Acute Heart Failure
Acute Heart Failure Lesson - Normal Echo, Normal Pulmonary ultrasound. A guided lesson plan.
Basics of Echocardiography and Pulmonary Ultrasound
You are in the critical care trauma area of the emergency room and you get a prenotification for a 65 year old man in respiratory distress. You prepare the room and ask yourself, what labs, radiology, and diagnostic studies should be ordered?
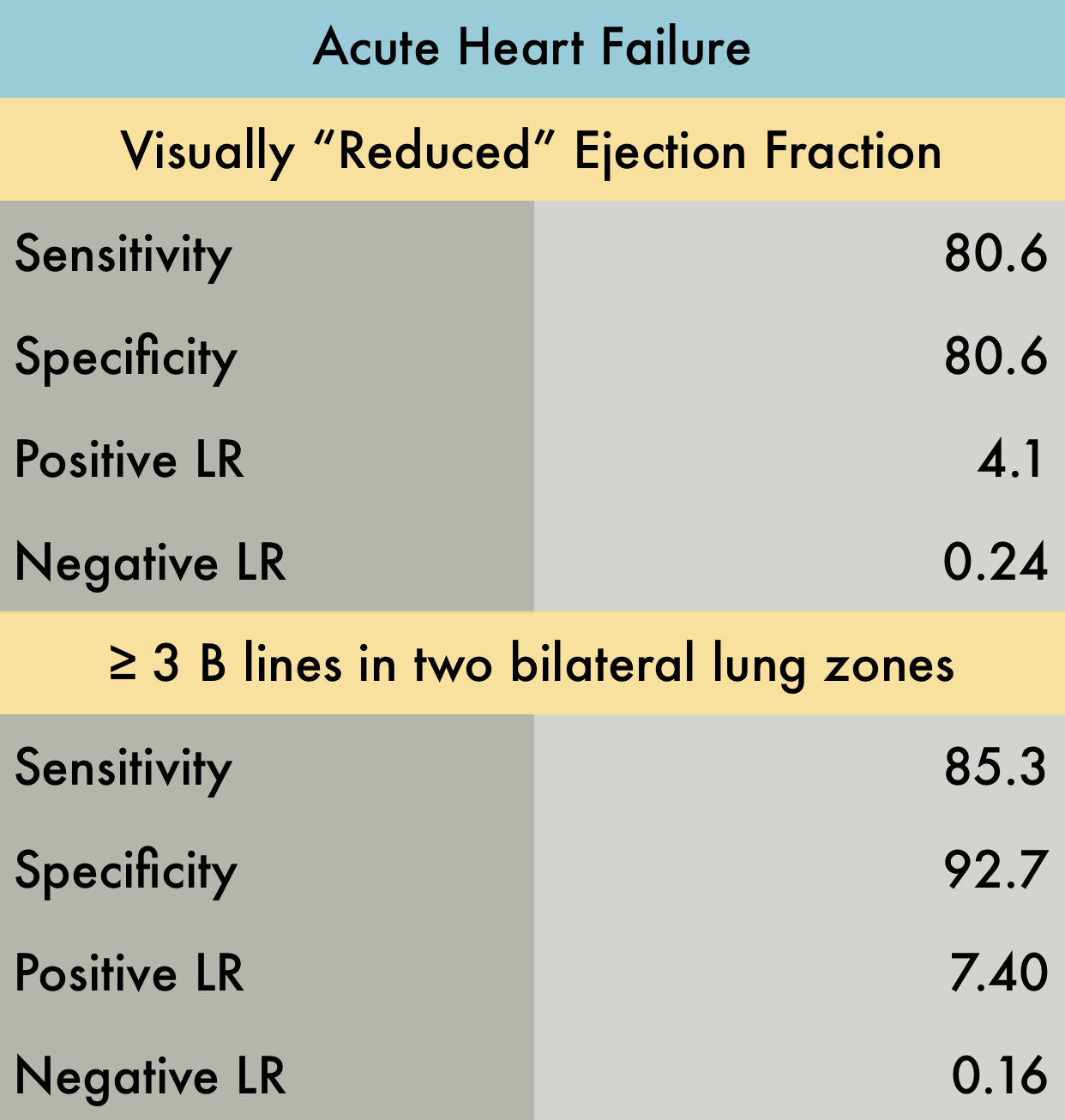
This was a large systematic review and meta-analysis (57 studies, n = 17,893) of the operating characteristics for diagnostic elements available to the emergency physician for diagnosing acute heart failure (AHF) including the history and physical, ECG, chest radiography, BNP/NT-proBNP (NPs), bedside echocardiography, lung ultrasound, and bioimpedance. They concluded that bedside lung US and echocardiography appear to the most useful tests for affirming the presence of AHF while NPs are valuable in excluding the diagnosis. Reduced ejection fraction was determined to have the highest +LR compared to other elements of the exam. However, the studied included in the final pooling appear to have only used "visual estimation" of reduced EF. With regards to lung US, a positive finding was defined in every study by the presence of at least three B lines in two bilateral lung zones.
