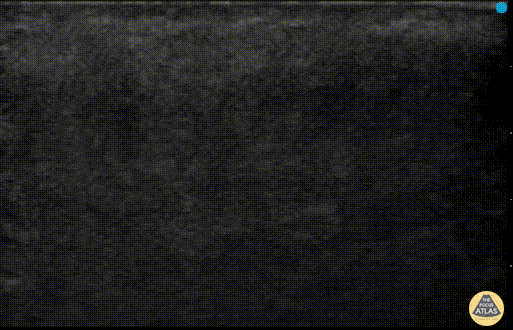
Soft Tissue Air in Necrotizing Fasciitis
POCUS can help distinguish simple abscess from necrotizing fasciitis. “Dirty air shadowing” visualized in the clip suggests a necrotizing soft tissue infection.
Dr. Farnam Kazi Ultrasound Faculty; Dr. Dimitri Livshits Ultrasound Fellow; Dr. Jane Belyavskaya Ultrasound Fellow (All at Kings County Hospital/SUNY Downstate)
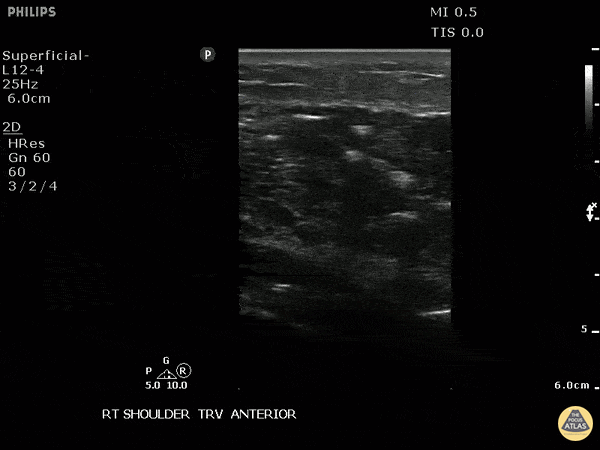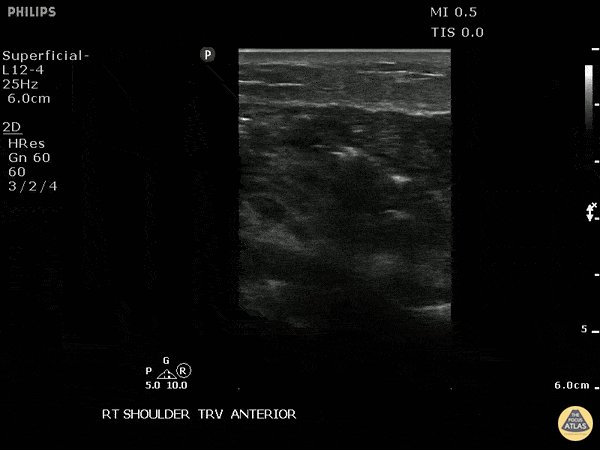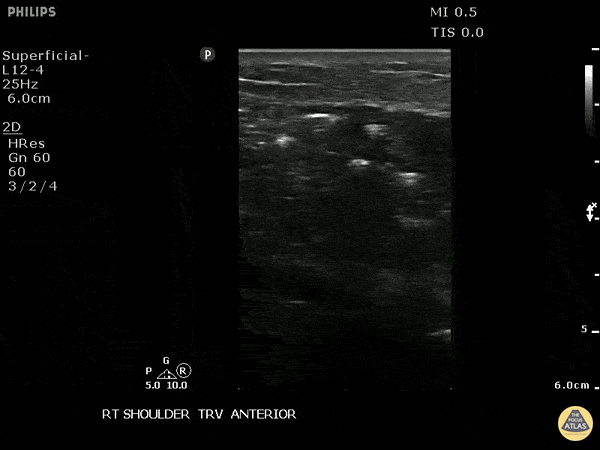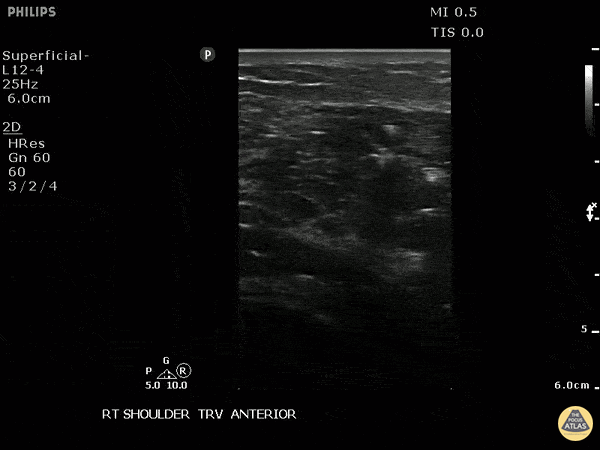
Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection Of The Shoulder
This is a transverse view of the anterior shoulder of a patient who presented to the emergency department with a fever and shoulder pain causing limited mobility. Looking closer, we can observe hyperechoic densities caused by air within the tissues, otherwise no signs of septic joint or bursitis.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
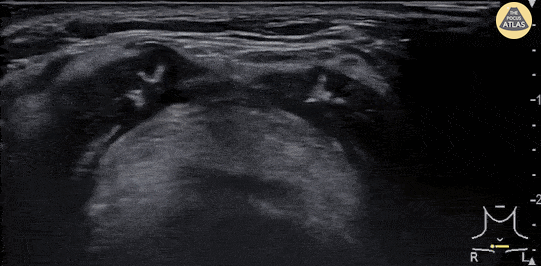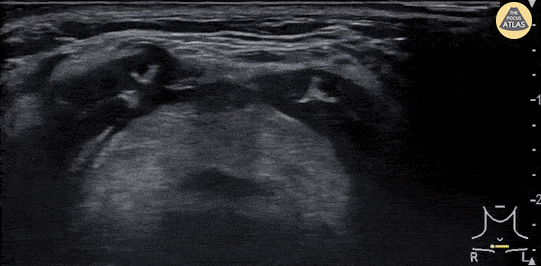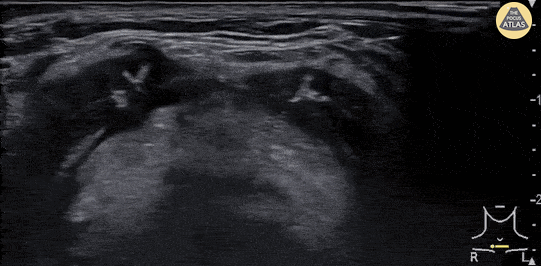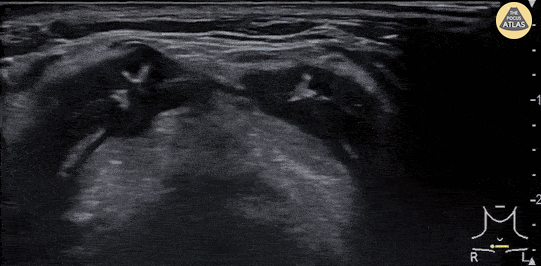
Epiglottitis
A 30 year-old female presented to the emergency department with high fever, severe sore throat and shortness of breath. POCUS of the neck was performed and revealed a swollen epiglottis, especially in the right side. Further X-ray of the neck revealed thumb sign and nasopharyngoscopy showed epiglottitis with swelling of right tongue base and arytenoid.
Although the normal range of the epiglottis thickness measured by ultrasound varied from 2 to 3 mm in previous studies, significant swelling and thickening of the epiglottis on ultrasound may indicate epiglottitis.
Chi-Hsin Chen
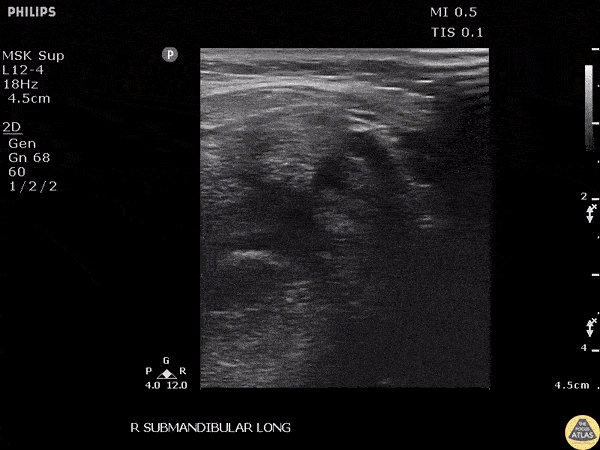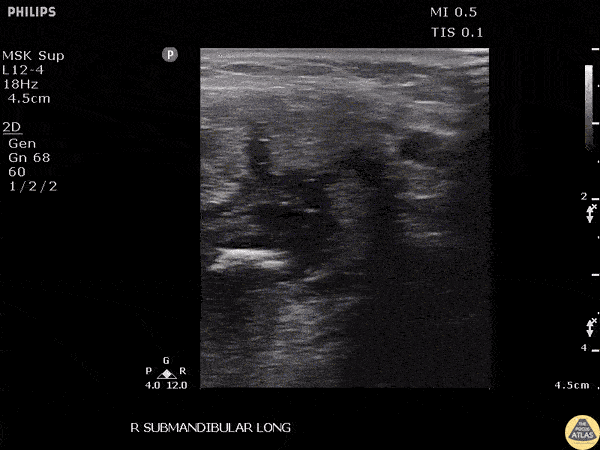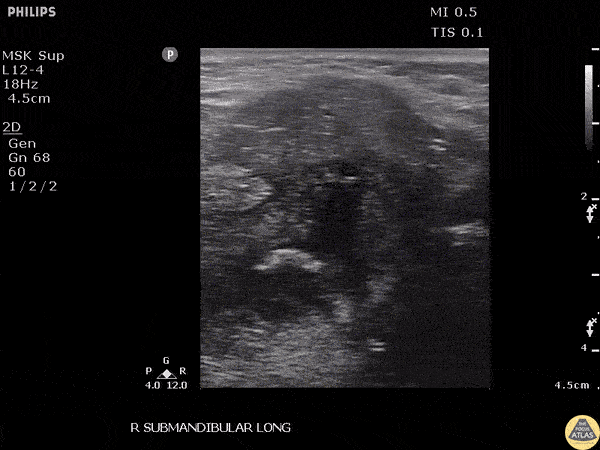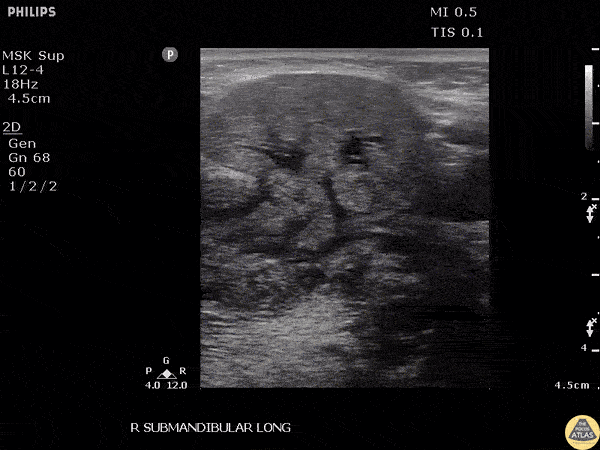
Submandibular Sialolithiasis
A male presented to the ED with submandibular pain and swelling. Ultrasound revealed a 0.942 cm stone within the submandibular gland.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
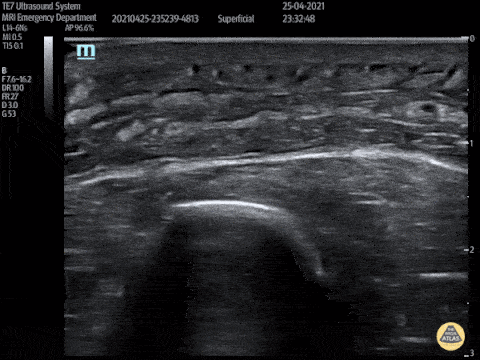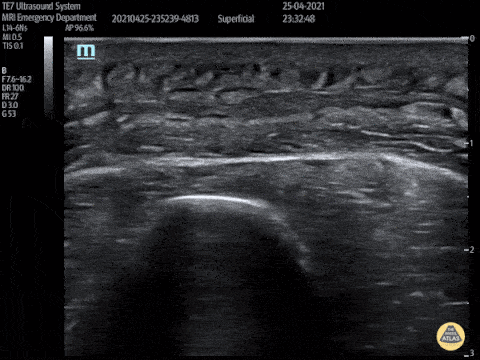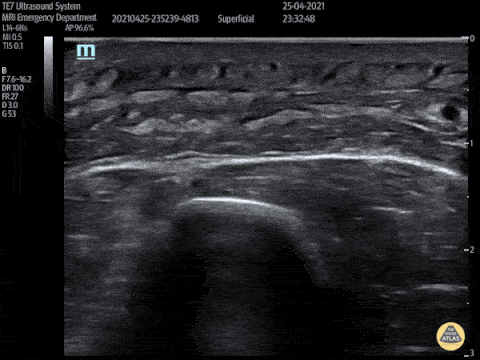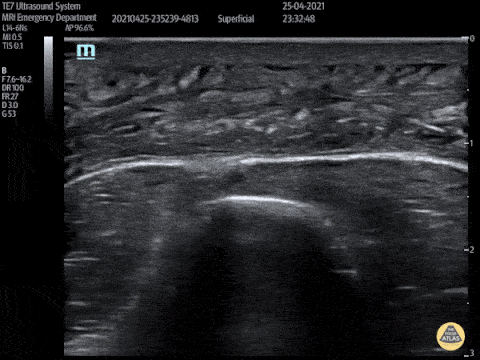
Post Stab Wound Cellulitis
This video shows a young man who presented 3 days after being stabbed to the arm. His wound had been sutured at the time but he had represented with erythema, pain and swelling to his forearm. POCUS showed cobblestoning consisent with cellulitis and excluded abscess and a foreign body.
Peter Hulme
Twitter: @Dr_Pete_EmMed
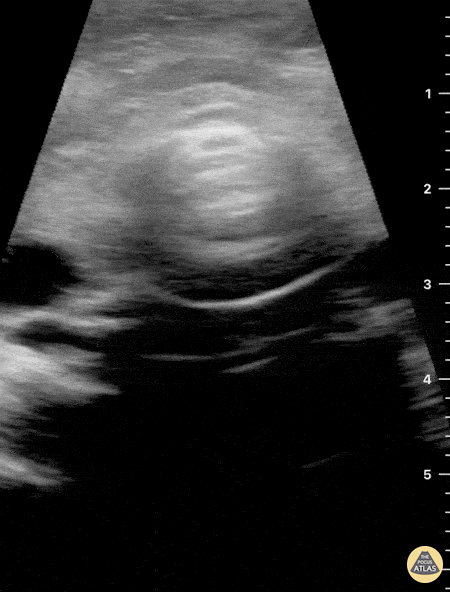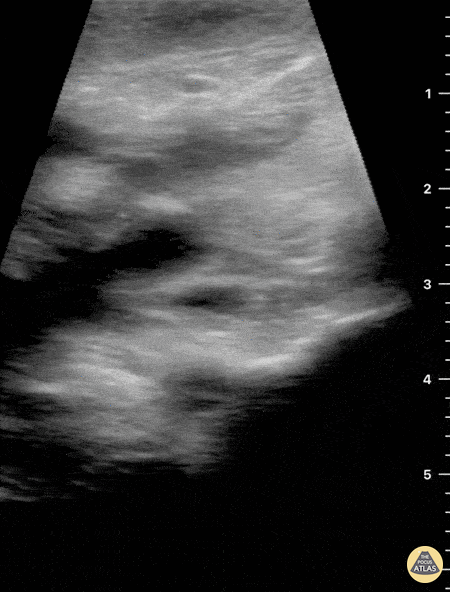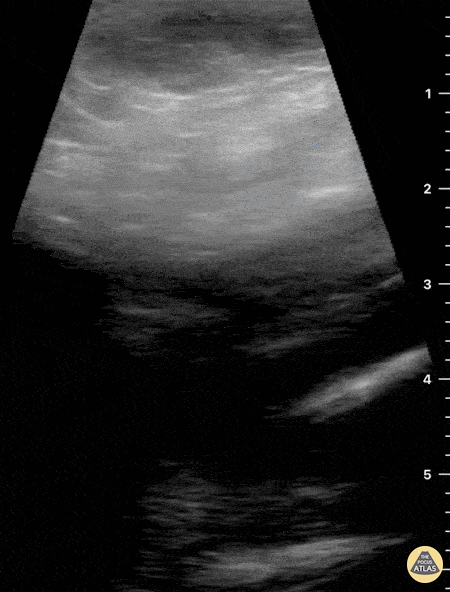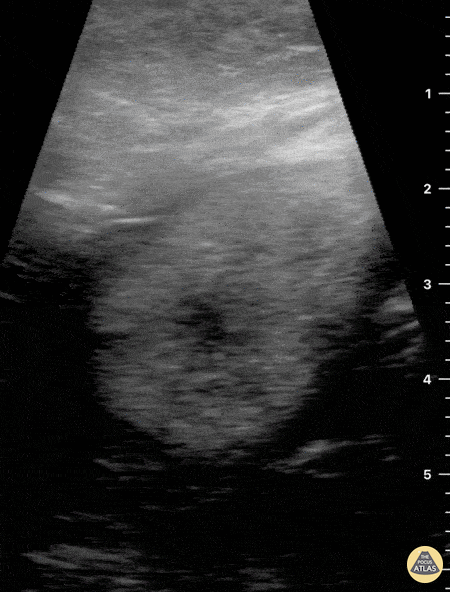
Not your classic blunt neck trauma: Case
12 hours after having a fall in her bathroom, an otherwise healthy 54 y/o female presented to the ED complaining of neck pain, dysphonia and difficult swallowing. Physical examination revealed hypertension, a HR of 109 bpm (sinus tachycardia) and 98% environmental O2Sat. She had no trouble breathing or speaking, although a coarse tone of voice was evident. Her skin revealed a mild linear abrasion with local upper right lateral neck swelling. A firm, tender submandibular mass was palpable.
Neck ultrasound seen here revealed the trachea in a central position and the carotid arteries with no obvious signs of injury. Jugular vasculature was also studied and showed no adjacent fluid collections (not visualized in this clip).
Sliding the probe to the right submandibular region revealed a well defined hypoechoic structure compatible with an enlarged salivary gland.
Dr. Felipe Urriola & Dra. Daniela Gallardo
Emergency Unit, Puerto Aysen Hospital. Chilean Patagonia
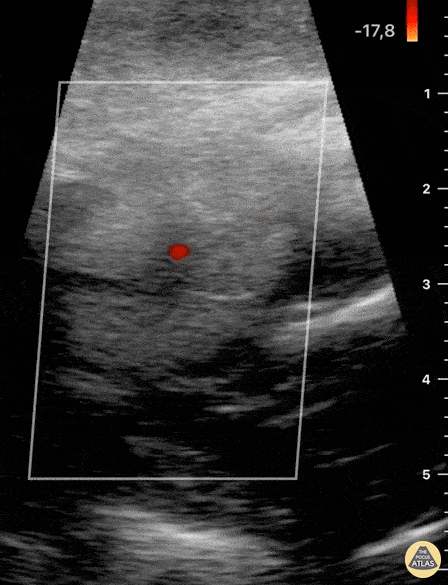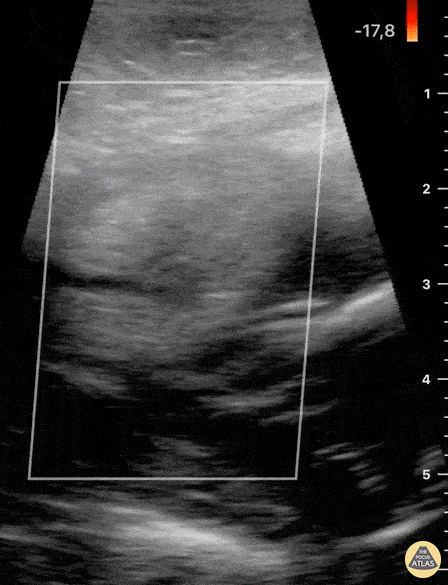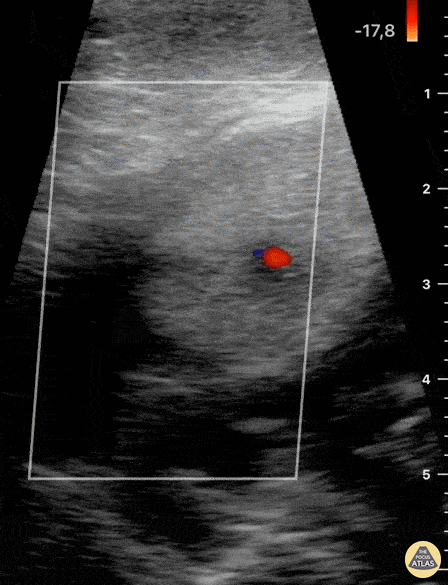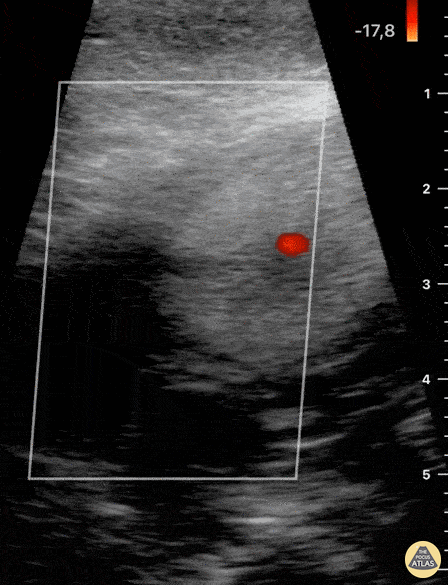
Blunt Neck Trauma (doppler)
Not your classic Blunt Neck Trauma: Doppler
Color doppler shows an absence of flow in the deeper anechoic level and apparent indemnity in the glands vasculature.
After the initial assessment, the patient remained hypertensive and tachycardia with HR of 120 bpm. Although there was no obvious worsening of airway status and no respiratory symptoms, the patient was referred to the regional centre for angio CT of the neck.
This modality confirmed a right submandibular gland fragmentation with significant adjacent edema extending to the airway. There was airway midline deviation to the left and notable calibre reduction at the level of the hypopharynx.
Dr. Felipe Urriola & Dra. Daniela Gallardo
Emergency Unit, Puerto Aysen Hospital. Chilean Patagonia
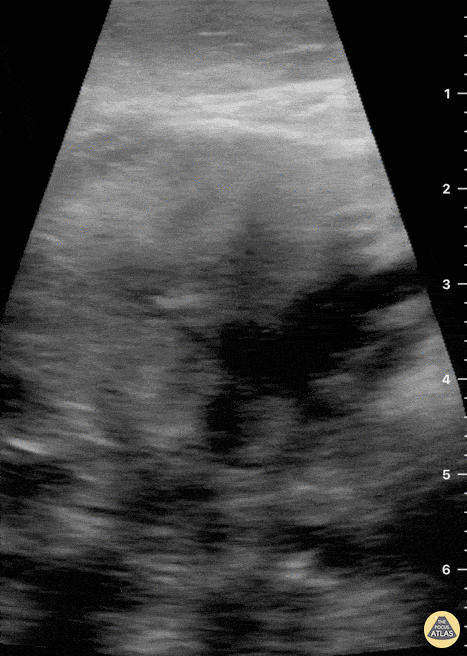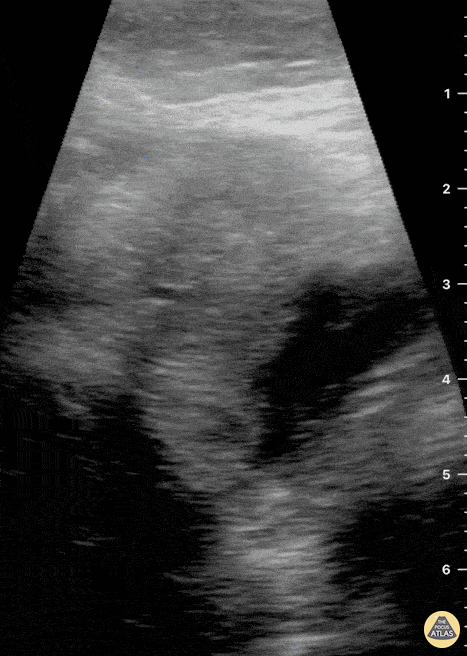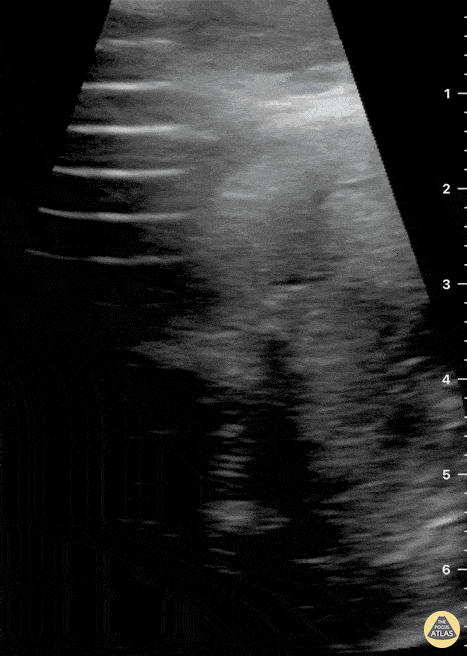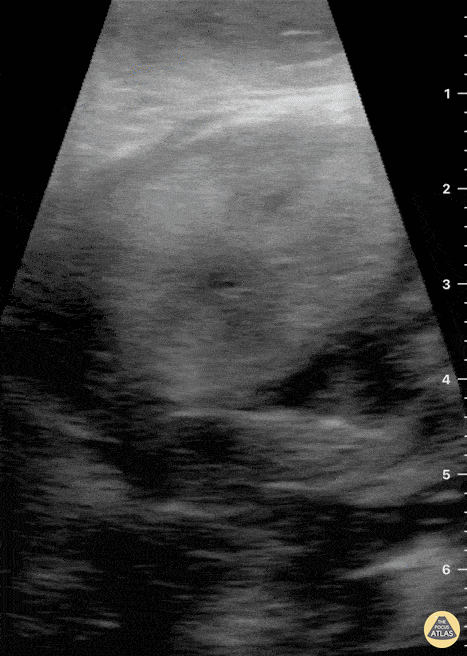
Submandibular Gland Fragmentation
Not your classic Blunt Neck Trauma: Submandibular Gland Fragmentation
A closer look to the right submandibular gland reveals a deep end with heterogeneous borders. There is also significant edema and free fluid invading deeper structures.
Dr. Felipe Urriola & Dra. Daniela Gallardo.
Emergency Unit, Puerto Aysen Hospital. Chilean Patagonia
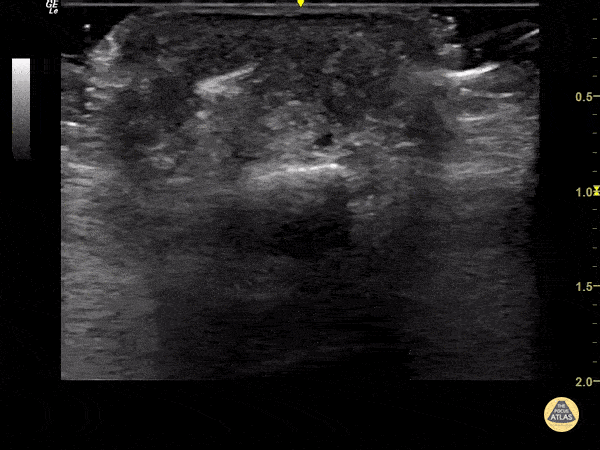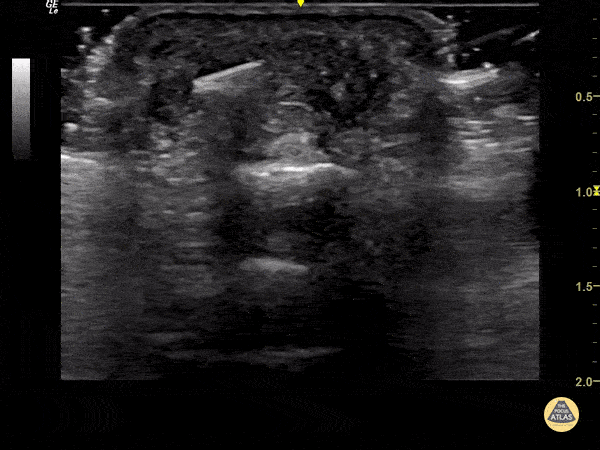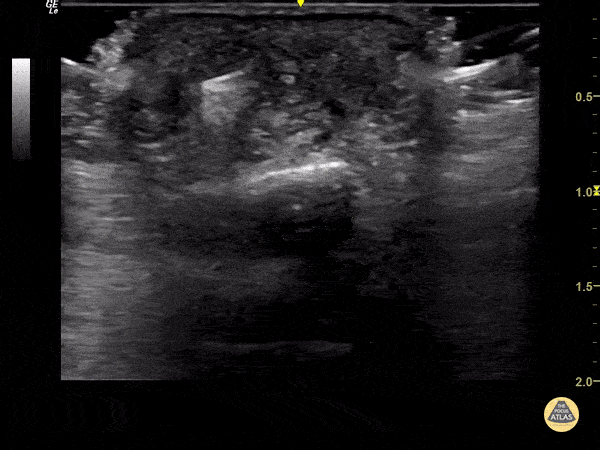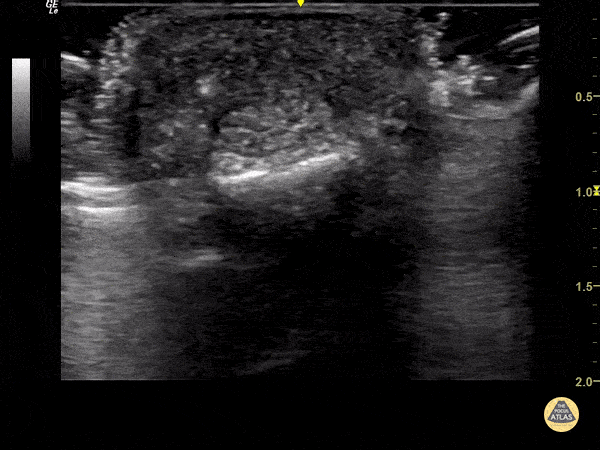
Foreign Body Flexor Tendon Sheath
65 year old female with pain and swelling over 4th phalanx, no history of trauma. Hyperechoic density located above flexor tendon sheath. Patient sent to Ortho for surgical exploration.
Dr. Magner
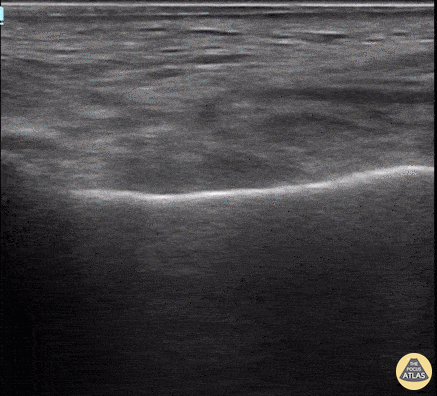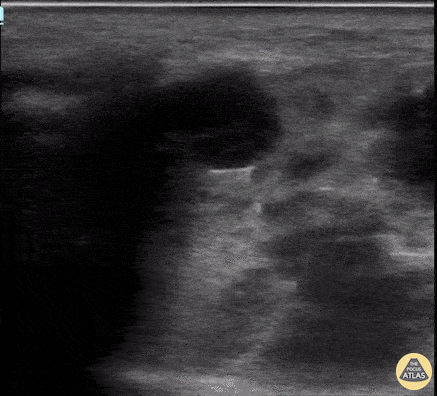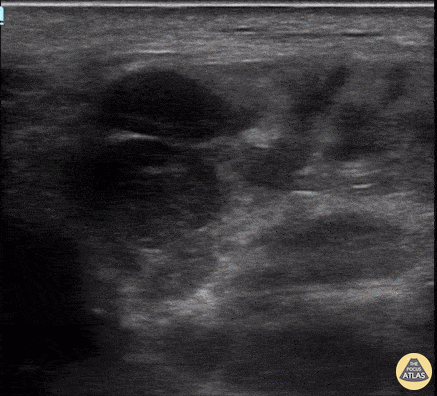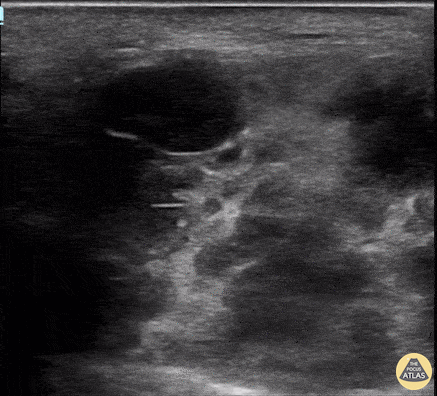
Parotid Gland Malignancy
A female patient with a history of Non-Hodgkin and Diffuse B-Cell Lymphoma presented for evaluation of subacute facial swelling. Physical exam revealed edema over the parotid gland without associated tenderness to palpation.
POCUS seen here demonstrated hypoechoic and septated cystic lesions within the parotid gland, concerning for malignancy. This finding prompted further evaluation with CT that confirmed recurrence of malignancy.
Lydia Mansour, DO, PGY2
Central Michigan University Emergency Medicine Resident
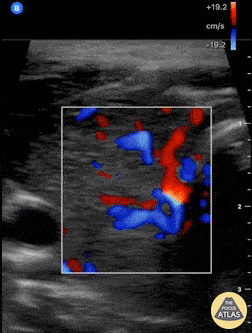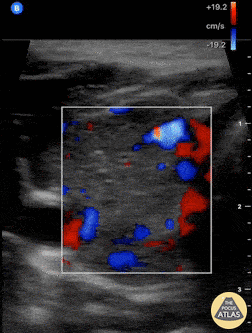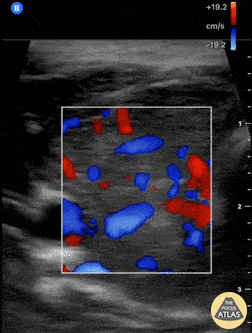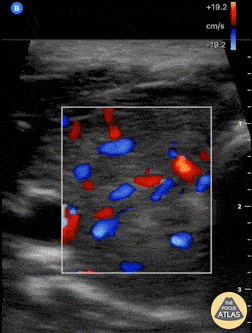
Thyroid Inferno
A patient with impending thyroid storm (BWPS score 25), an undetectable TSH level, and a T4- 4.2, had diffusely enlarged goiter. POCUS as shown here revealed hypervascular “thyroid inferno” that occurs in Graves disease, less commonly Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Shane Solger
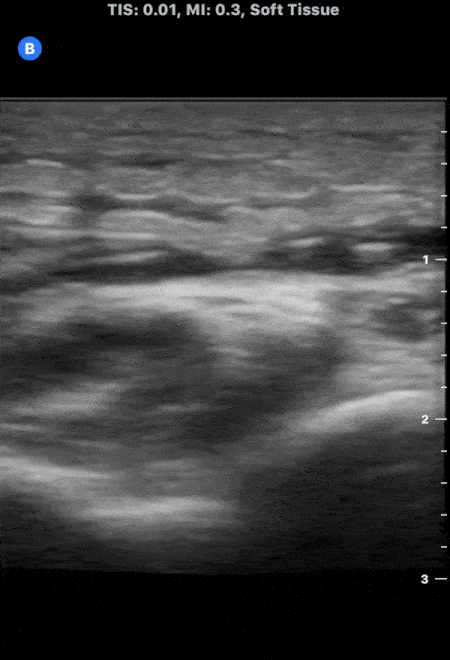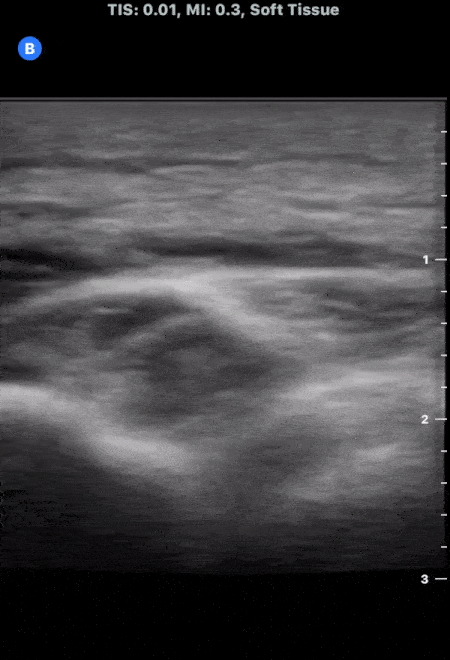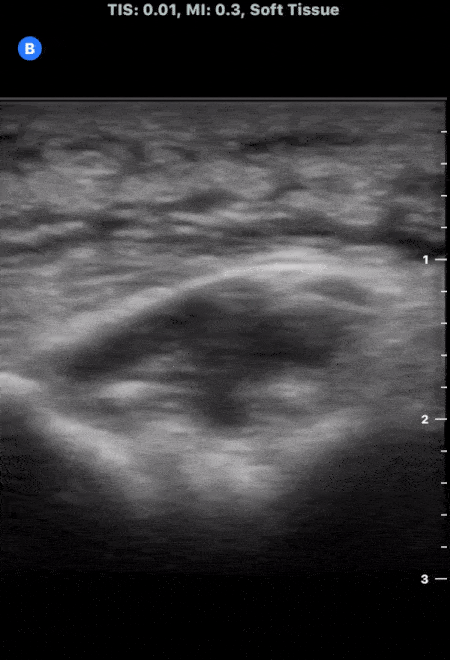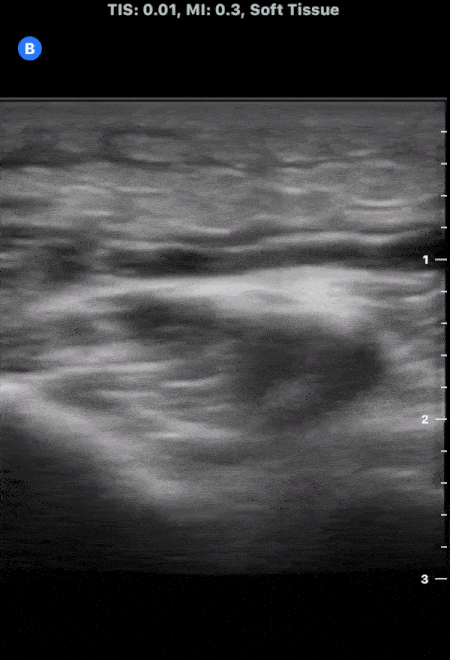
Cobblestoning in Cellulitis
This image demonstrates the common finding of cobblestoning seen in cellulitis. Note the anechoic areas surrounding islands of subcutaneous tissue.
Michael Macias, MD

Large Soft Tissue Abscess
This is an example of a large soft tissue abscess. Note the presence of a large well circumscribed fluid collection taking up the screen. Particulate can be seen throughout the fluid collection signifying increased density from purulent material.
Michael Macias, MD
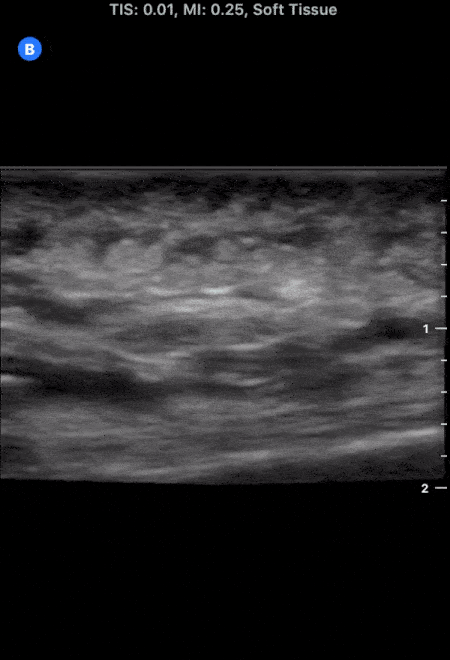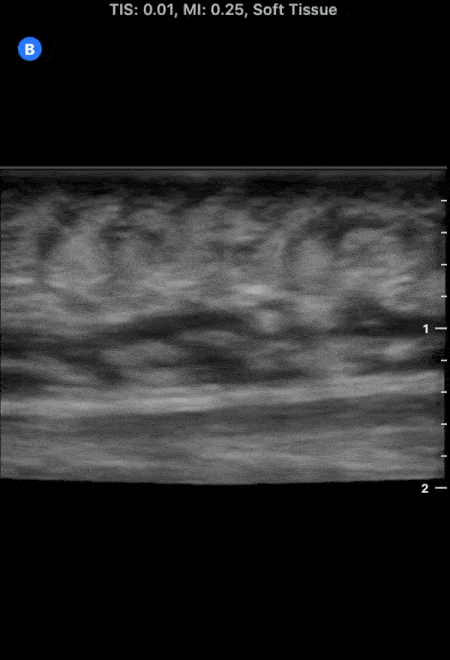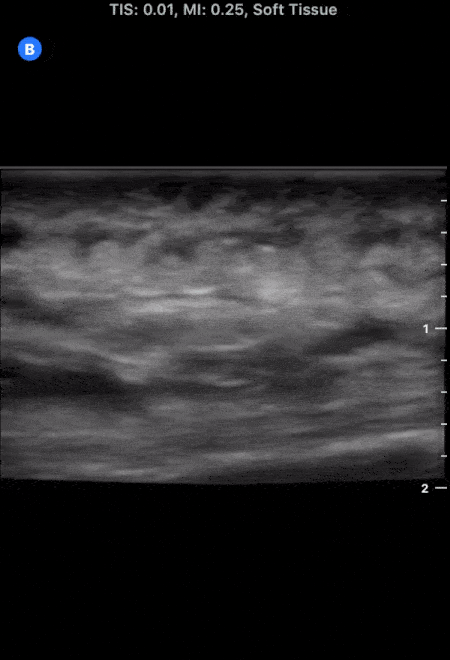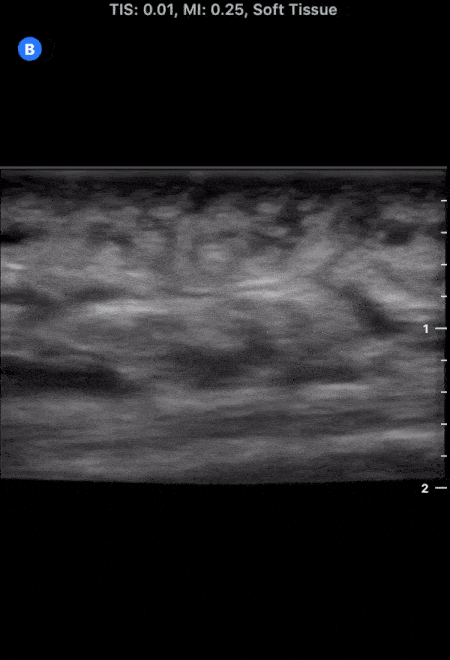
More Cobblestoning in Cellulitis
This image demonstrates the common finding of cobblestoning seen in cellulitis. Note the anechoic areas surrounding islands of subcutaneous tissue.