PMID: 26910112
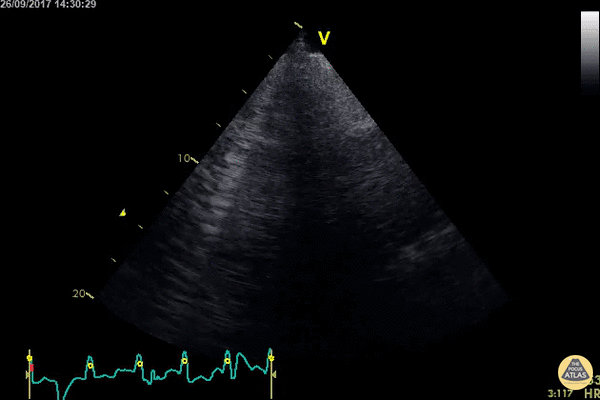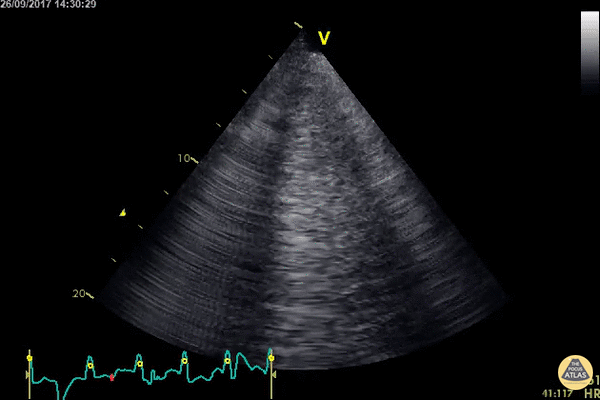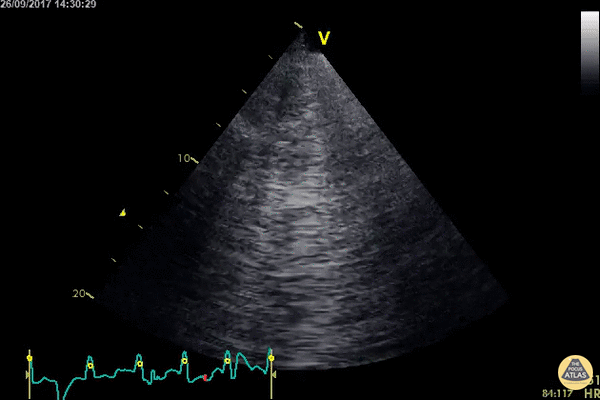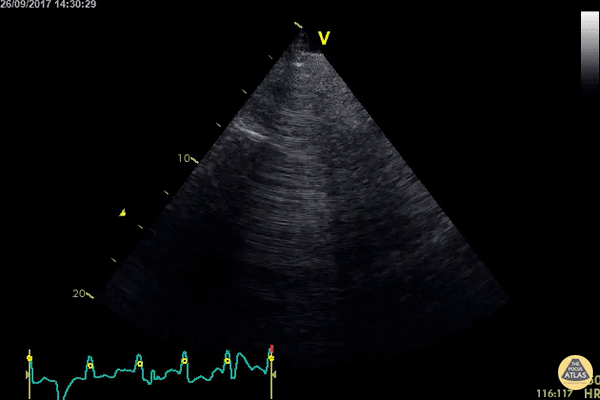
Echocardiography: Normal and Abnormal
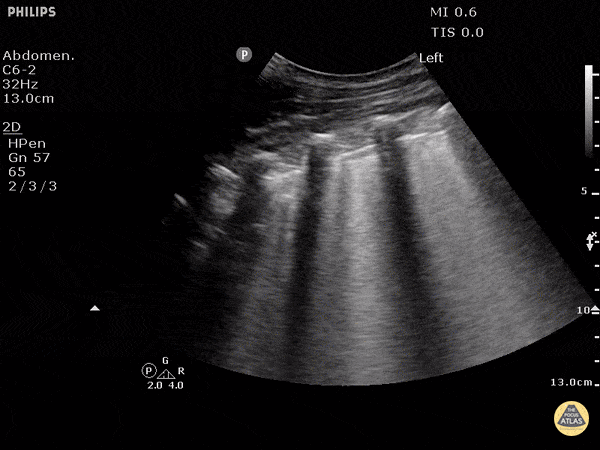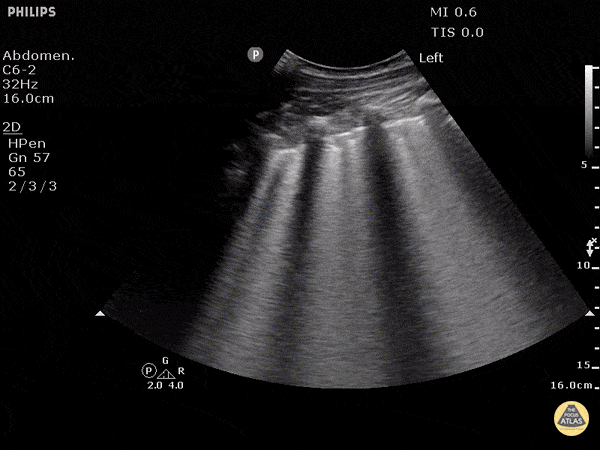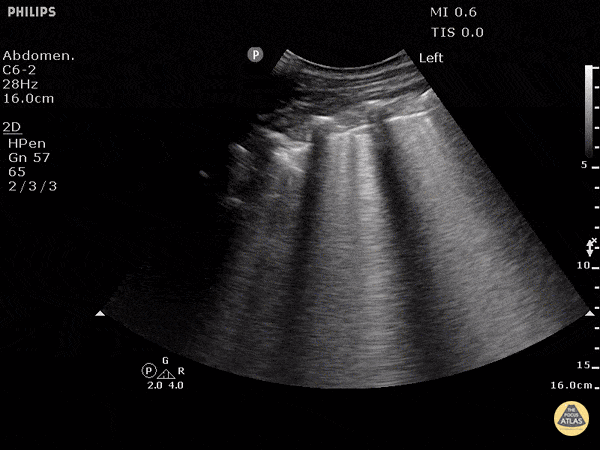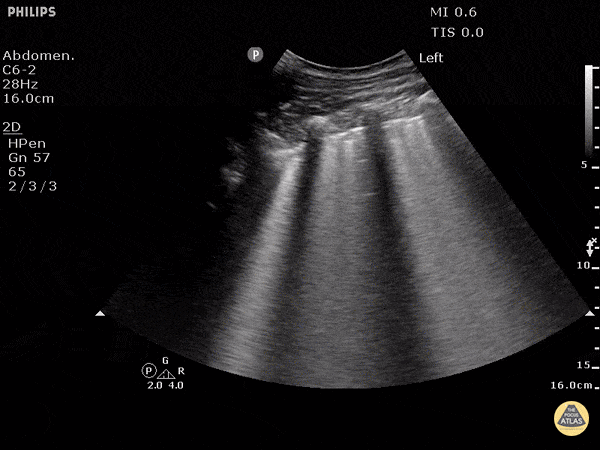
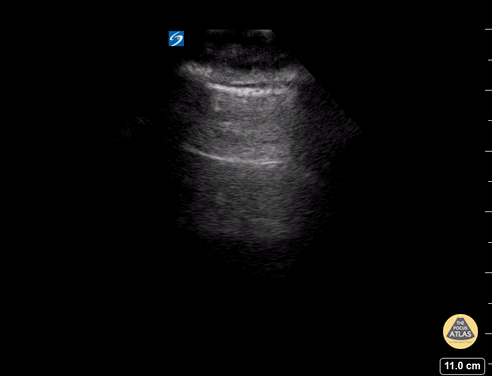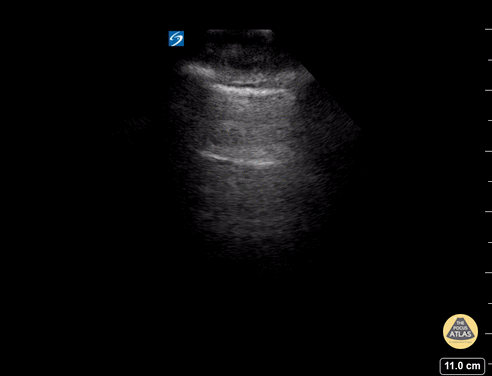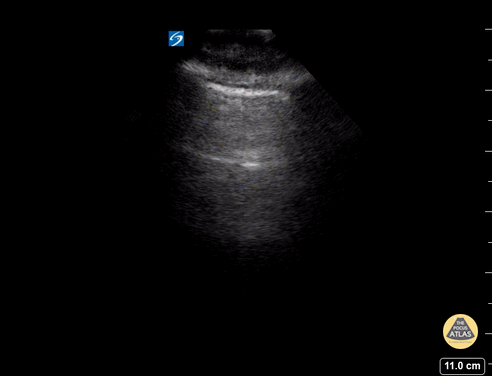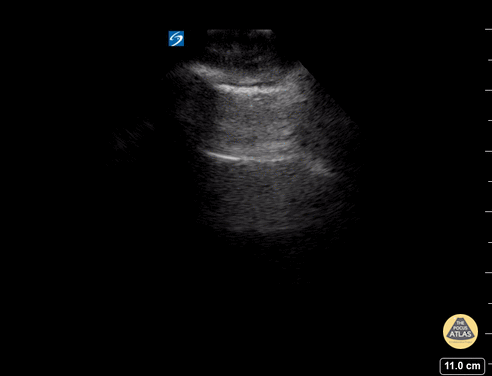
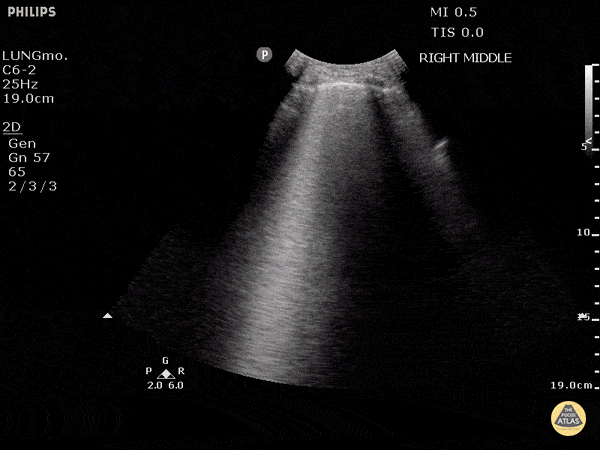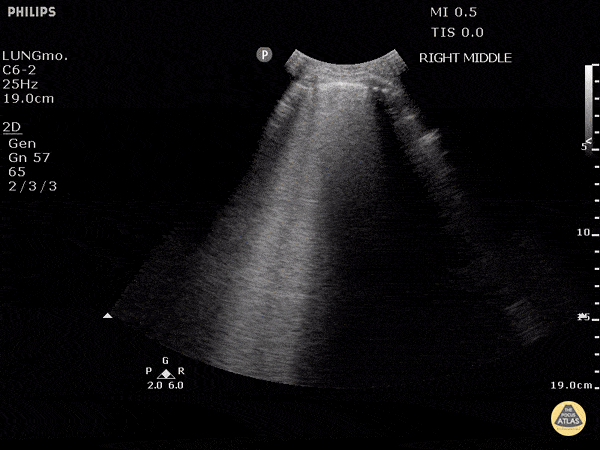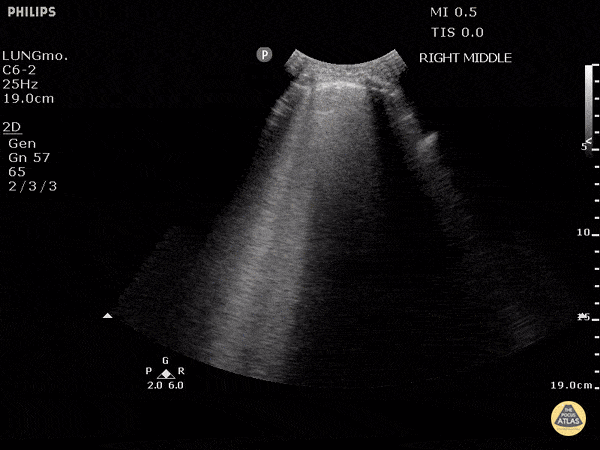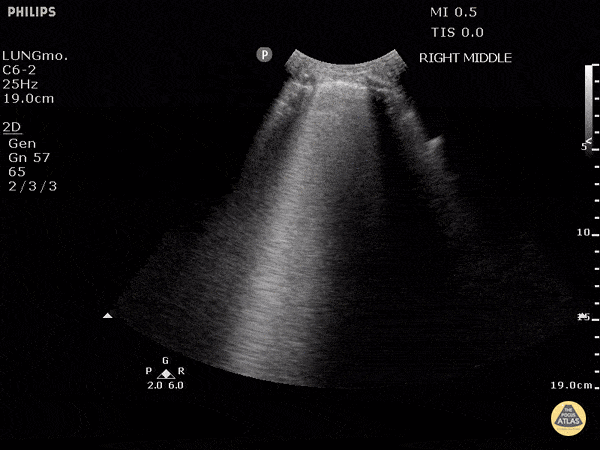
B-lines obtained with curved probe.