Michael Macias, MD
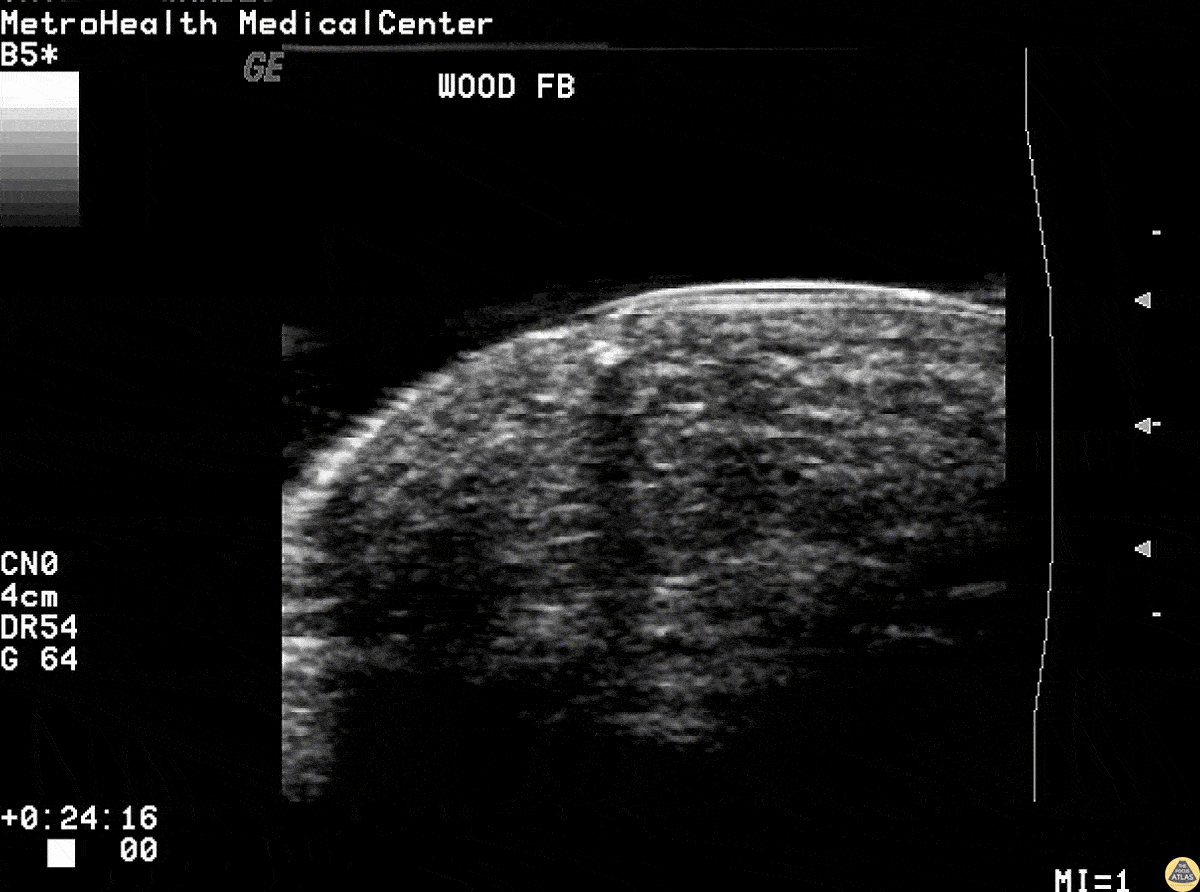
Wood Splinter Foreign Body
Wooden splinter in the fingertip of a patient. Ultrasound revealed the foreign body with posterior acoustic shadowing present.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
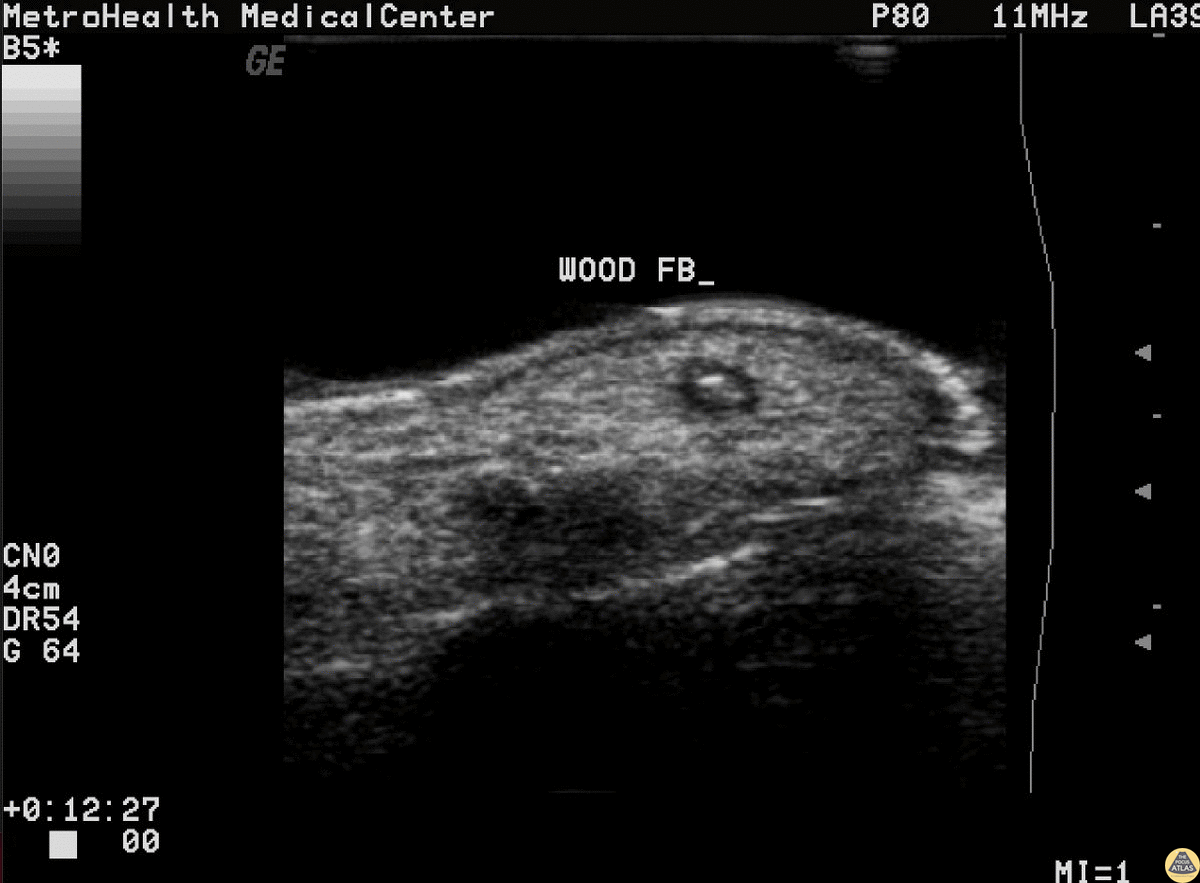
Wooden Splinter
Wooden splinter located in the distal fingertip. Ultrasound shows a halo indicative of edema surrounding the foreign body.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
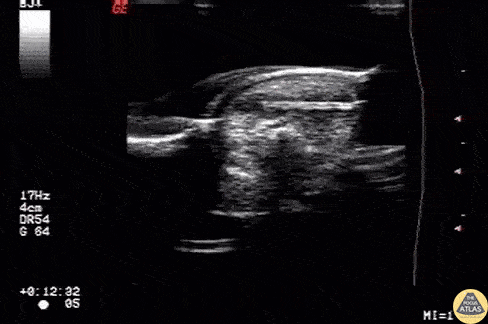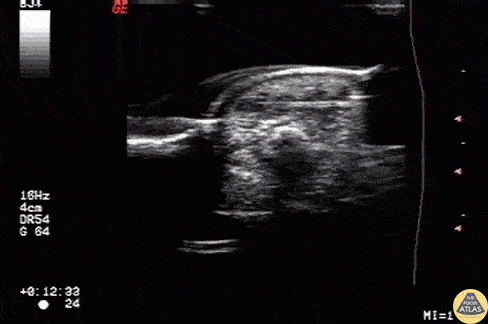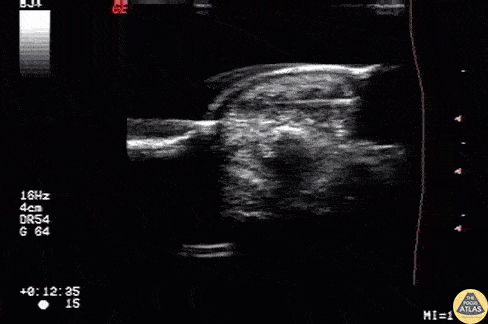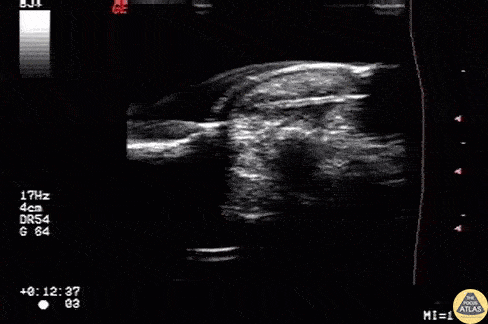
Foreign Body: Wooden Splinter
Wooden splinter located in the fingertip originally diagnosed as felon.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
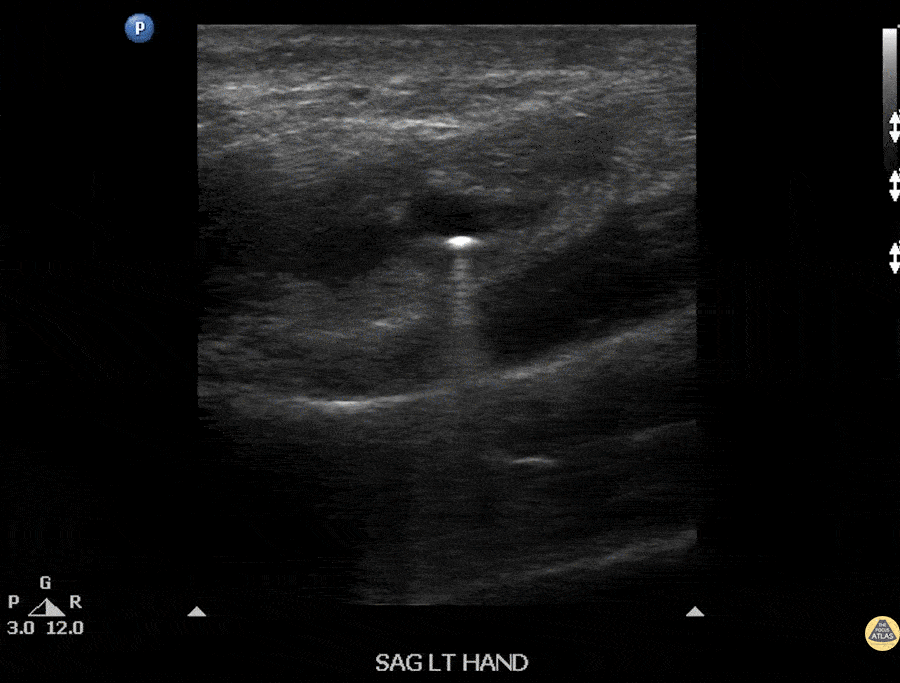
Foreign Body: BB within Hand
Ultrasound image of a BB lodged within a patient’s hand. Note the comet-tail artifact often seen deep to many solid structures.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
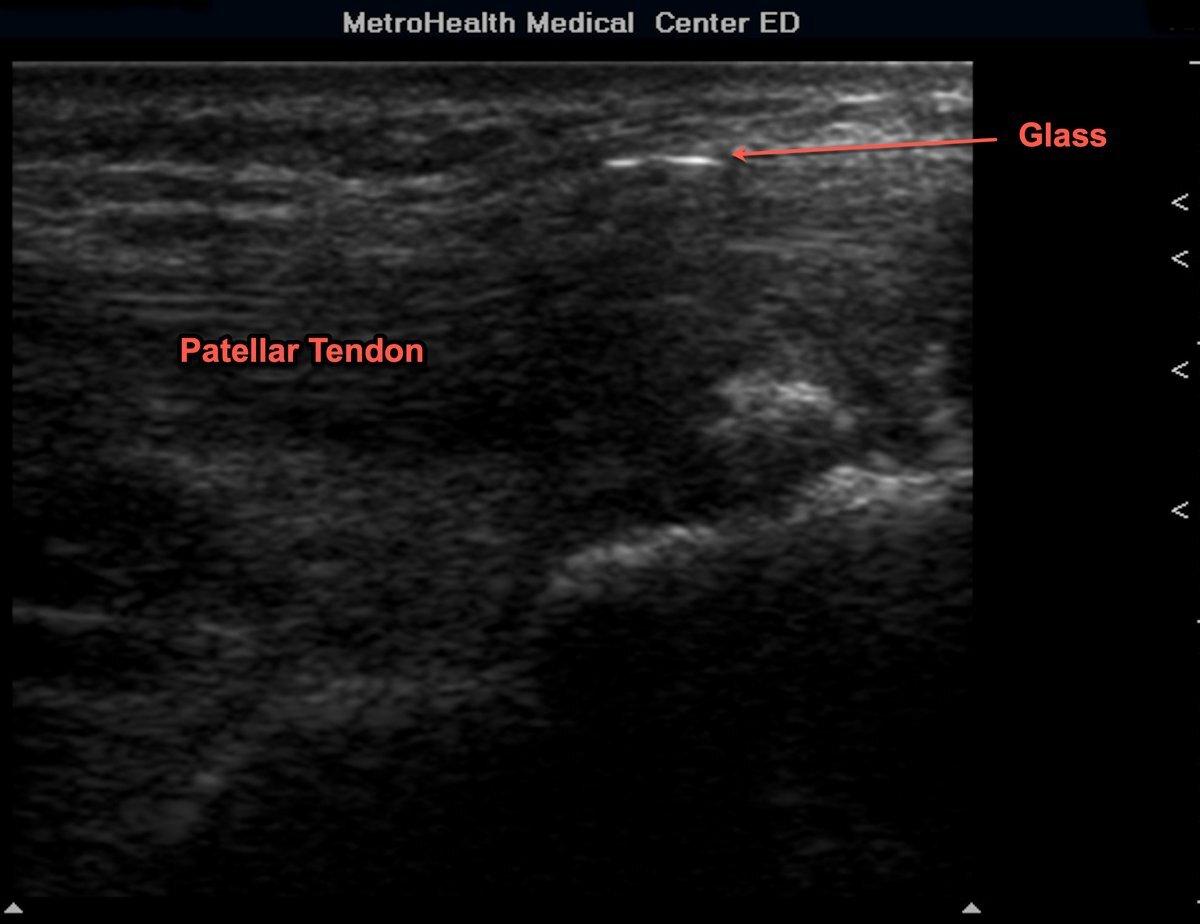
Foreign Body: Glass in the Patellar Tendon
A shard of glass located superficially within the patellar tendon.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
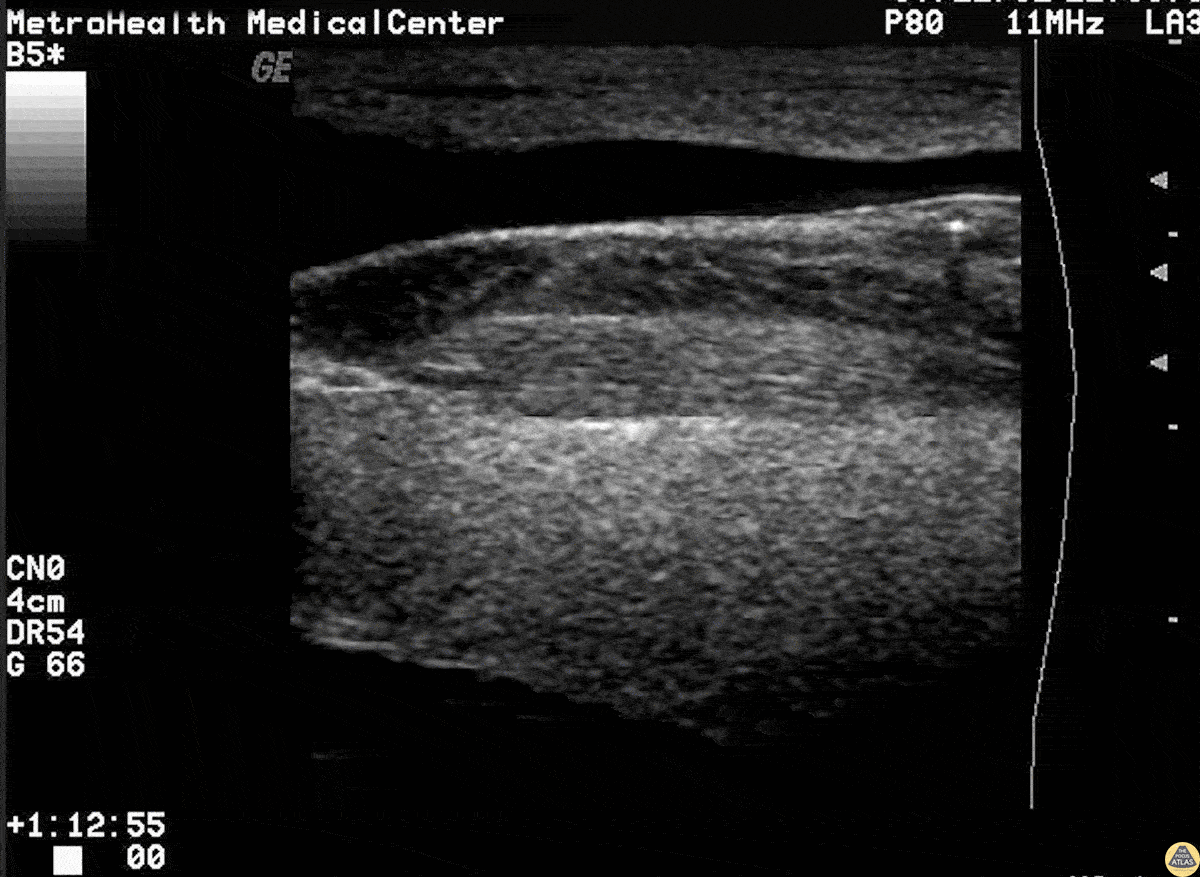
Broken Needle
This is a short axis view of a needle that is broken off just posterior to the external jugular. Note the posterior acoustic shadowing.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
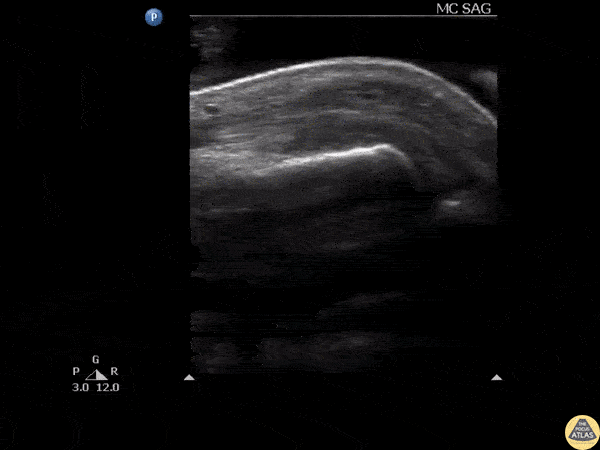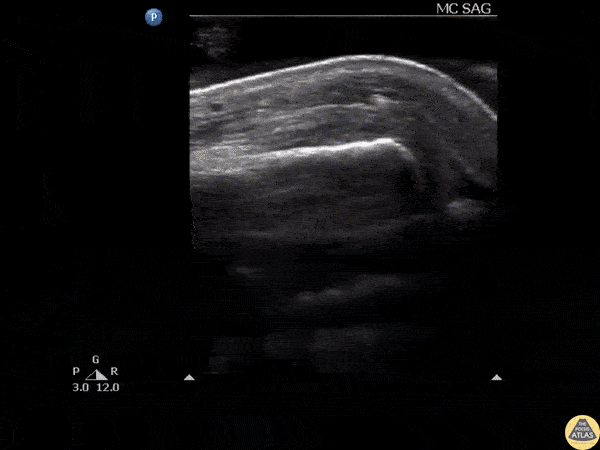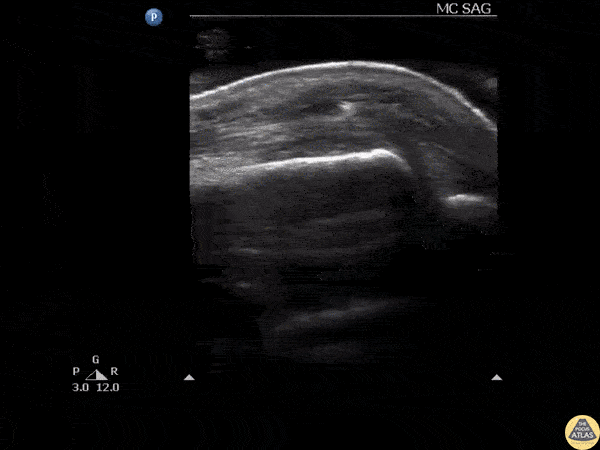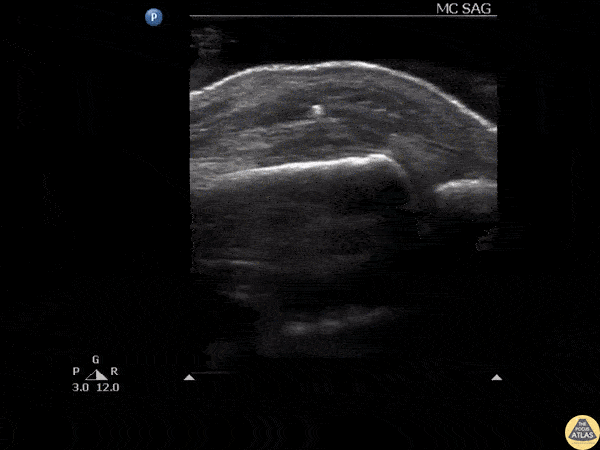
Glass FB in Extensor Tendon
Ultrasound clip reveals a shard of glass broken off and lodged in the extensor tendon over an MCP joint.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
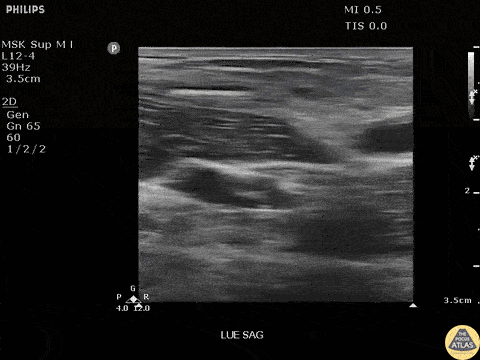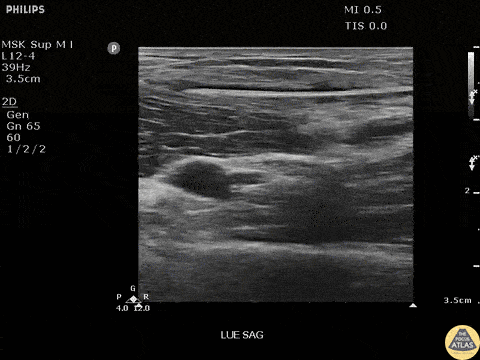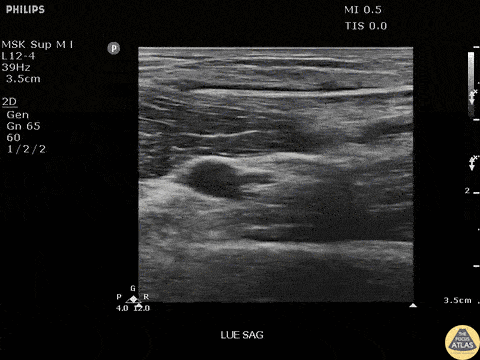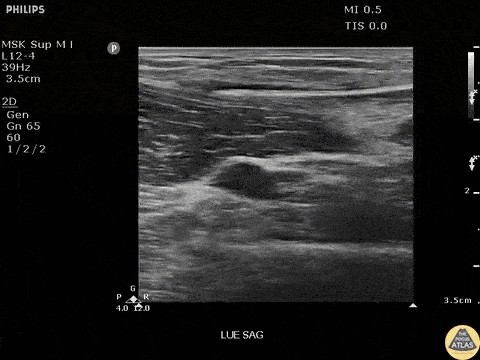
Bamboo Foreign Body
Seen here is a fragment of bamboo broken off in a patients arm. Patient had negative x-rays, emphasizing the importance of POCUS in identifying radiolucent foreign bodies.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
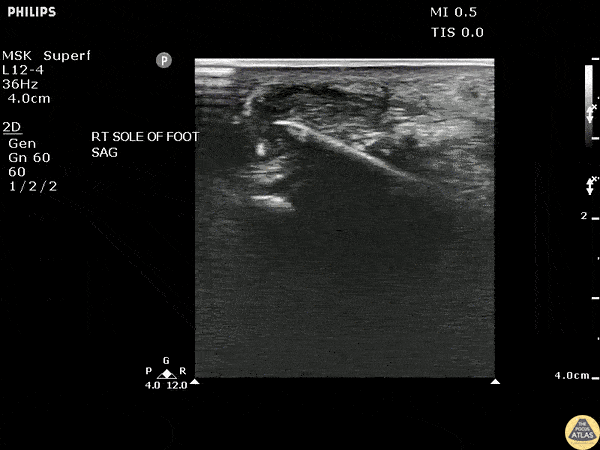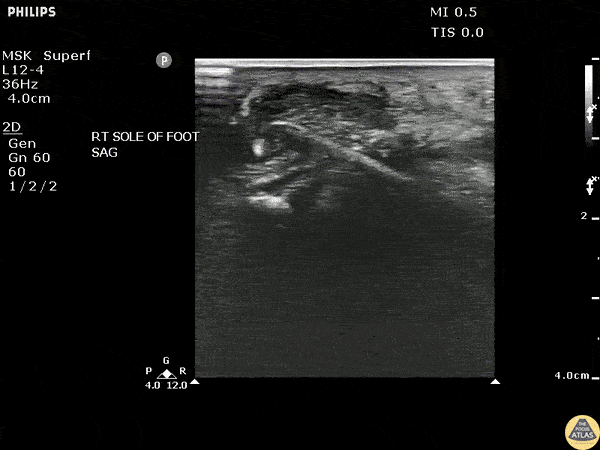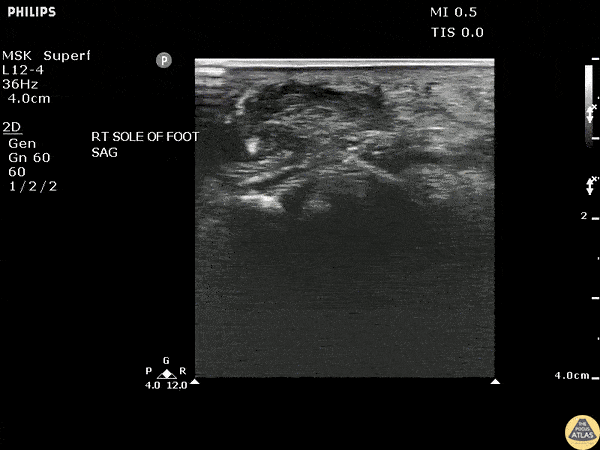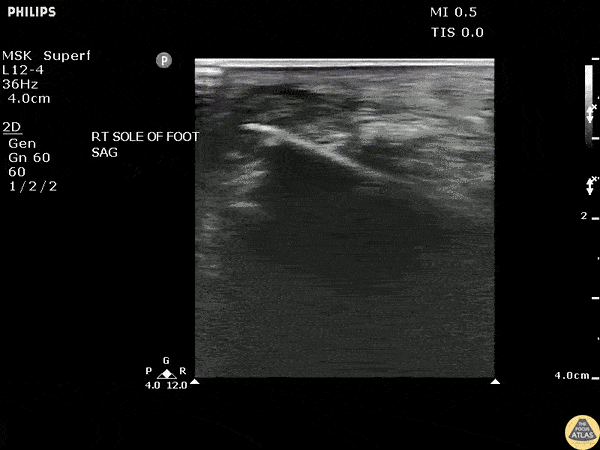
Toothpick Foreign Body
POCUS revealed a toothpick broken off in a patient’s heel in a long axis view.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
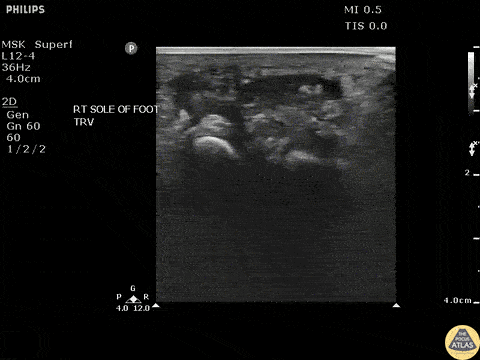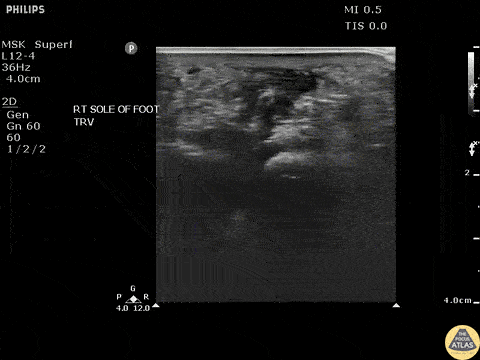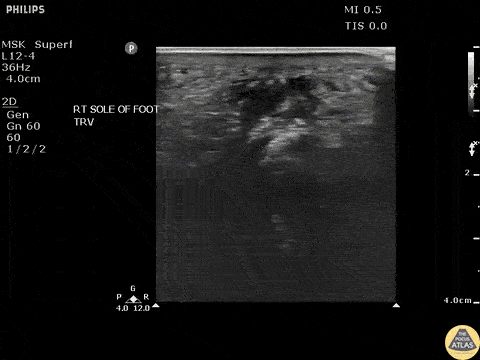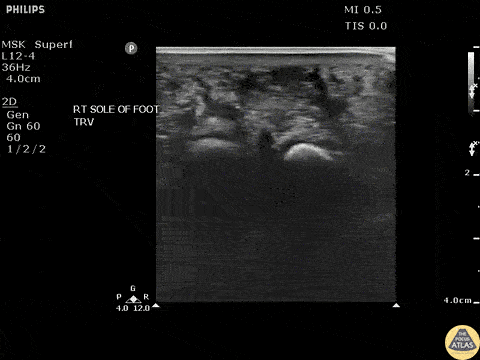
Toothpick Foreign Body
Transverse view of a toothpick foreign body exhibiting posterior acoustic shadowing.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
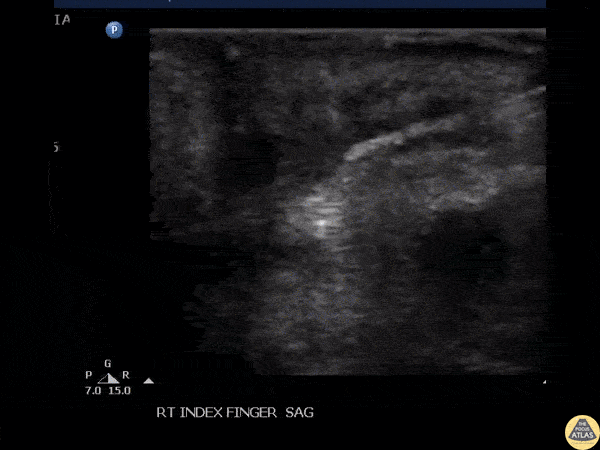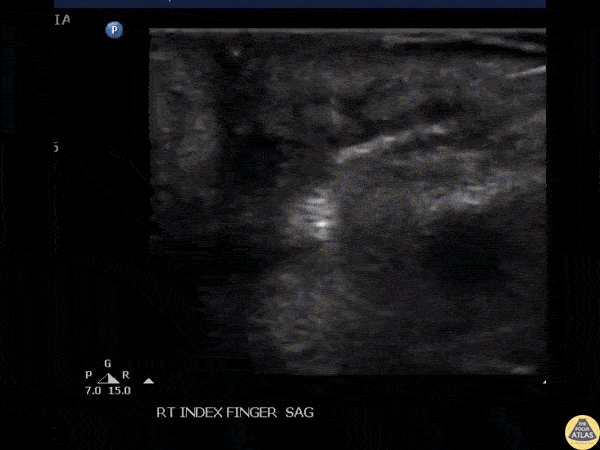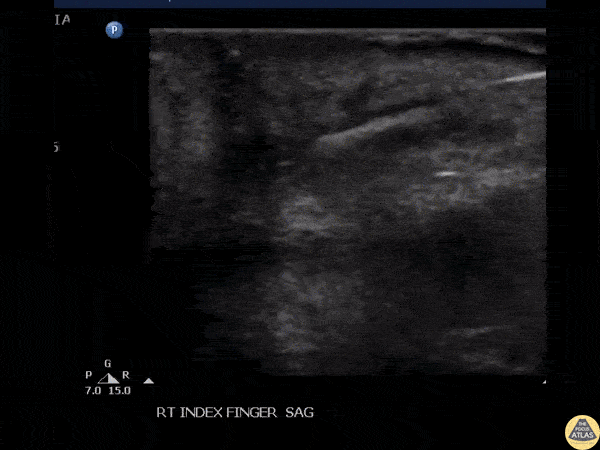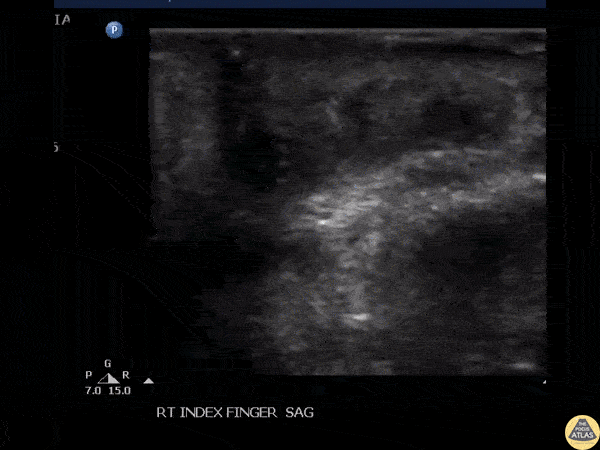
Foreign Body Removal
POCUS guided foreign body removal of a wooden splinter in the distal volar finger using alligator forceps.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
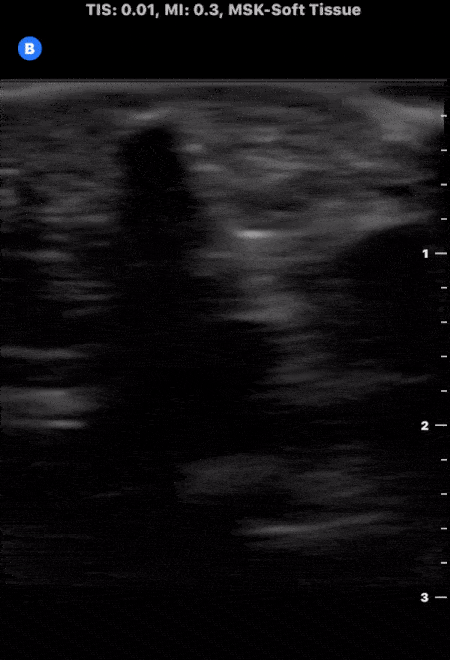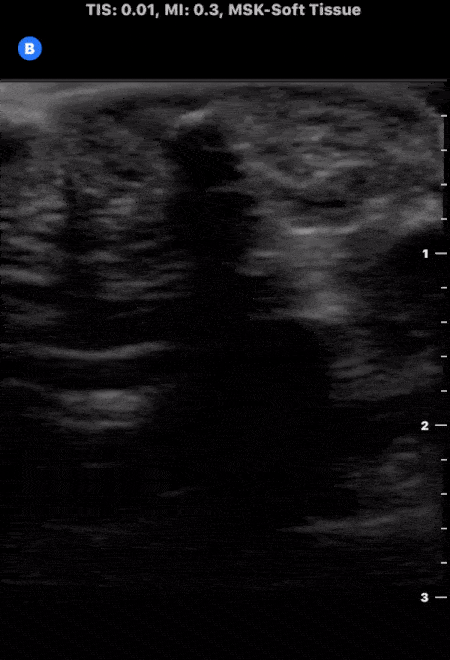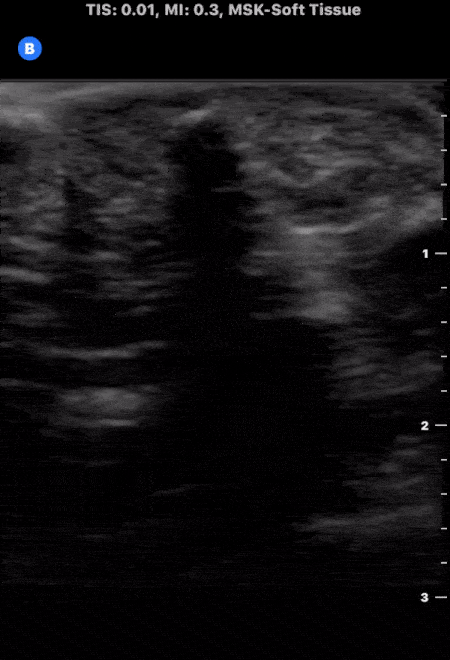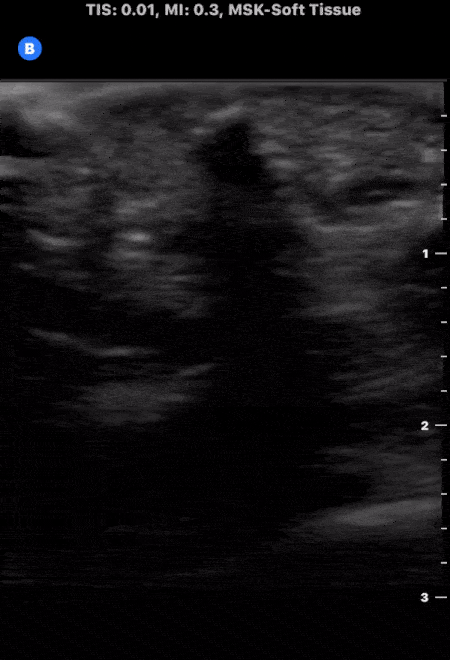
Soft Tissue Foreign Body
A patient presented to the emergency department following puncture by the tip of a palm frond. A puncture wound was noted with a palpable object under the skin. Soft tissue ultrasound was performed which demonstrated evidence of superficial foreign body as noted by the small hyperechoic structure with associated shadowing. The foreign body was successfully removed without issue.
Image courtesy of The POCUS Atlas Team
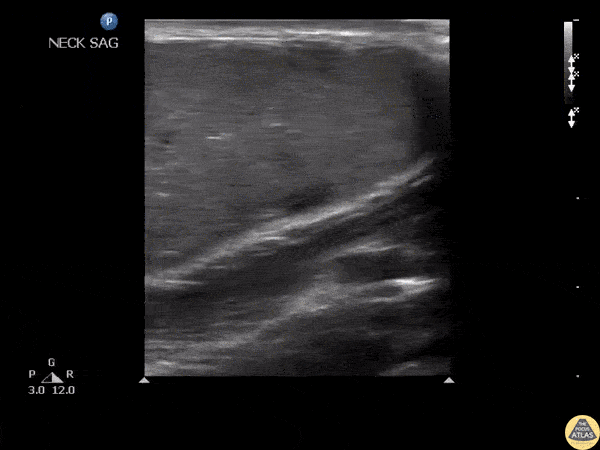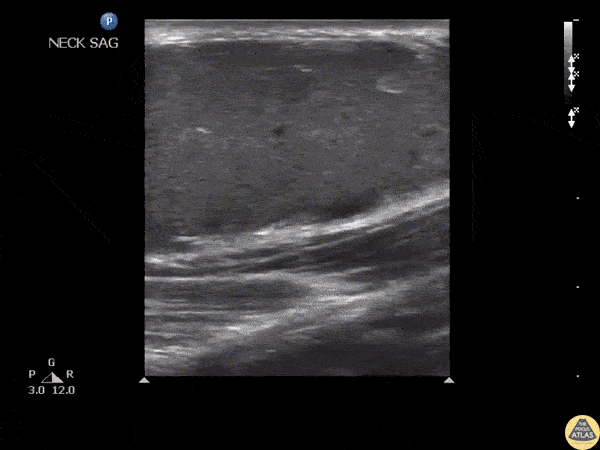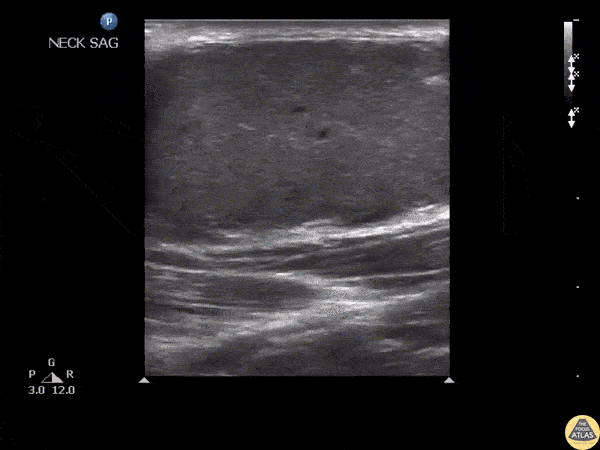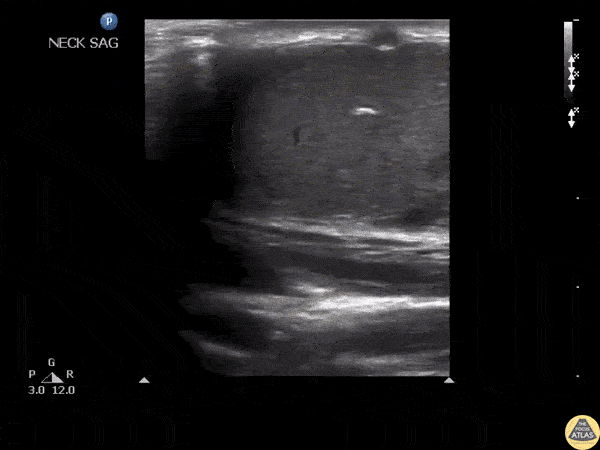
Epidermoid Cyst
An adult male presented to the ED with a tender mass on his neck with overlying erythema. Ultrasound revealed an epidermoid cyst characterized by the pseudo-testis appearance of the cyst.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
Original Twitter Post can be found here.
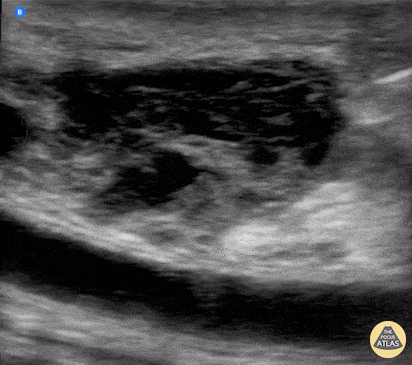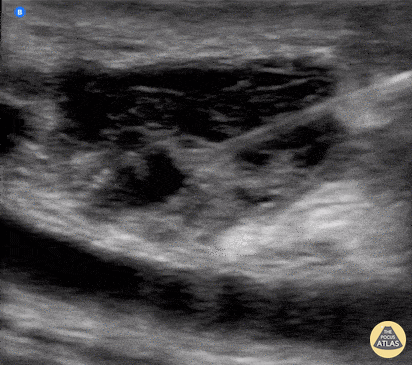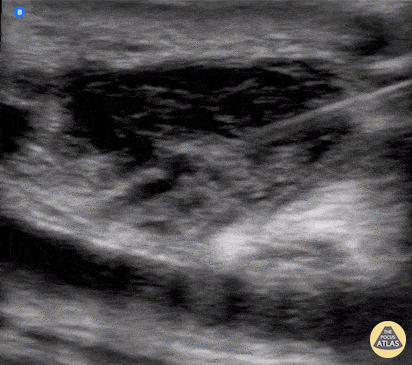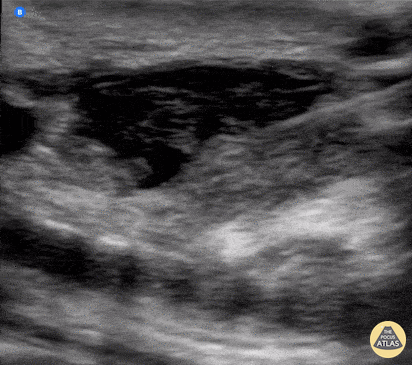
Image-Guided Needle Aspiration
Needle aspiration of a fluid collection superficial to a femoropopliteal bypass.
Wolfgang Geisser, @fentanyl05
Bayern, Deutschland
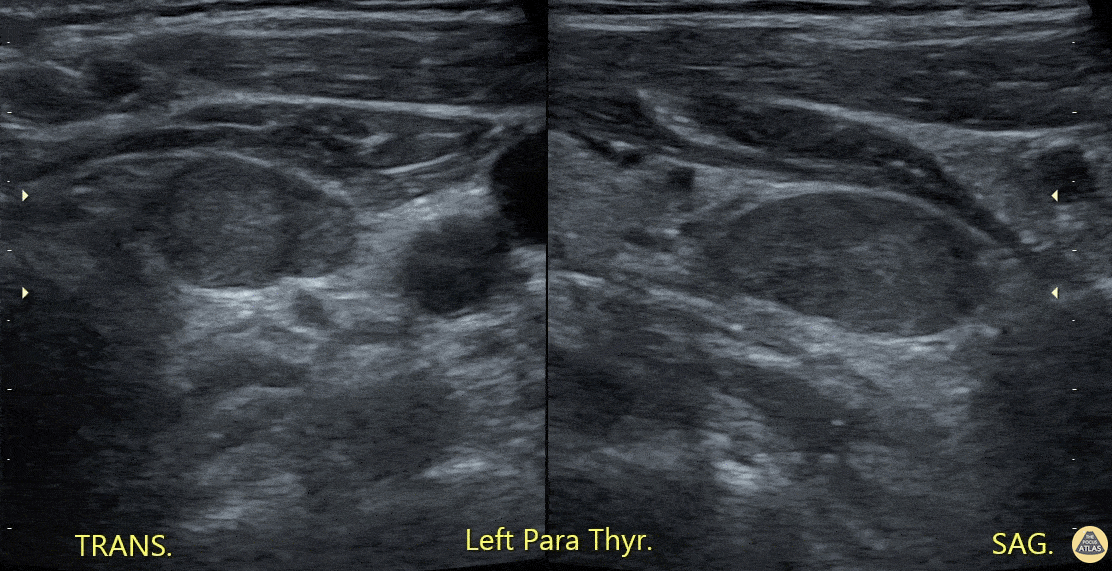
Parathyroid Mass
A patient with clinical and laboratory evidence of hyperparathyroid function underwent POCUS of thyroid/parathyroid region. Seen here is a slightly hypoechoic rounded, vascular structure (imaged in both transverse and saggital planes) felt to represent the culprit lesion.