B-lines are vertical artifacts that move with respiration from the pleural surface. They represent increased water in an area of the lung. In the right clinical context this could represent pulmonary edema. An increase in B-lines correlates with the degree of pulmonary edema.
3 B-lines in an intercostal space represent a "positive" region of the lung, and if there are two regions of the lung that are positive, you can diagnose pulmonary edema.
Dr. Justin Bowra et al. (Dr. D Browne and Dr. J Knights)
Pulmonary: Normal and Abnormal
A lines appear as horizontal lines that represent normal aerated lung (dry interlobular septa). They are a reverberation artifact caused by the sound waves bouncing off the highly echogenic pleura and back to the probe, and repeating.
Hannah Kopinski (MS4) and Dr. Lindsay Davis - NYU Emergency Medicine, Matthew Riscinti - Kings County Emergency Medicine
B-lines are vertical artifacts that moves with respiration from the pleural surface. They represent increased water in an area of the lung. In the right clinical context this could represent pulmonary edema. An increase in B-lines correlates with the degree of pulmonary edema.
Keep in mind that in different clinical contexts, they can represent different diagnoses including pulmonary contusions and pneumonia.
Justin Bowra MBBS, FACEM, CCPU Emergency Physician, RNSH et al.
B-lines obtained with curved probe.
B-lines are vertical artifacts that move with respiration from the pleural surface. They represent increased water in an area of the lung. In the right clinical context this could represent pulmonary edema. An increase in B-lines correlates with the degree of pulmonary edema.
3 B-lines in an intercostal space represent a "positive" region of the lung, and if there are two regions of the lung that are positive, you can diagnose pulmonary edema.
Dr. Justin Bowra et al. (Dr. D Browne and Dr. J Knights)
WCUME 2017 Submission for "Best POCUS"
An acutely dyspnoeic patient presents with ventricular tachycardia and has no response to initial chemical cardioversion. Lung POCUS shows widespread bilateral confluent B lines indicating acute pulmonary edema. Unstable tachycardia terminated using synchronized electrical cardioversion.
Dr. Cian McDermott - Dublin, Ireland