Abdulmajid Mubarak, @mjed136
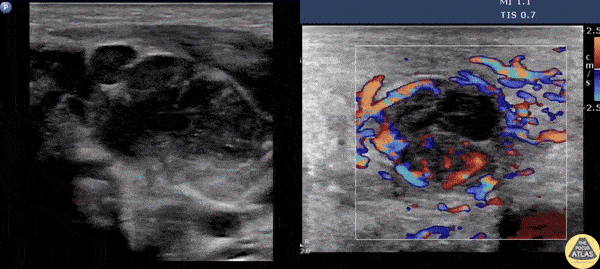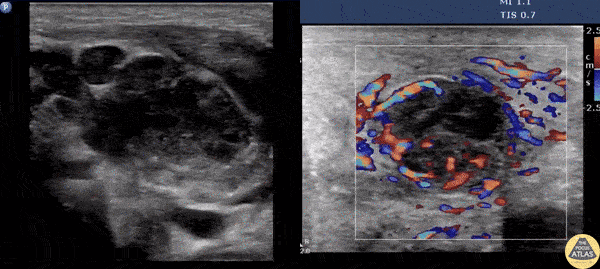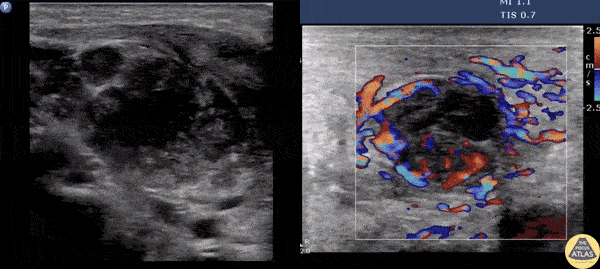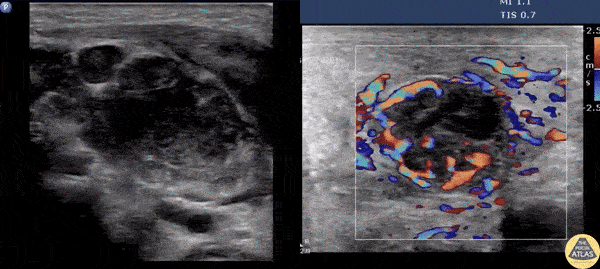
Suppurative Lymphadenitis
A male presents with a left neck mass that is erythematous and edematous with a prior history of MRSA. Contemplating incision and drainage, ultrasound was switched to doppler flow. Doppler revealed increased flow surrounding an inner hypoechoic region suggesting suppurative lymphadenitis. Because of this, I & D was not indicated, and differential includes necrosis/hemorrhage into metastatic node.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
COVID-19 Thyroiditis
An 18-year-old female with 2 week hx COVID presented to an outpatient clinic where labs included a TSH <0.01 and Free T4 6.75. She was sent to ED for further evaluation of tachycardia (HR 130 bpm). ED evaluation included POCUS that was notable for bilateral thyroid lobe enlargement without nodules, findings consistent with COVID-induced thyroiditis.
Paul Khalil, PEM POCUS Fellow at Denver Health/University of Colorado
@Khalil3Paul
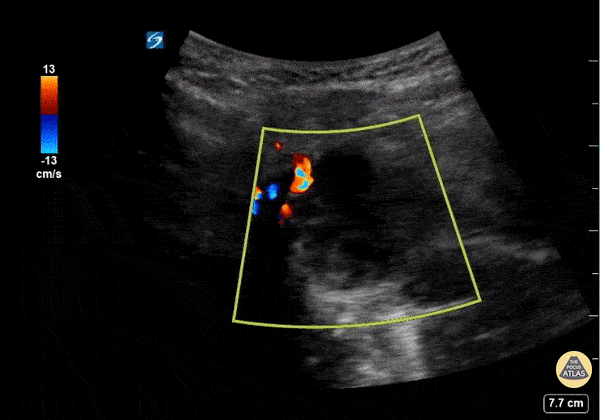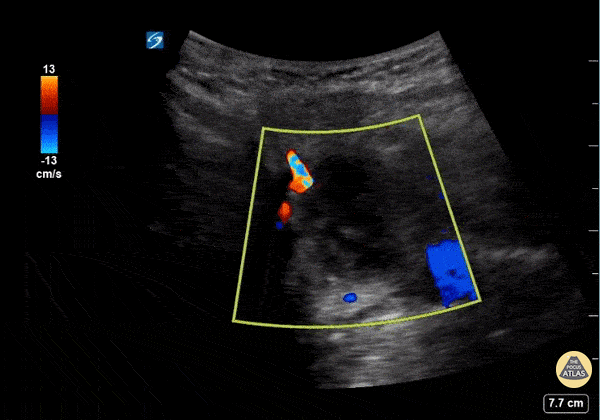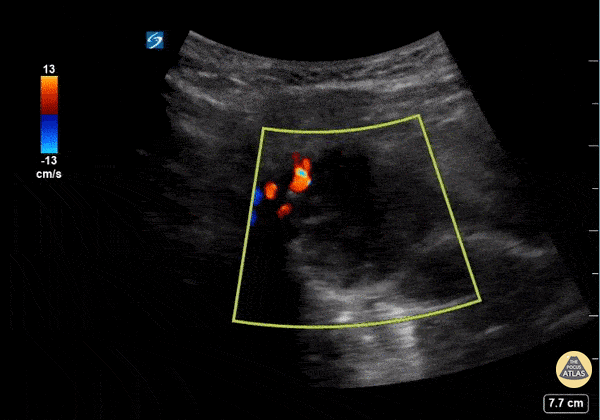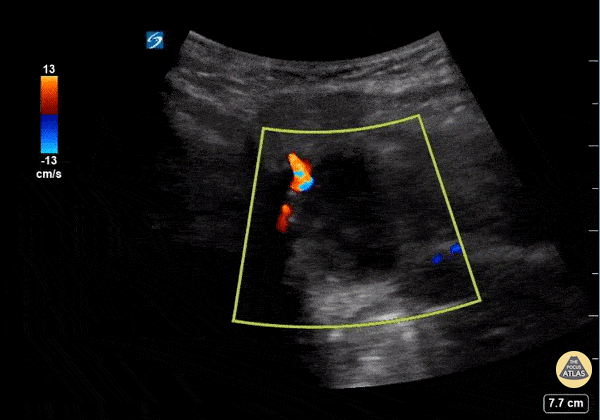
Submandibular Abscess
This is a submandibular view of a peritonsillar abscess. Color doppler is used to visualize blood vessels immediately deep to the abscess. By convention, the left side of the screen is posterior and the right side of the screen is anterior.
Garrett Ghent, Resuscitationist/Diagnostician; Norfolk, VA
@garrettghentMD

Necrotizing Fasciitis
Hyperechoic gas (screen left) obscure the typical architecture of soft tissues (screen right). There is a small amount of edema in the superficial soft tissues.
Dr. Bell
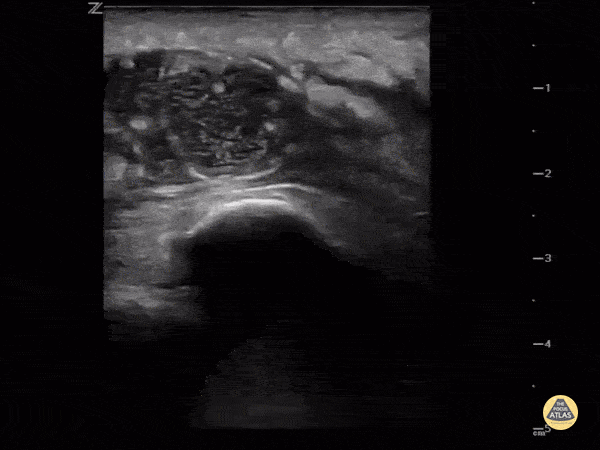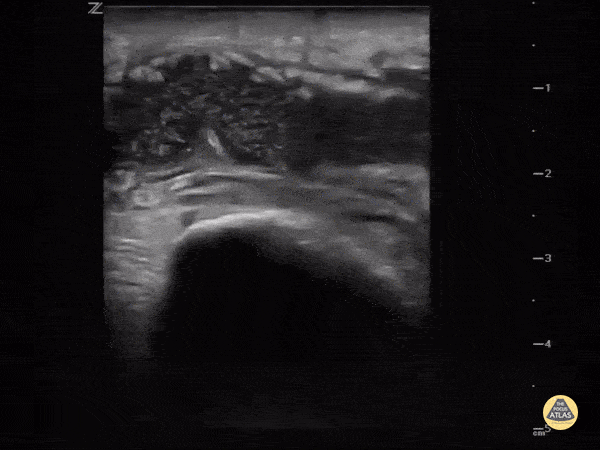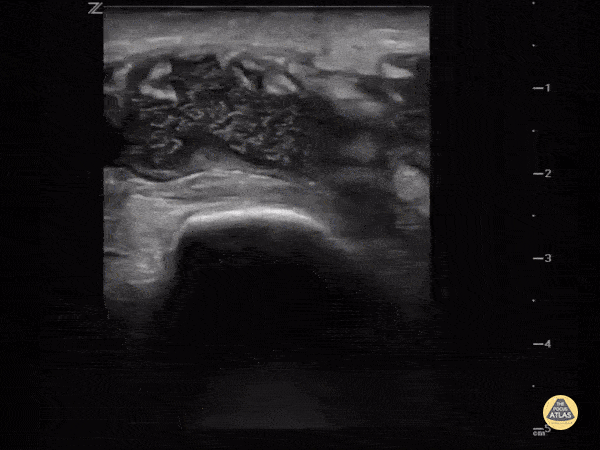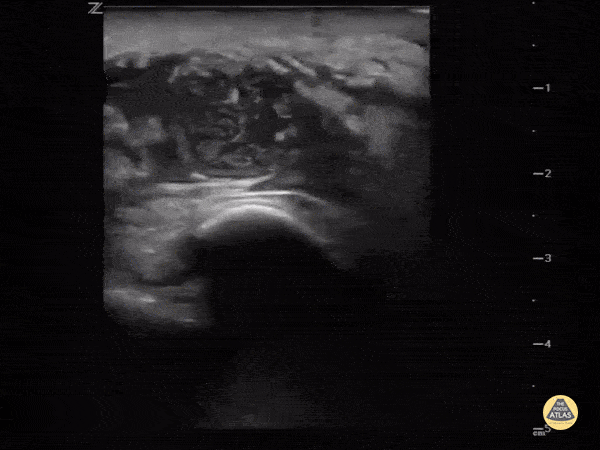
Intra-articular or extra-articular?
Sometimes it's hard to tell if the knee is septic or just the bursa. Ultrasound can help. This image demonstrates a hypoechoic fluid collection ABOVE the patella consistent with pre-patellar bursitis.
Image courtesy of IUEM Ultrasound
Original Twitter Post can be found here.
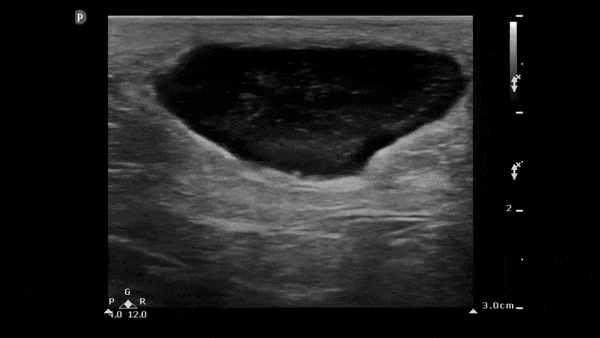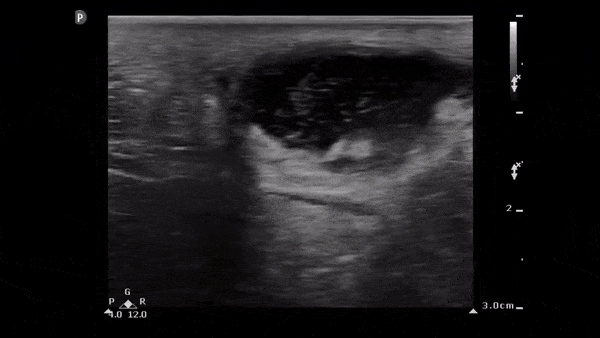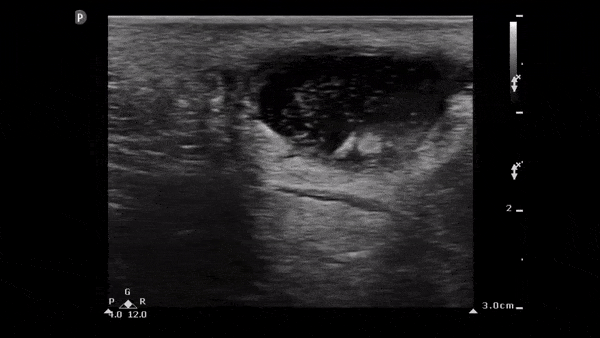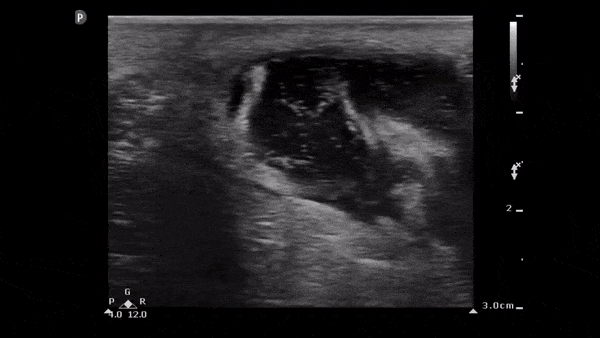
Soft Tissue Abscess
The image below demonstrates a well circumscribed fluid collection in the soft tissue consistent with an abscess. Note the scattered punctate echogenic densities moving within the abscess fluid which suggest high cell/protein content of the fluid.
Image obtained from 5 Minute Sono.

Sialadenitis (Postoperative)
55 y/o F with recent shoulder surgery 4 days prior, with three days of dysphagia and swelling under R jaw.
POCUS reveals swollen submandibular gland with multiple hypoechoic areas, similar to cobblestoning, scattered through normal glandular tissue. CT demonstrated inflammation of submandibular gland and surrounding platysma with prominent ducts and an obstructing stone.
Drs. Surriya Ahmad and John F Kilpatrick - Kings County/SUNY Downstate Emergency Medicine
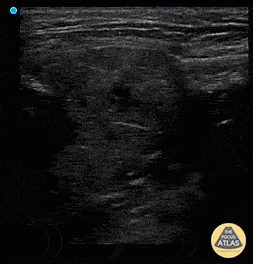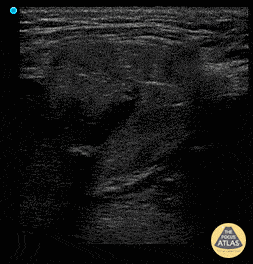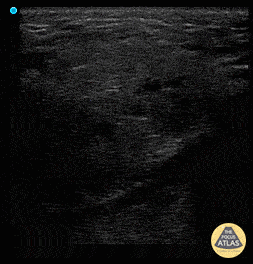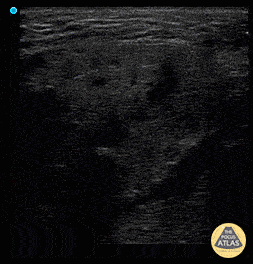
Sialadenitis
Patient has painless left sided facial swelling and no dental issues. See left submandibular gland swelling with ductal dilation and hyperechoic density in the far field representing sialolith and surrounding inflammation sialadenitis.
Dr. Dustin Morrow
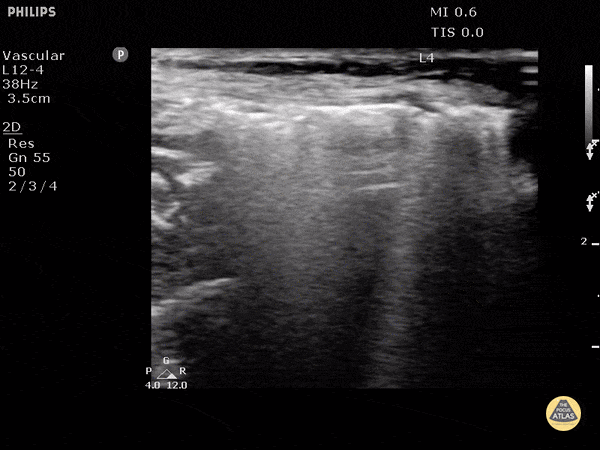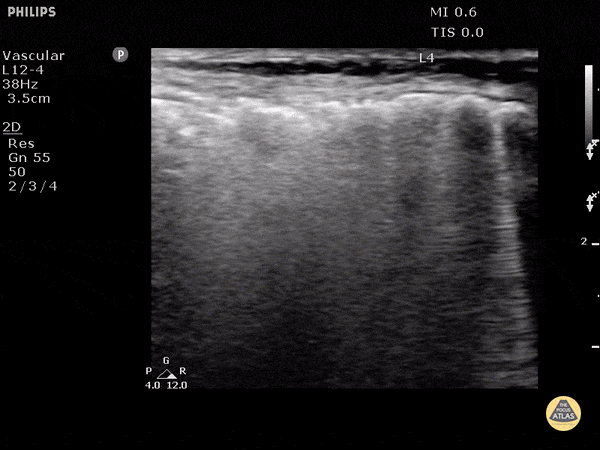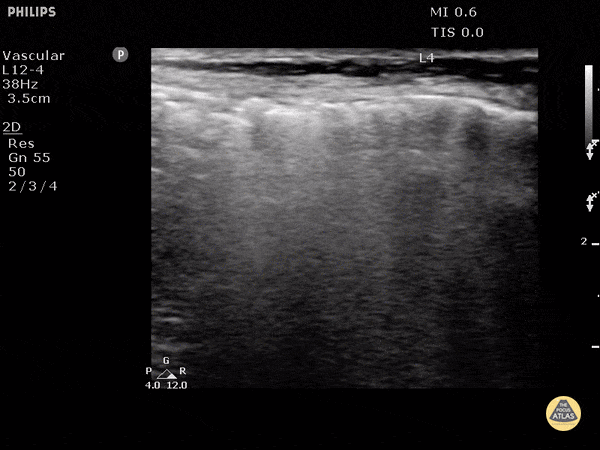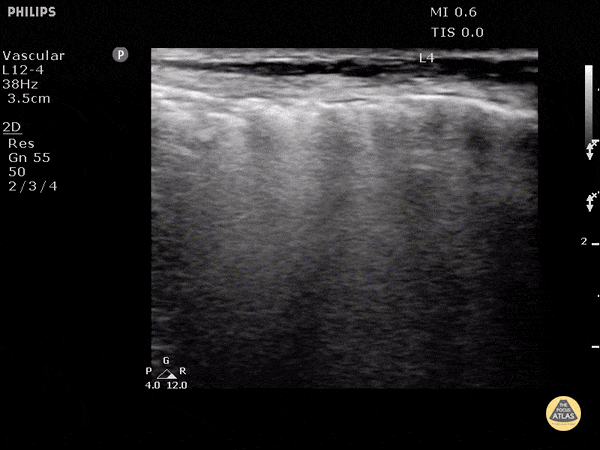
Subcutaneous Emphysema
Air poorly transmits ultrasound waves and when fluids or solids interface with air, they lead to echogenic irregularities with comet tails that can often obscure the tissue behind it.
Dr. Justin Bowra et al.
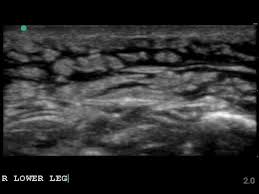
Cobblestoning
This is the classic appearance of subcutaneous edema which in the appropriate clinical setting (overlying redness and warmth) would be consistent with a cellulitis

Compression for Abscess Identification
While typically an abscess will appear as a hypoechoic fluid filled structure, sometimes it can be missed as its echotexture is similar to other surrounding soft tissue structures. To improve sensitivity, gentle compression should be applied to identify a subtle abscess as seen above.
Image obtained from Ultrasound of the Week.
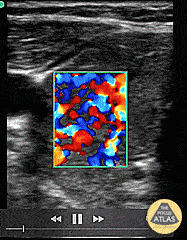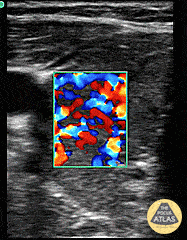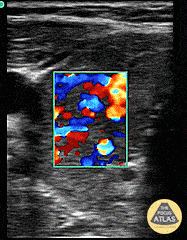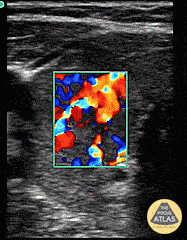
Thyroid Storm (Inferno Sign)
Thyroid Storm (Inferno Sign)
Patient with a history of “glandular problems” as per the family presented from urgent care with confusion, slurred speech, tremors and fever. TSH was sent out. The patient was started on treatment for thyroid storm after color flow over an enlarged thyroid demonstrated the inferno sign. Patient improved on thyroid storm treatment. Infectious workup was negative. 48 hour T4 serial dilutions resulted at 2000.
Dr. Dustin Morrow
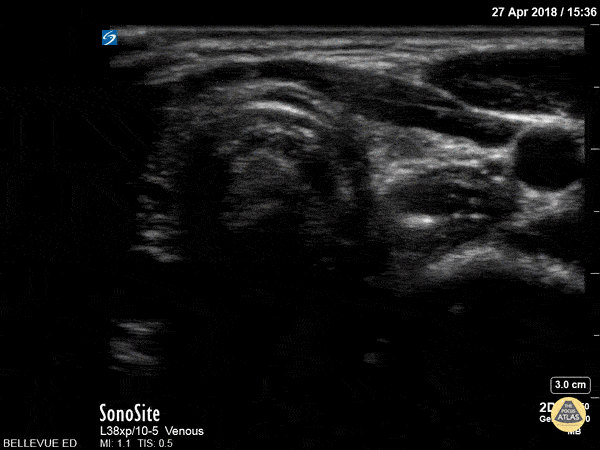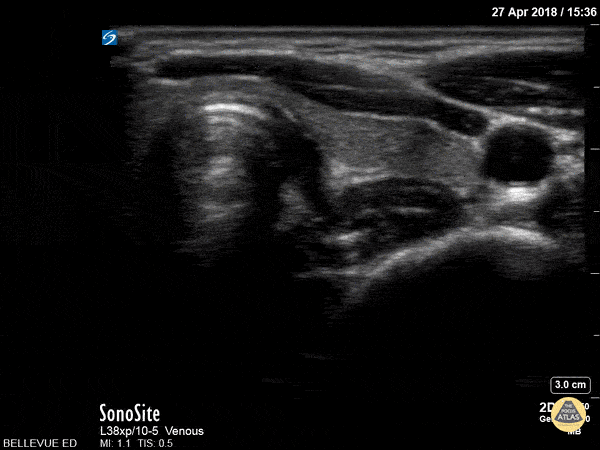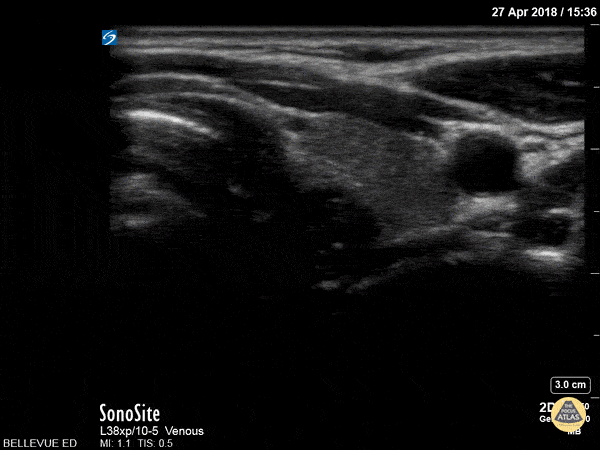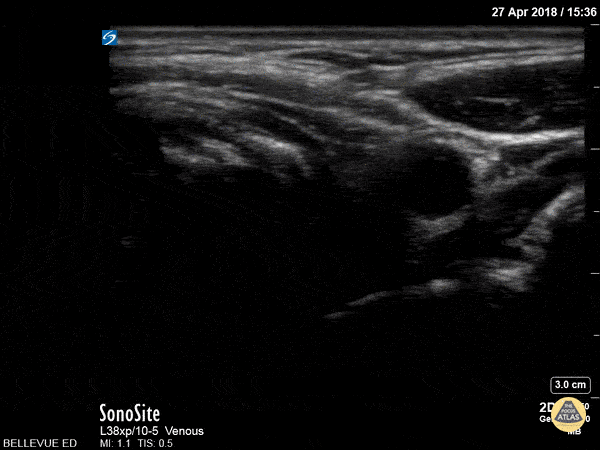
Thyroid Left Lobe
In this view we see half of the thyroid gland, which has similar echogenicity to the liver. The thyroid isthmus overlies the trachea, while the left thyroid lobe overlies the esophagus and is medial to the left carotid artery.
Hannah Kopinksi and Dr. Lindsay Davis - NYU Emergency Medicine
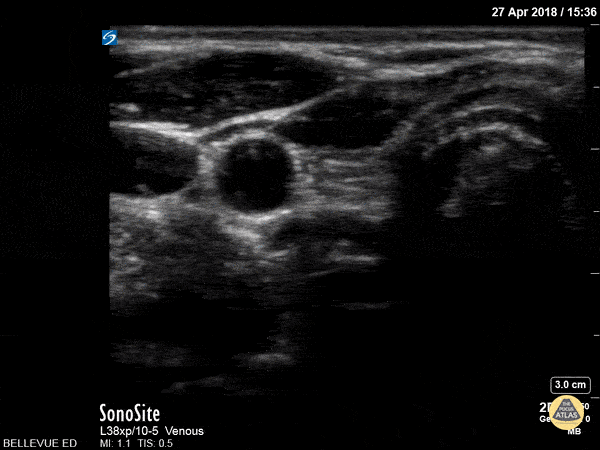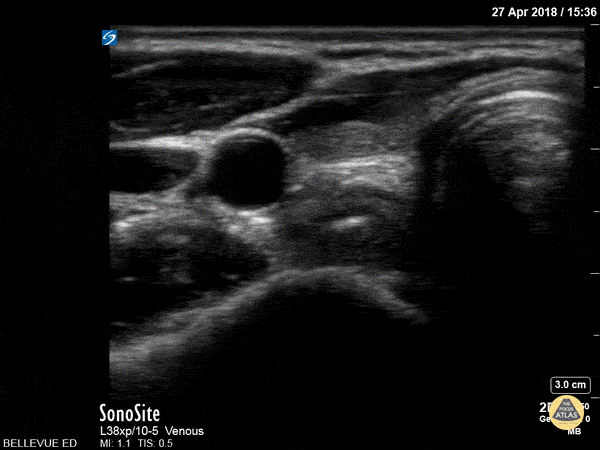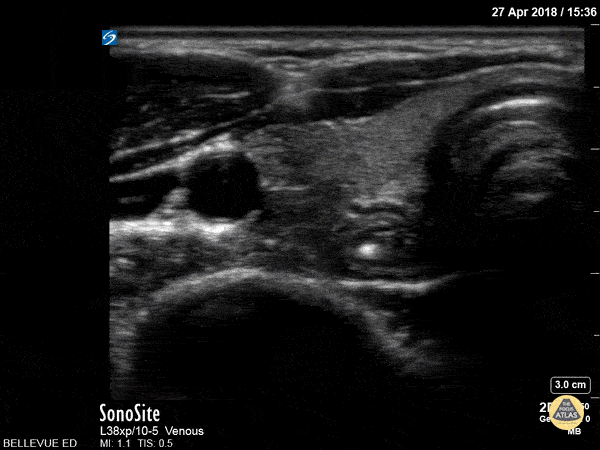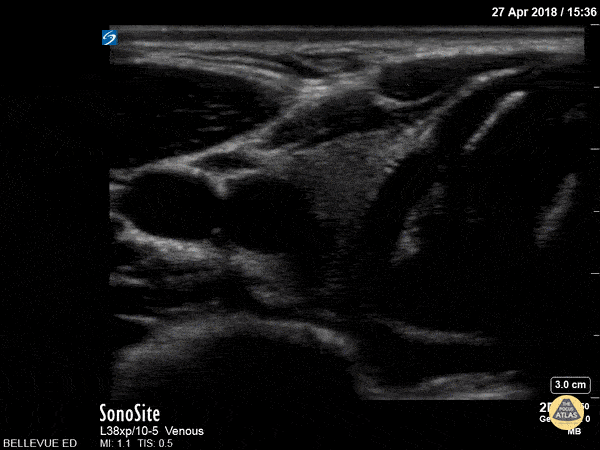
Thyroid Right Lobe
In this view we see half of the thyroid gland, which has similar echogenicity to the liver. The thyroid isthmus overlies the trachea and it extends into the right thyroid lobe which lies medial to the pulsatile right carotid artery. Lateral to the carotid we see the right internal jugular vein. Superficial to the IJ and carotid we see the large sternocleidomastoid muscle; medial to that, superficial to the trachea and thyroid on the right side of the screen, are the strap muscles.
Hannah Kopinksi and Dr. Lindsay Davis - NYU Emergency Medicine
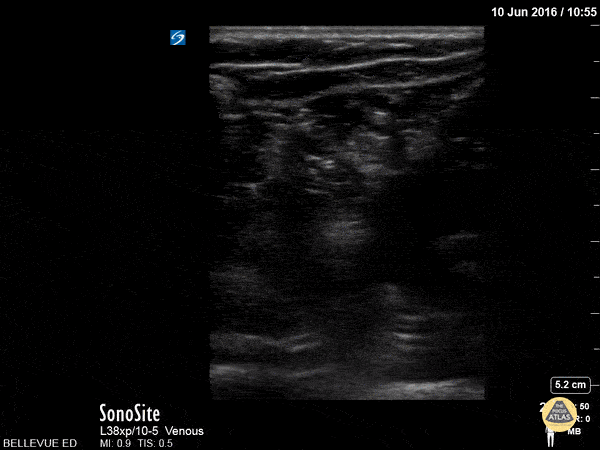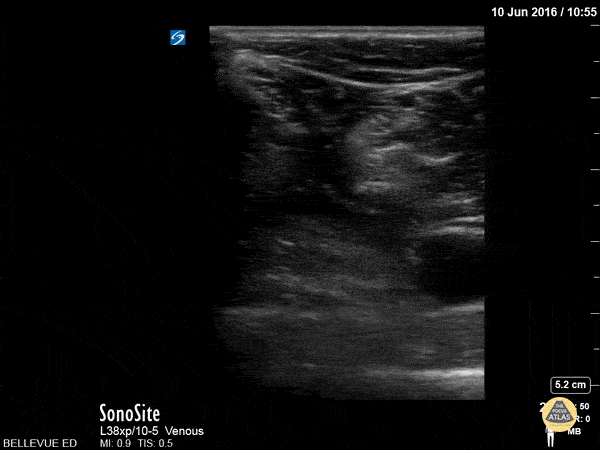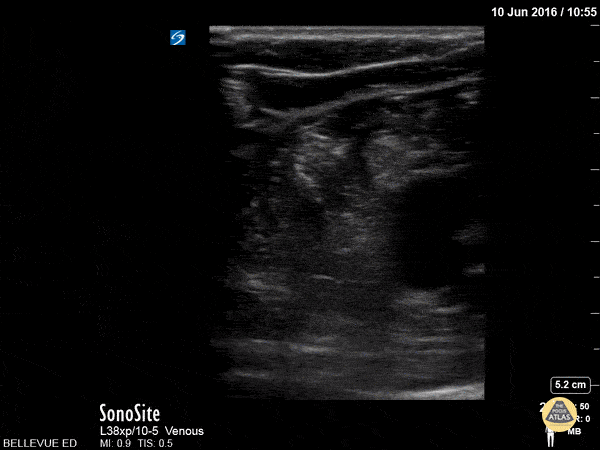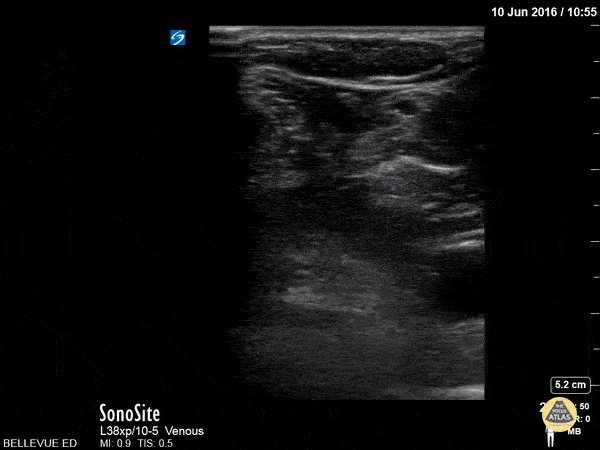
Sciatic Nerve
Here we see the tibial nerve and the common fibular nerve come together to form the sciatic nerve as the probe is moved proximally up the posterior aspect of the leg. The popliteal vein is seen deep to the nerves.
Hannah Kopinksi and Dr. Lindsay Davis - NYU Emergency Medicine
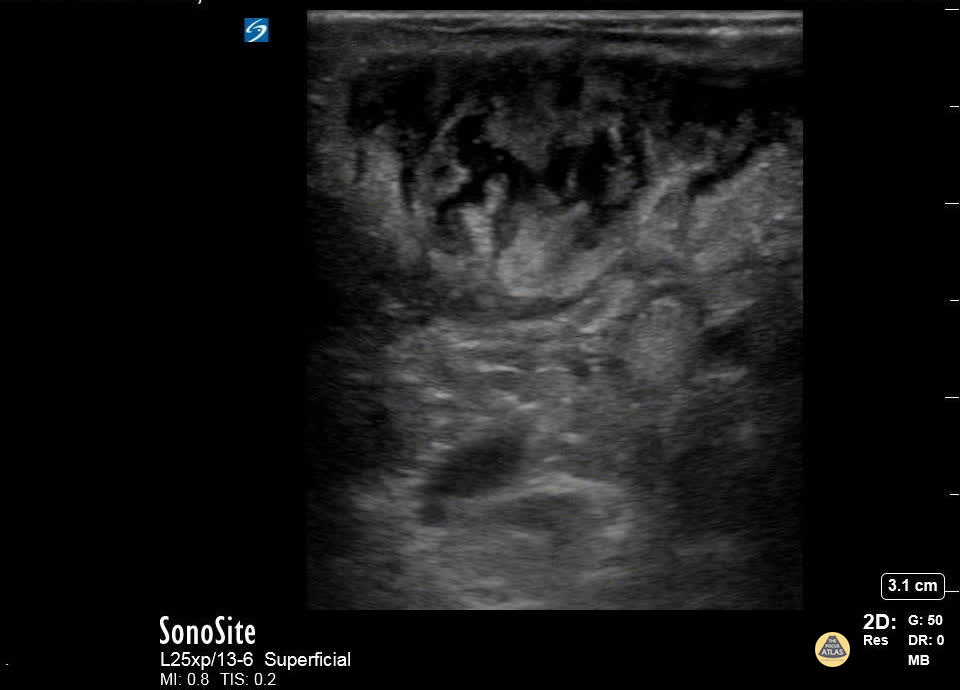
Abscess Identification
A patient with cerebral palsy and quadriplegia presented with her mother for evaluation of a fluctuant mass in her right axilla. Ultrasound imaging of the mass showed an abscess with multiple septations. The abscess was incised and drained, and the patient was discharged on antibiotics.
Katy Van Donselaar, Emergency Medicine Resident
Christopher Heberer, Emergency Medicine Resident
Simhadri Botta, 4th year Medical Student

Panniculitis
Diffuse cobblestoning typically seen with cellulitis.
In this case it is biopsy proven panniculitis.
Dr. Gordon Johnson
@pdxfutebol
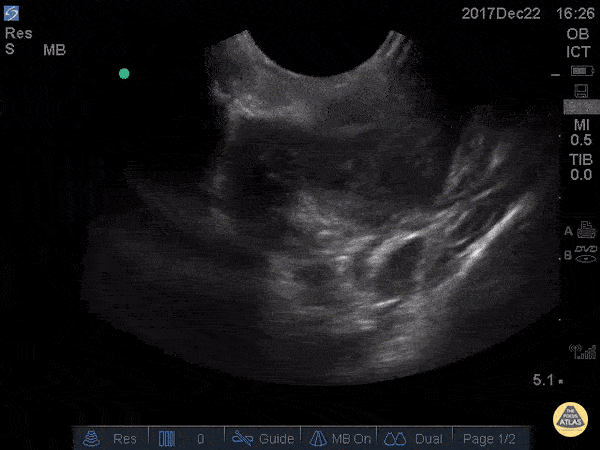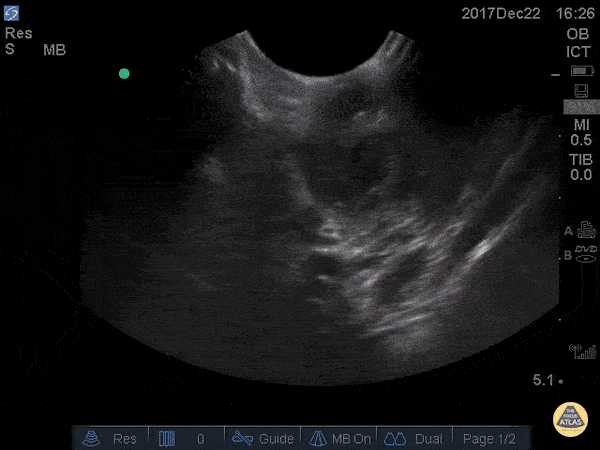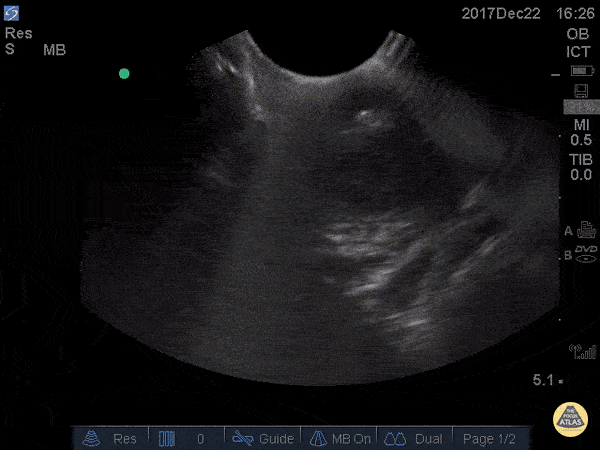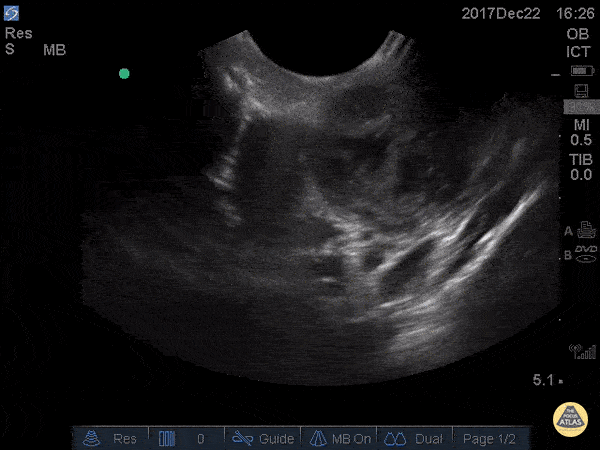
Peritonsillar Abscess
This is an example of a peritonsillar abscess as seen with a high-frequency endocavitary probe. About 3ml of pus was drained with significant relief. Notice that just deep to the abscess is big red. It's not always lateral!
Dr. Jason Tanguay
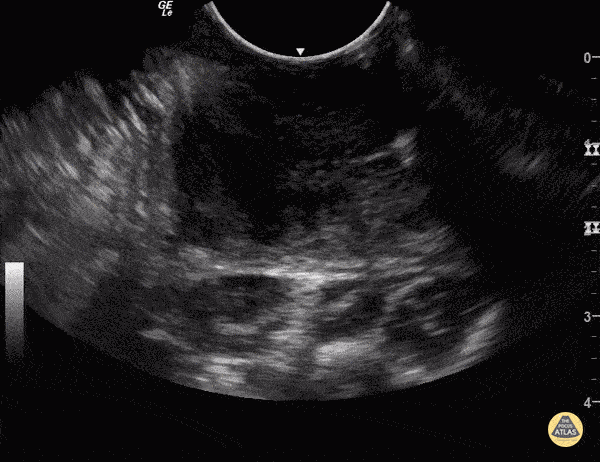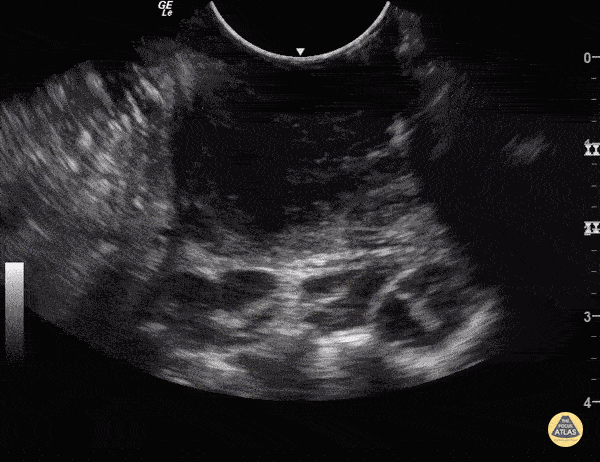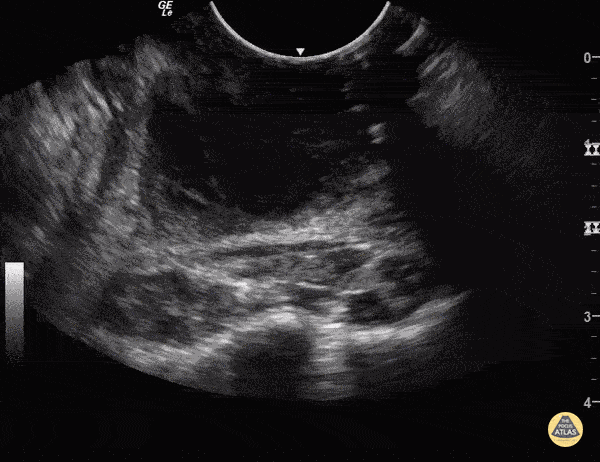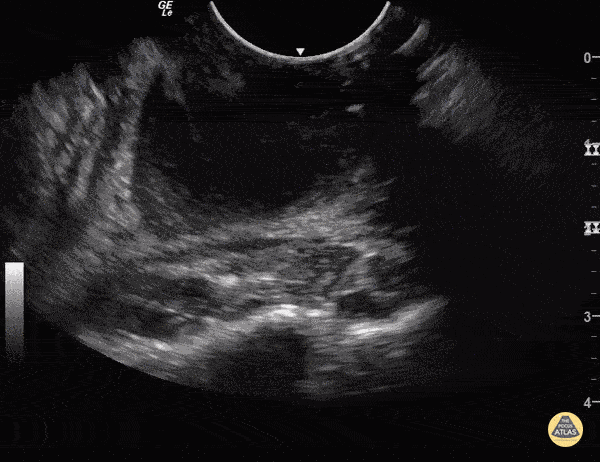
Peritonsillar Abscess
Some people like to know what they're aiming at before they stick needles in the back of people's throats.
You can use an endocavitary probe for an intraoral approach... to make sure it's not just cellulitis. Your patient will thank you. As with any abscess, look for a relatively hypoechoic circumscribed area representing a collection of fluid.
Sukh Singh, MD Caption: Matthew Riscinti, MD

Facial Tumor
WCUME 2017 Submission for "Novel Indication"
Face mass with bone erosion due to tuberculosis.
Dr. Atim Uya - San Diego, California

Atypical Abscess
The image above demonstrates a well circumscribed fluid collection within the soft tissue, without evidence of surrounding cellulitis. The above abscess was incised with immediate release of a large volume of purulent material. The patient did well.
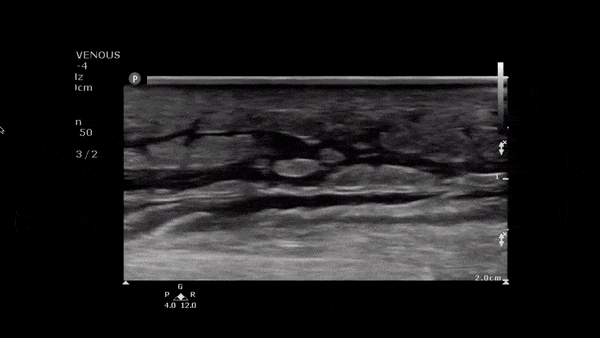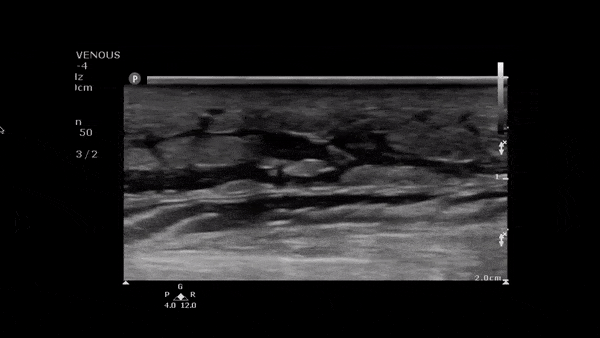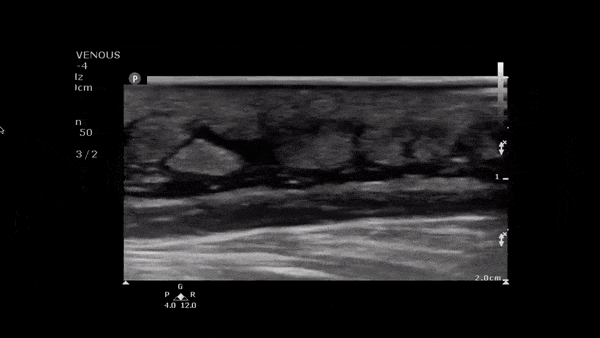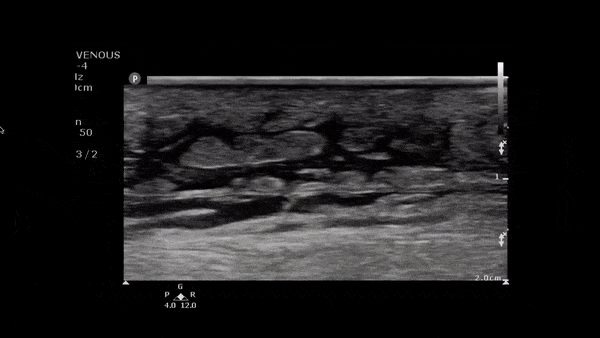
Cobblestoning in Cellulitis
This image demonstrates anechoic fluid surrounding islands of soft tissue. In the setting of infectious signs and symptoms this is consistent with a cellulitis.
Image obtained from 5 Minute Sono.
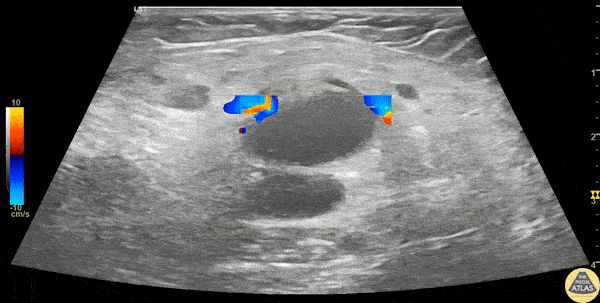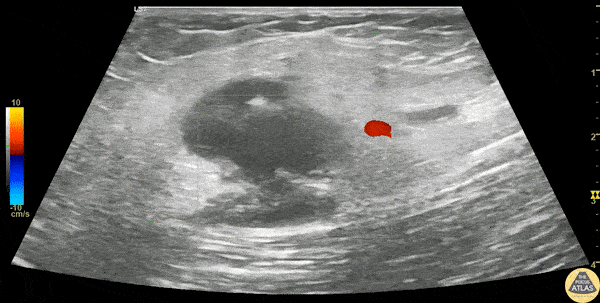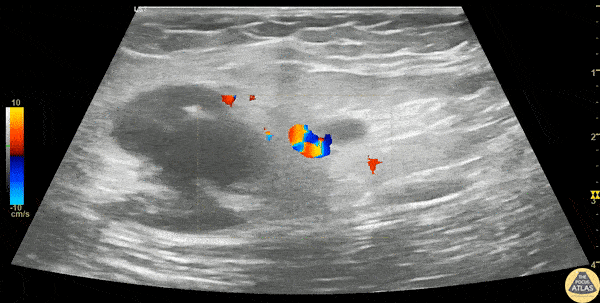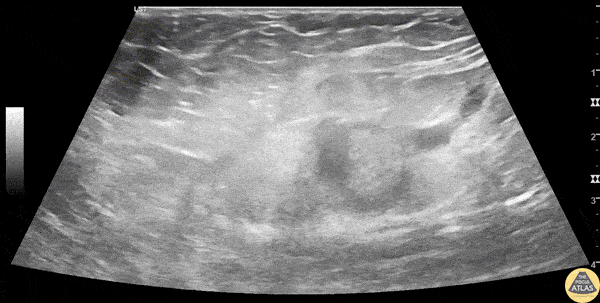
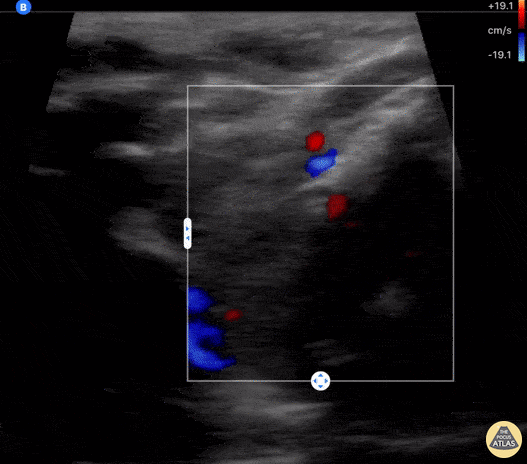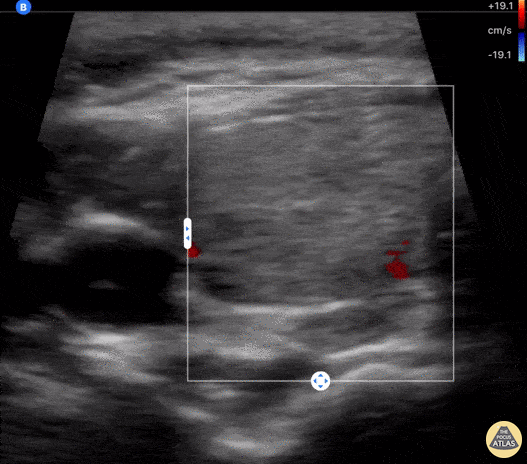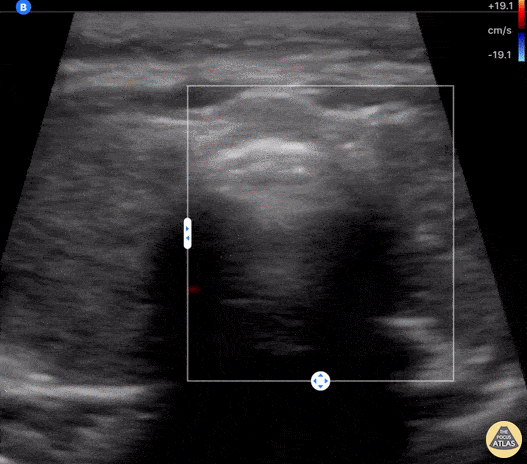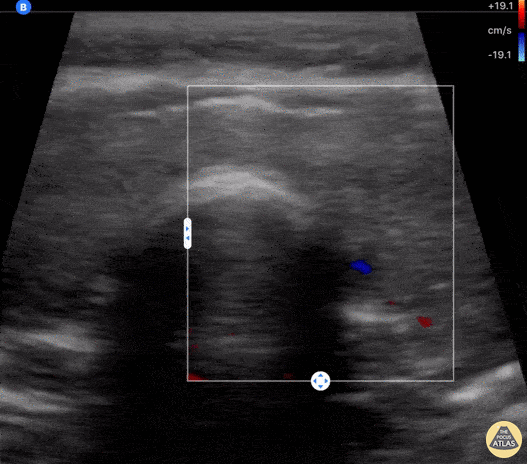
Inguinal Lymphadenitis
A 30s F presented with L groin pain and swelling. On exam she had pain and focal soft tissue swelling over her inguinal crease. POCUS was performed which demonstrated this enlarged lymph node, suggesting lymphadenitis. In this clip, the lymph node is shown using color doppler, which shows a small amount of flow at the lymph node hilum, without other areas of flow in the node. In the last part of the clip, compression with the probe does not change the shape of the node, differentiating it from an abscess or cyst. This patient was treated symptomatically and discharged with outpatient follow up of her lymphadenitis.
Dr. Stephen Wolf
Denver Health Medical Center
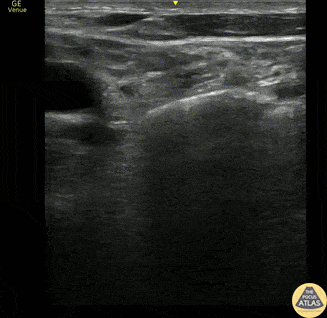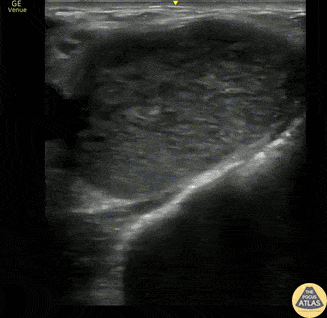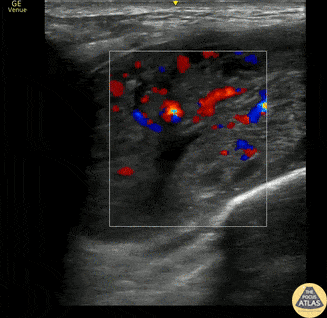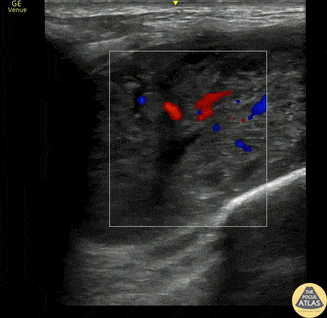
Supraclavicular Lymphadenopathy
This is a 60s y.o. gentleman w/ PMHx remote axillary abscess who was found to have a nontender supraclavicular mass. When scanning medial to lateral in the supraclavicular fossa, the mass is revealed to be a ~3x4cm lymph node. The wedge shaped hypoechoic structure seen represents the hilum, and color doppler reveals organized blood flow. Peripheral hypoechoic regions may represent necrosis. These findings are suspicious for malignancy vs reactive lymphadenopathy.
Dr. Geoff Hogan
Denver Health Residency in Emergency Medicine
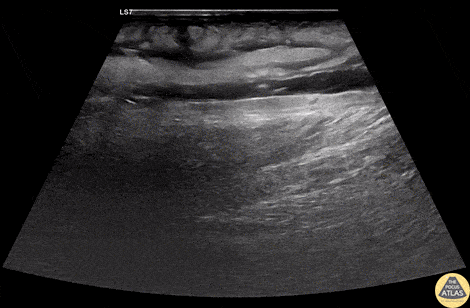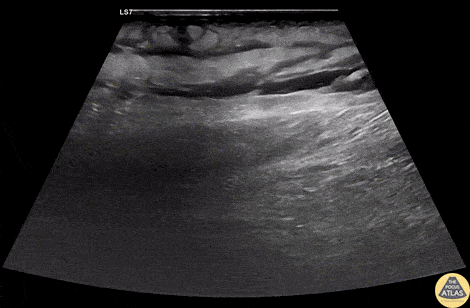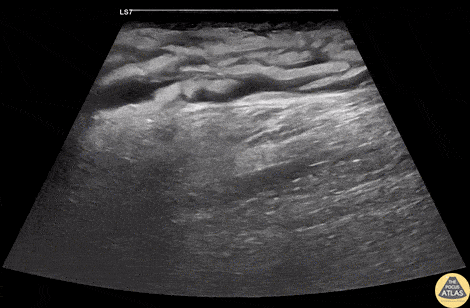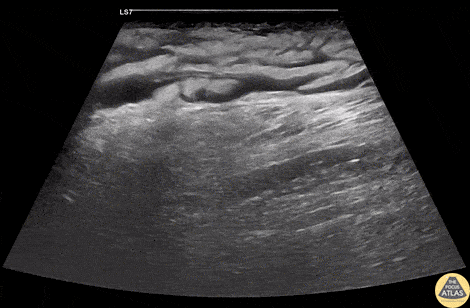
Group A Strep Necrotizing Fasciitis
A 60s M with multiple medical co-morbidities including type 2 diabetes mellitus with multiple prior toe amputations, CHF, COPD and chronic alcohol abuse presented with rapidly worsening leg pain after minor trauma the day prior to presentation. He was in significant pain and had a warm, red, and edematous lower extremity with a focal wound overlying the anterior lower leg. He was febrile and tachycardic, but normotensive. He was resuscitated and given broad spectrum antibiotics and rapid surgical consultation was obtained. POCUS of the affected area was performed and is shown here. In these longitudinal views of the affected area, cobblestoning is seen superficially, indicating cellulitis. Fluid is also seen tracking more deeply along the fascial planes, just superficial to the muscle. This patient was taken emergently to the OR where debridement confirmed necrotizing fasciitis without involvement of the underlying muscles. The patient was kept in the surgical ICU for further resuscitation, his blood cultures and tissue culture became positive for Group A Strep pyogenes, and he underwent multiple subsequent debridements for further management.
Dr. Phil Breslow, PGY2 and Dr. Anna Engeln
Denver Health Residency in Emergency Medicine
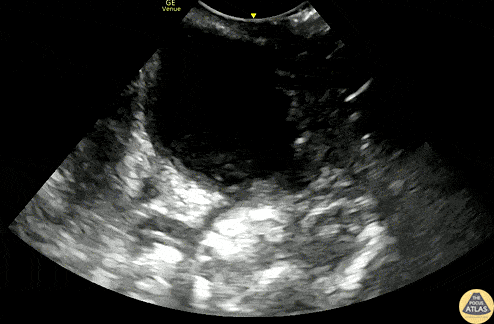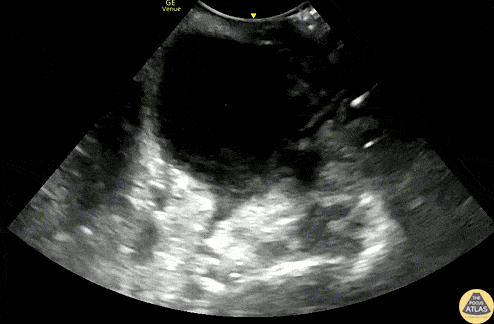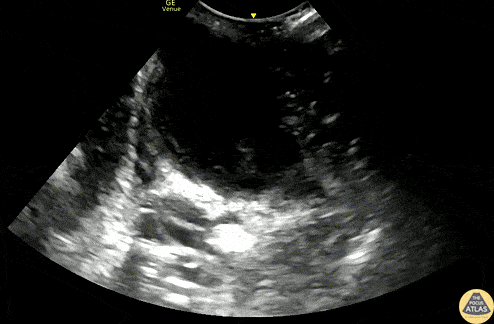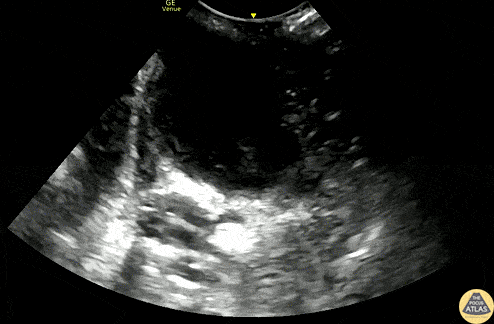
Peritonsillar Abscess
A 20s F with PMH of prior peritonsillar abscess presented with about 1.5 weeks of sore throat, and had been maintained on oral antibiotics with no improvement. Her PCP identified a PTA on clinical exam and referred her to the ED for drainage. This US clip demonstrates the peritonsillar abscess, with an area of hypoechoic, heterogeneous fluid. Posteriorly (far field or bottom of image), the carotid artery is seen pulsating. US in preparation for PTA I&D is particularly helpful in determining the size of the abscess and location of the carotid artery, allowing proper measurement of the plastic guard on the aspiration needle, to prevent inadvertently deep puncture.
Dr. Michael Heffler, PGY3
Denver Health Residency in Emergency Medicine
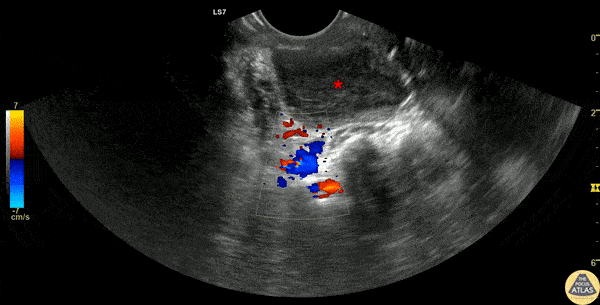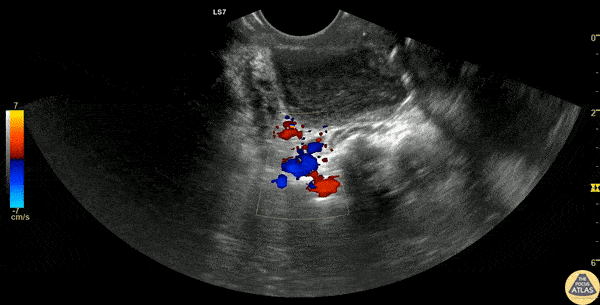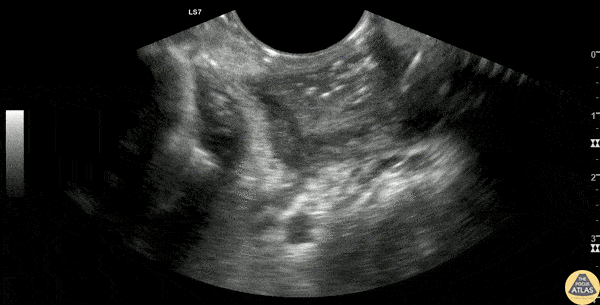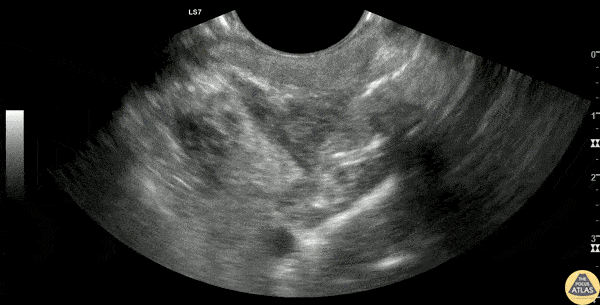
Peritonsillar Abscess Drainage
30s F presented with a week of sore throat which had not improved despite corticosteroids and antibiotics. She was referred to the ED by her primary care provider who noted asymmetric swelling in her throat and had concern for peritonsillar abscess (PTA). Evaluation in the ED confirmed this finding, and POCUS was performed, demonstrating a large PTA. The first half of this clip shows a transverse view of the peritonsillar space, where a circumscribed heterogeneous hypoechoic region is seen superficially, which is the PTA (*). Color doppler identifies the carotid artery posterior to the PTA, a critical structure to identify to prevent inadvertent arterial puncture or laceration. The second half of the clip shows the PTA after needle aspiration of 15cc purulence, demonstrating a collapsed abscess cavity with scattered air and significantly reduced abscess size. The patient had immediate relief of her symptoms after needle aspiration, and was discharged with antibiotics and outpatient ENT follow up.
Dr. Michael Heffler, PGY-4
Denver Health Residency in Emergency Medicine
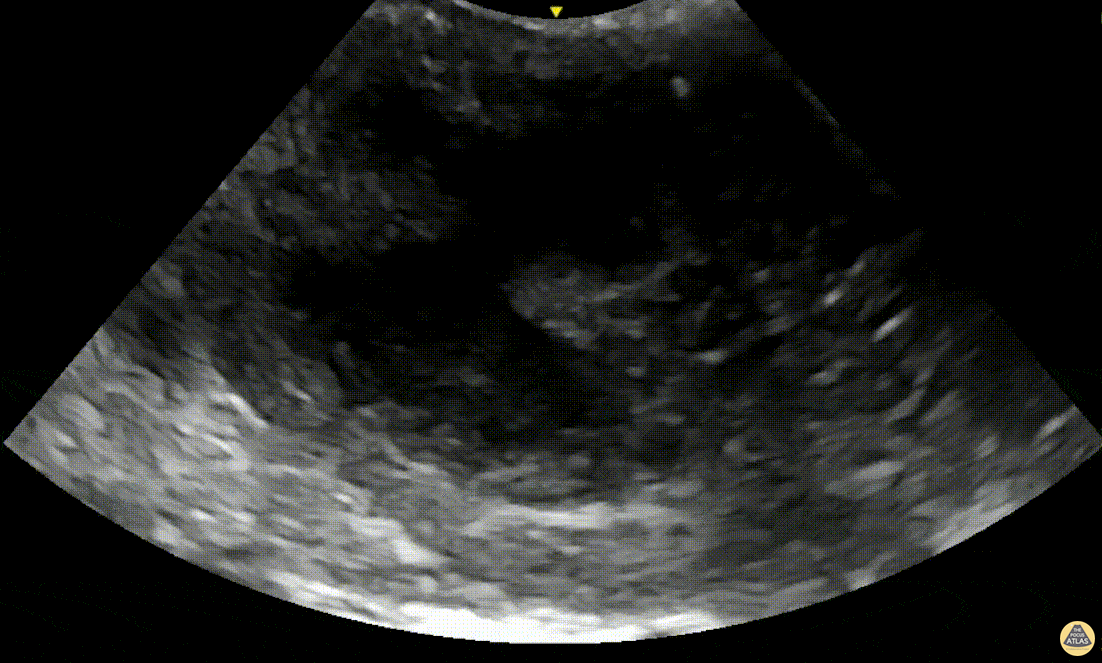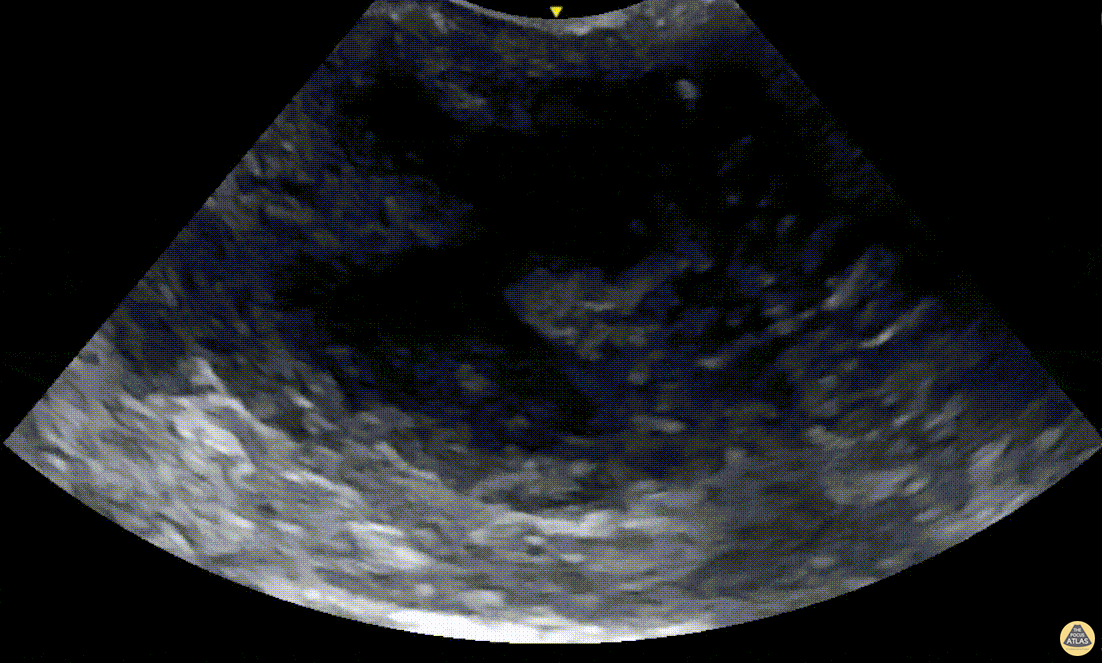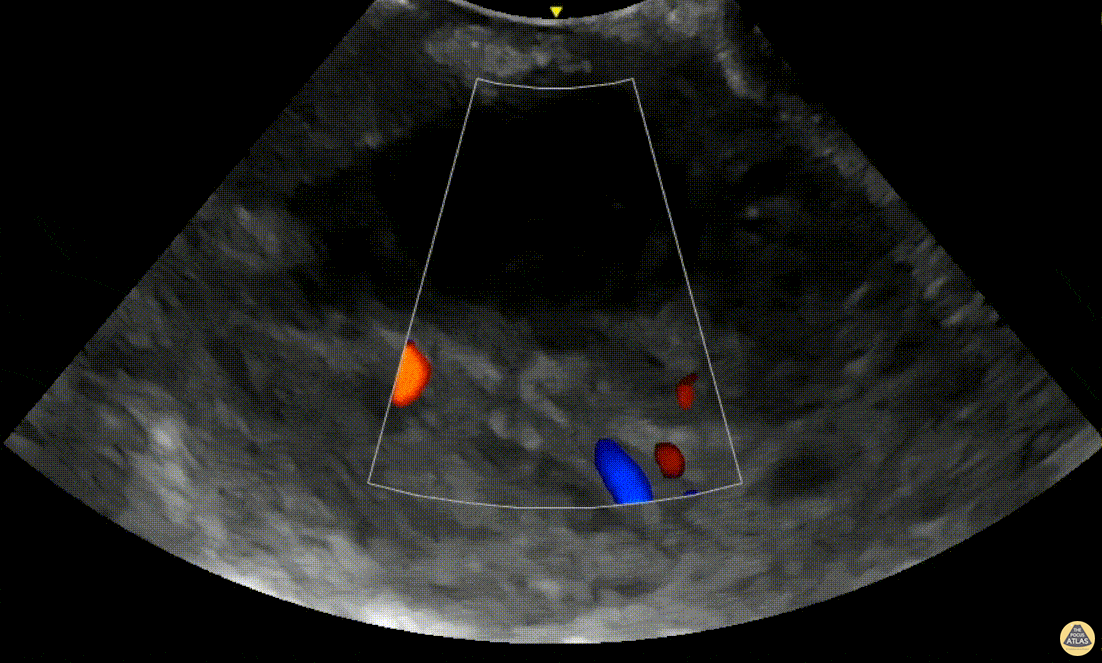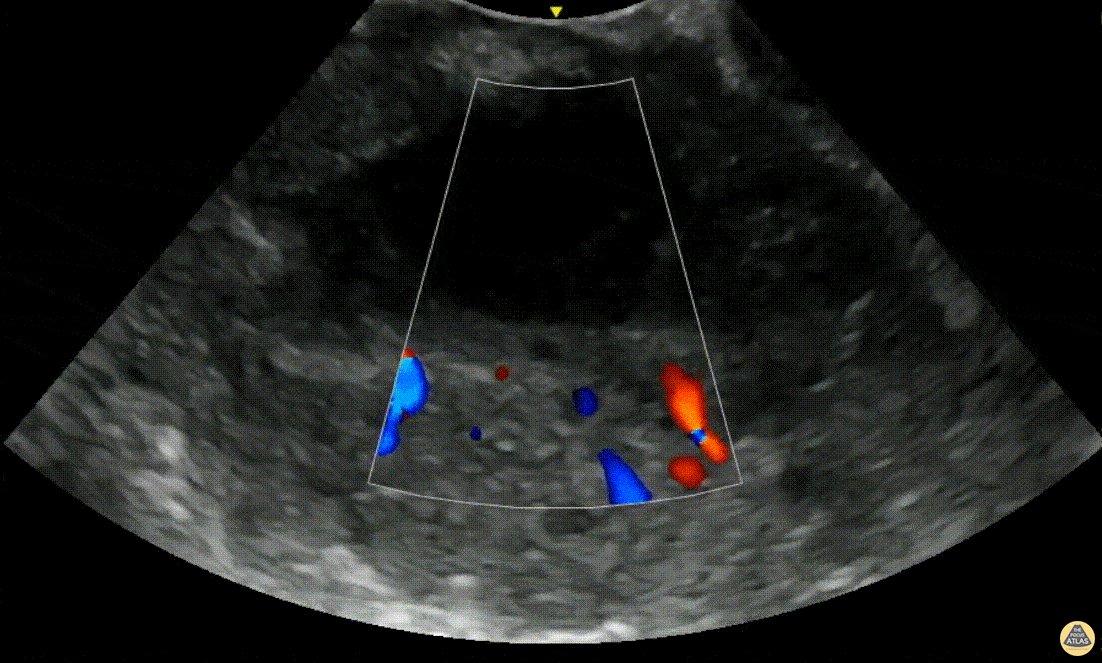
Peritonsillar Abscess with Posterior Color Flow
A 24-year-old male presented to the ED with 3 days of fever, headache and sore throat. On exam he was noted to have oropharyngeal erythema with a fluctuant area in the left peritonsillar region. A POCUS was performed of the area using an endocavitary probe, revealing clear circumscribed hypoechoic region without internal color flow. Aspiration of the PTA was performed with moderate purulent drainage.
Dr. Elizabeth Hanson, Denver Health Emergency Medicine
Alexandra Netto, PA, Denver Health Emergency Department
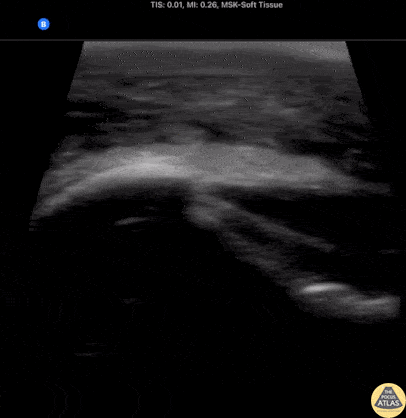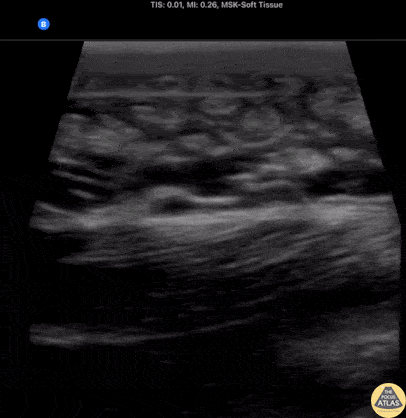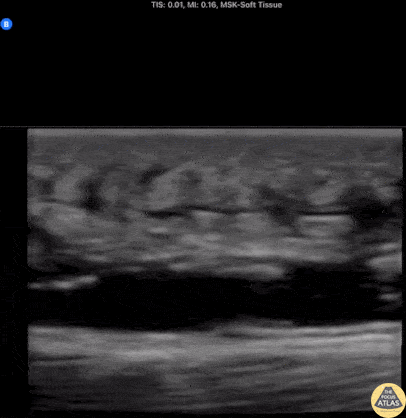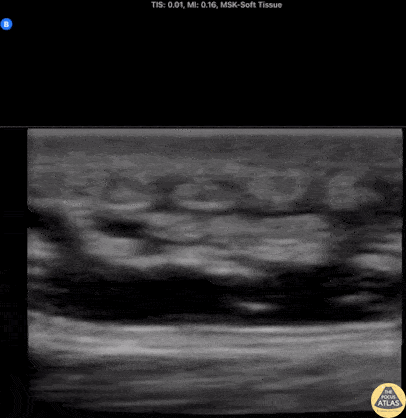
Deep Cellulitis with Phlegmon
20s M with PMH IVDU presented with R elbow wound for a few days. On exam, there was a focal wound with purulence near the R elbow with extensive erythema, induration, and tenderness to the R forearm and distal upper arm. The patient was hemodynamically stable. Labs were concerning for a markedly elevated white blood cell count and CRP. Given the clinical concern for necrotizing soft tissue infection (NSTI), POCUS was performed of the affected area. Shown here, the POCUS demonstrates extensive cobblestoning with fluid seen along the fascial planes superficial to the muscle. Orthopedic surgery was consulted with concern for NSTI, and performed a bedside I&D which did not suggest NSTI, and the patient was admitted for IV antibiotics and management of the severe cellulitis.
Dr. Nhu-Nguyen Le, Ultrasound Fellow
Denver Health Ultrasound Fellowship
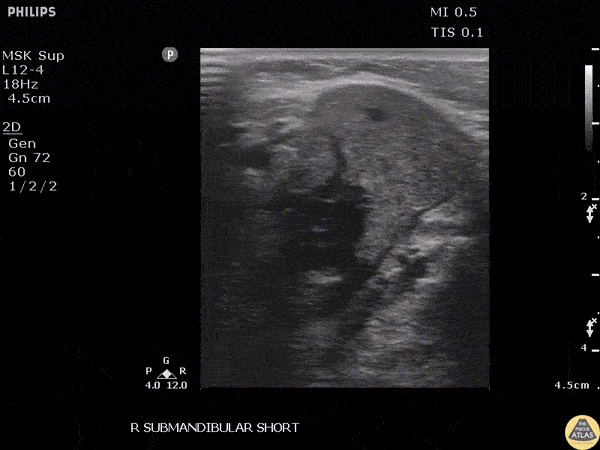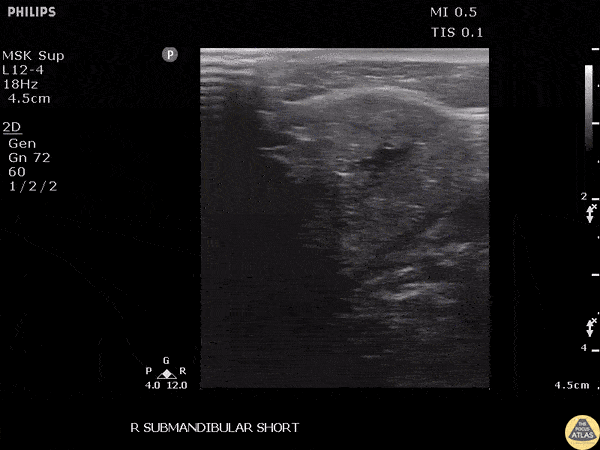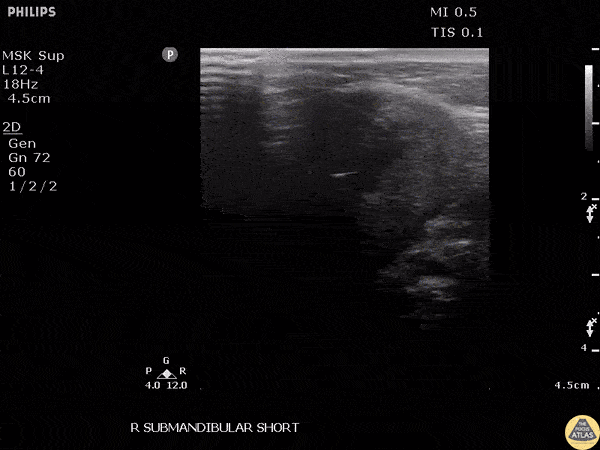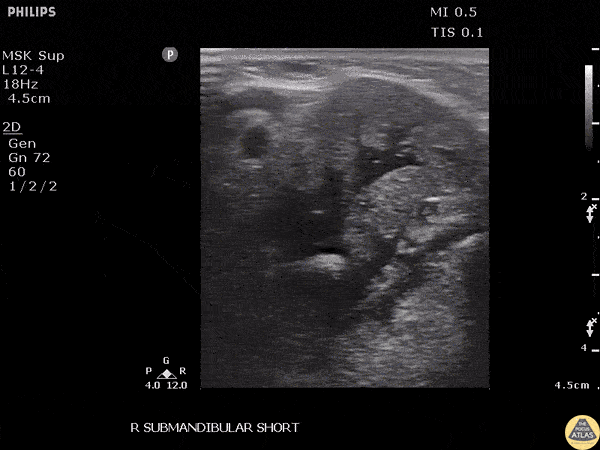
Submandibular Sialolithiasis
Patient with submandibular swelling was found to have a stone obstructing the submandibular duct, noted as a hyperechoic structure.
Image courtesy of Robert Jones DO, FACEP @RJonesSonoEM
Director, Emergency Ultrasound; MetroHealth Medical Center; Professor, Case Western Reserve Medical School, Cleveland, OH
View his original post here
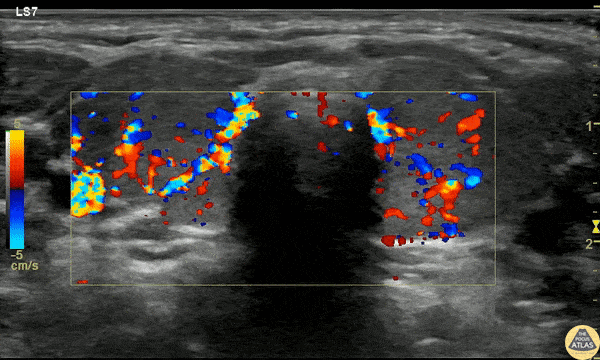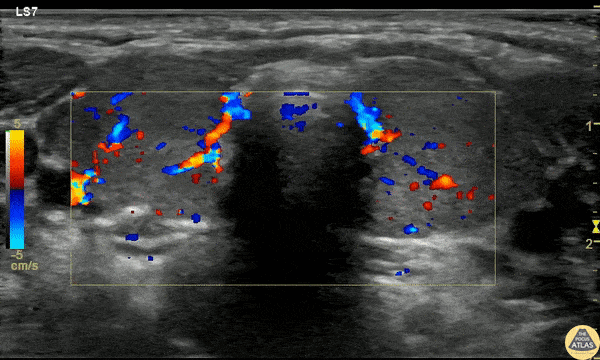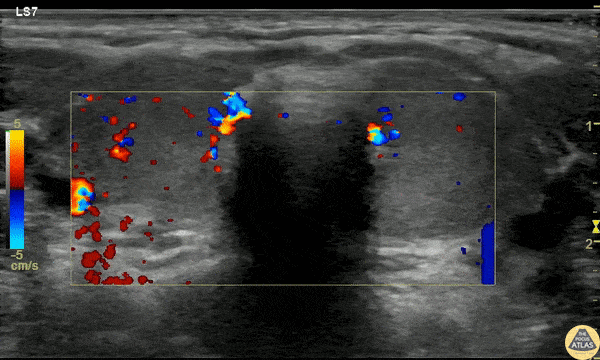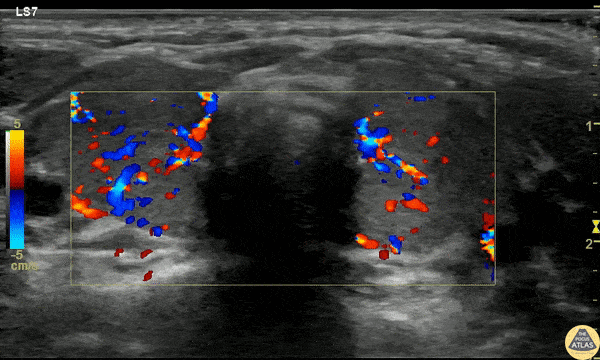
Pediatric Thyrotoxicosis
A 23mo F with PMH known Graves disease presented with a 10min generalized tonic/clonic seizure. IM Versed en route stopped the seizure. The patient was given 2 mL/kg D10 for hypoglycemia but remained hypoglycemic and refractory to D10 boluses. She was afebrile and not felt to be in thyroid storm but there was concern for thyrotoxicosis with adrenal insufficiency.
POCUS was performed to asses cardiac function due to elevated pulse pressures of 60-70 mmHg and the risk of high-output failure risk, although cardiac POCUS was reassuring and clinically the patient didn’t fit high-output failure.
Thyroid POCUS was performed after the TSH resulted at 0. The exam is shown here with diffuse increased flow in the thyroid, consistent with thyrotoxicosis and Graves disease.
The patient received stress dose steroids (but was already on propranolol and methimazole) and was admitted for definitive management.
Dr. Anthony Rodriguez, PGY1, Denver Health Residency in Emergency Medicine
Dr. Cailin Frank, Ultrasound Fellow, Denver Health Ultrasound Fellowship
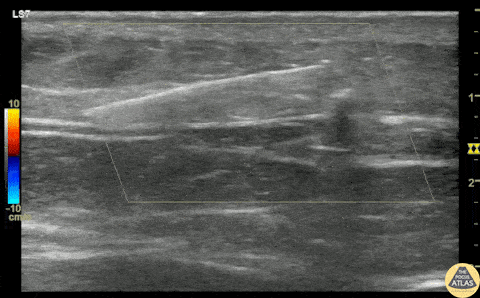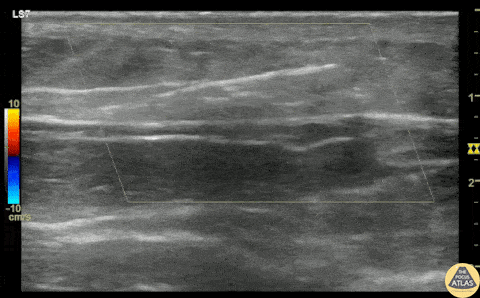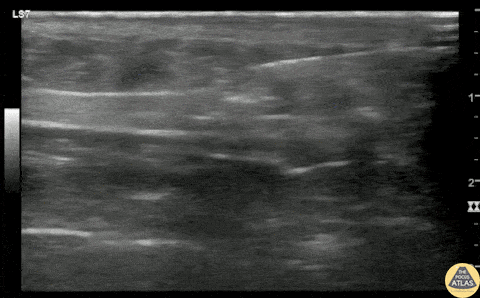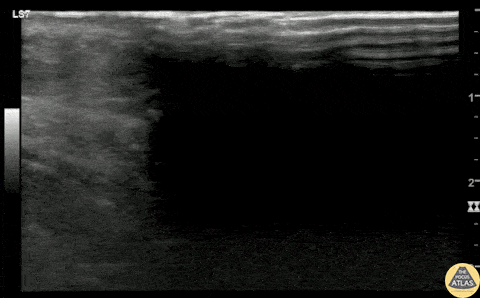
Glass Foreign Body Removal
A teenaged female presented with a retained foreign body after she laid on top of a broken glass hand mirror. She removed one glass shard prior to ED arrival but one piece remained that she could feel under her skin. On exam, there was a tiny laceration but a 1-2 cm palpable foreign body under the skin. Blind foreign body removal under local anesthesia was not successful, so POCUS was employed to aid in visualization of the foreign body. A linear hyperechoic foreign body is seen in this clip, and was able to be removed under real-time US guidance using forceps and a hemostat. Repeat POCUS showed complete removal of the foreign body, and the patient was able to be discharged.
Dr. Keren Eyal, PGY1, Children’s Hospital Colorado Pediatric Residency
Dr. Michael Heffler, PGY4, Denver Health Residency in Emergency Medicine
Dr. Nhu-Nguyen Le, Fellow, Denver Health Ultrasound Fellowship
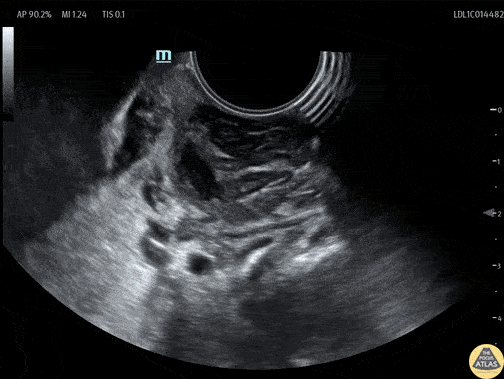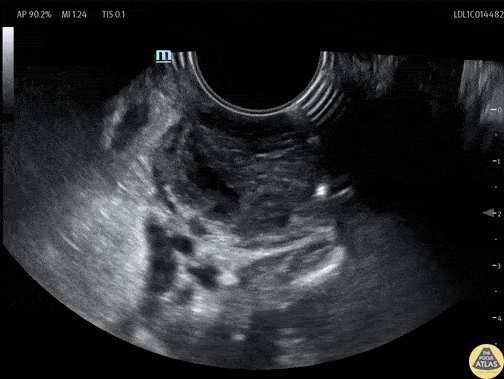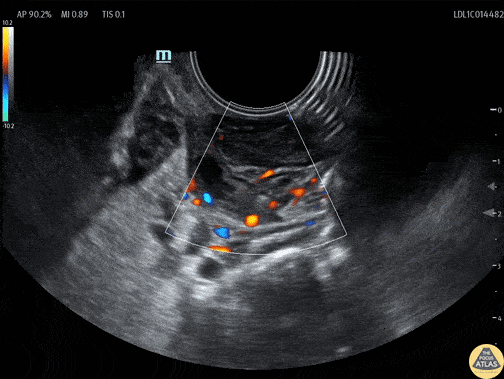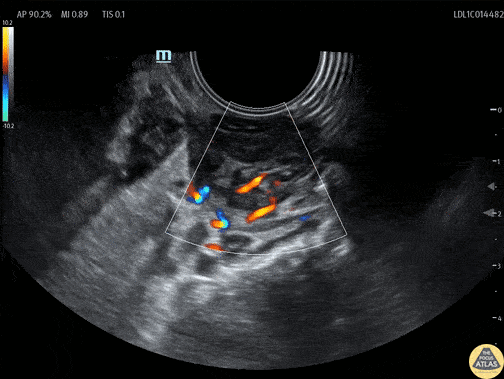
Tonsillar Abscess
A teenaged female presented with sore throat and was noted to have asymmetric tonsillar edema on physical exam. POCUS was performed using an endocavitary probe intraorally. The findings are shown here, with edema of the tonsil and a small circumscribed area of hypoechoic fluid which has no color doppler signal. This indicates tonsillitis with a small tonsillar abscess. Given this patient’s physical exam and small size of the abscess, conservative management was recommended with oral antibiotics without incision and drainage in the ED.
Dr. Cailin Frank, Fellow, Denver Health Ultrasound Fellowship
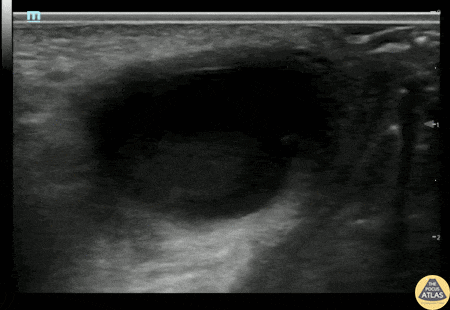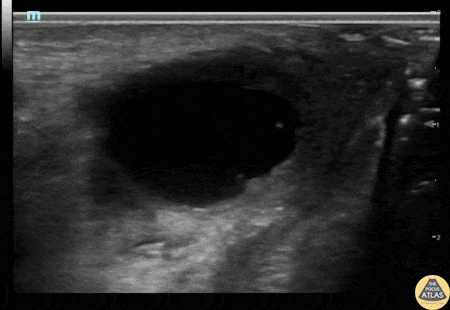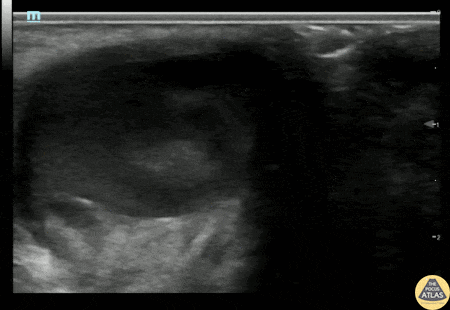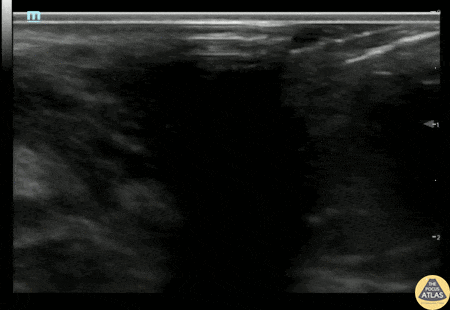
Bartholin's Gland Abscess
20s F with past medical history of multiple bartholin gland abscesses requiring drainage presented with genital pain and swelling. I&D of the abscess was attempted which was initially unsuccessful, so POCUS was performed to confirm the location of the abscess. Gynecology was then consulted for drainage and was able to successfully drain the abscess.
Alexandrea Netto PA, Denver Health and Hospital Authority
Katie McCabe MD, Attending Physician, Denver Health Residency in Emergency Medicine


































































